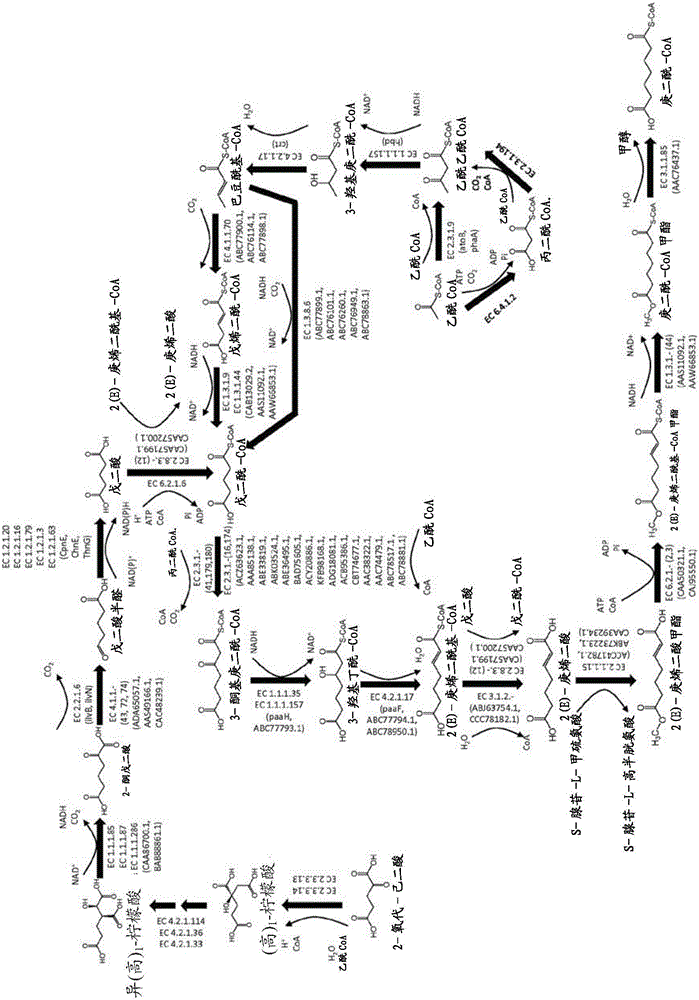
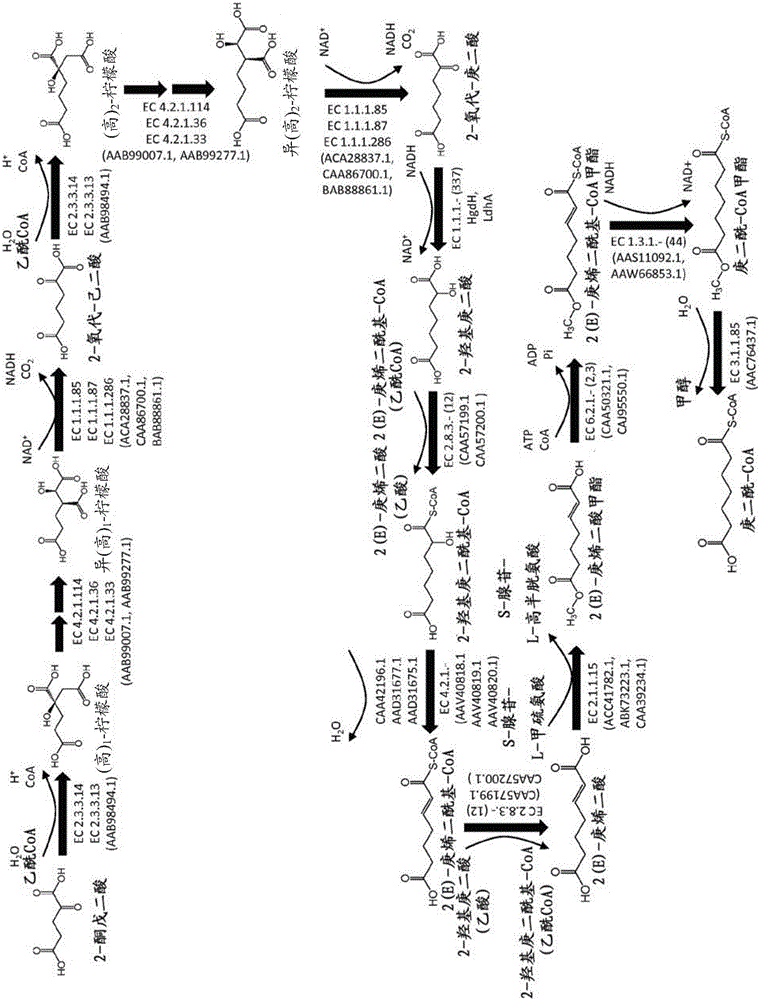
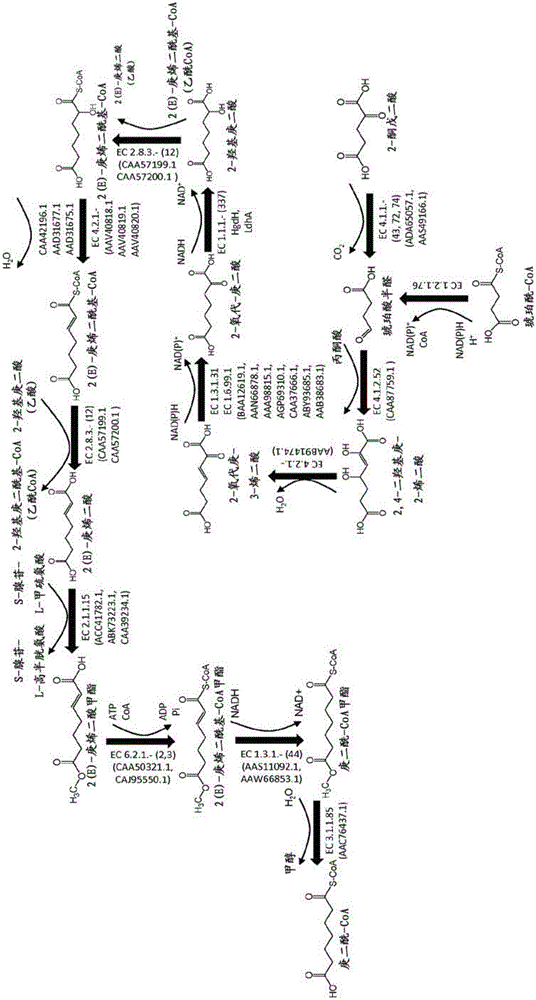
Methods, reagents and cells for biosynthesizing compound
A carboxyl-functionalized and reactive technology, applied in the field of carbon chain aliphatic backbone
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0319] Enzymatic activity of thioesterases that use pimeloyl-CoA as a substrate and form pimelic acid
[0320] The sequence encoding the N-terminal His-tag was added to the tesB gene (SEQ ID NO:21, see Figure 9 ), allowing the generation of N-terminally HIS-tagged ω-transaminases. The modified tesB gene was cloned into the pET15b expression vector under the control of the T7 promoter. The expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host. The resulting recombinant E. coli strains were grown in 500 mL shake flask cultures containing 50 mL of Luria Broth (LB) medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37°C with shaking at 230 rpm. Each culture was induced overnight at 17°C with 0.5 mM IPTG.
[0321] The pellet from each induced shake flask culture was harvested by centrifugation. Resuspend the pellet and in Y-per TM solution (ThermoScientific, Rockford, IL). Cell debris was separated from the supernatant by centrifugation. Thioesterase was purified from th...
Embodiment 2
[0324] Enzymatic activity of omega-transaminase using pimelate semialdehyde as substrate and forming 7-aminoheptanoic acid
[0325] Sequences encoding N-terminal His-tags were added to omega-transaminases from Chromobacterium violaceum, Pseudomonas syringae, Rhodobacter sphaericus, and Vibrio fluvialus encoding the ω-transaminases of SEQ ID NOs: 13, 15, 16, and 18, respectively. gene (see Figure 9 ), allowing the generation of N-terminally HIS-tagged ω-transaminases. Each of the resulting modified genes was cloned into the pET21a expression vector under the control of the T7 promoter, and each expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host. The resulting recombinant E. coli strains were grown in 250 mL shake flask cultures containing 50 mL LB medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37° C. with shaking at 230 rpm. Each culture was induced overnight at 16°C with 1 mM IPTG.
[0326] The pellet from each induced shake flask culture was harvested by centrif...
Embodiment 3
[0332] Enzymatic activity of carboxylic acid reductases that use pimelic acid as a substrate and form pimelic semialdehyde
[0333] A sequence encoding a His-tag was added to the genes from Segniliparus rugosus and Segniliparus rotundus encoding the carboxylic acid reductases of SEQ ID NO: 9 and 12, respectively (see Figure 9), allowing the generation of an N-terminally HIS-tagged carboxylic acid reductase. Each modified gene was cloned into the pETDuet expression vector together with the sfp gene encoding the His-tagged phosphopantetheinyl transferase from Bacillus subtilis, both under the T7 promoter. Each expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host, and each resulting recombinant large intestine was grown in a 250 mL shake flask culture containing 50 mL LB medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37°C with shaking at 230 rpm Bacillus strains. Each culture was induced overnight at 37°C using autoinduction medium.
[0334] The pellet from each induc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com