Micro-wave-regular sintering method of structural ceramic
A microwave sintering, conventional technology, applied in the field of microwave-conventional sintered structural ceramics, can solve the problems of low dielectric loss, difficulty in sintering large products, and rapid temperature rise, reducing requirements and losses, facilitating observation and testing, and reducing temperature. The effect of gradient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
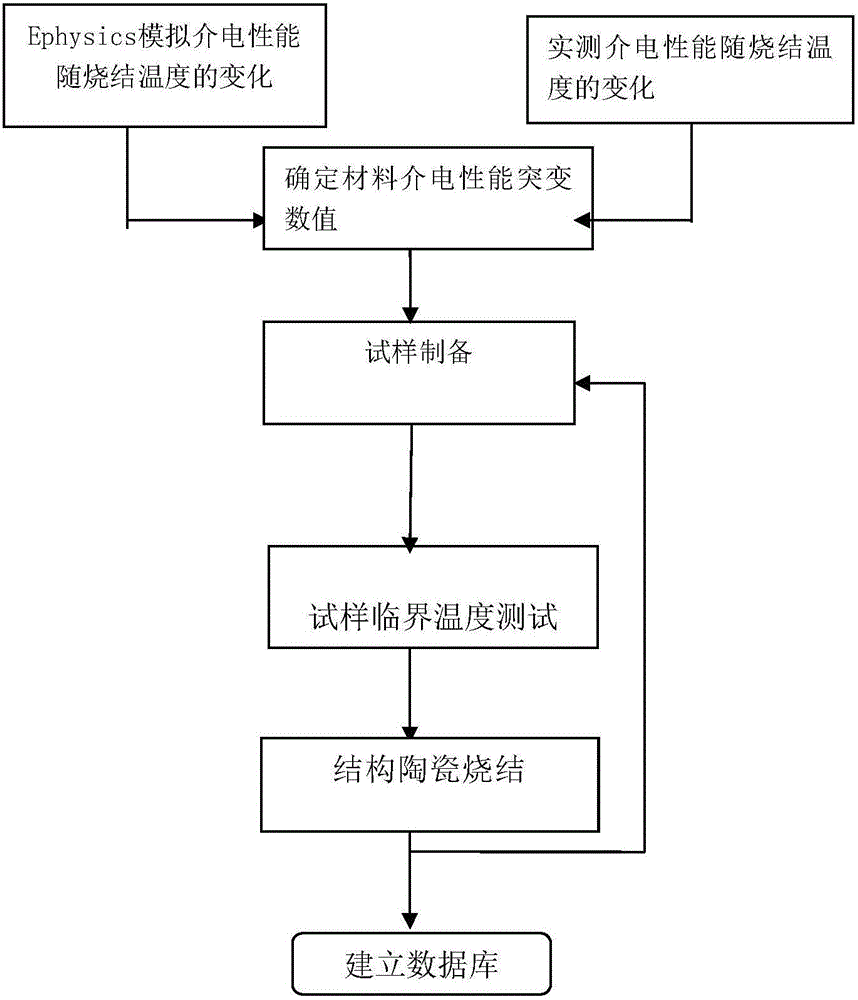
[0026] In this embodiment, the 3Y-TZP zirconia ceramic green body is preheated to the critical temperature in the microwave-conventional mixed heating high-temperature pusher kiln, and then microwave sintering is carried out to avoid the formation of local hot spots in the low-temperature stage of the green body. When the temperature reaches the critical temperature and the whole body has a strong coupling ability to microwaves, the microwave energy is basically absorbed by the body. The specific process is:
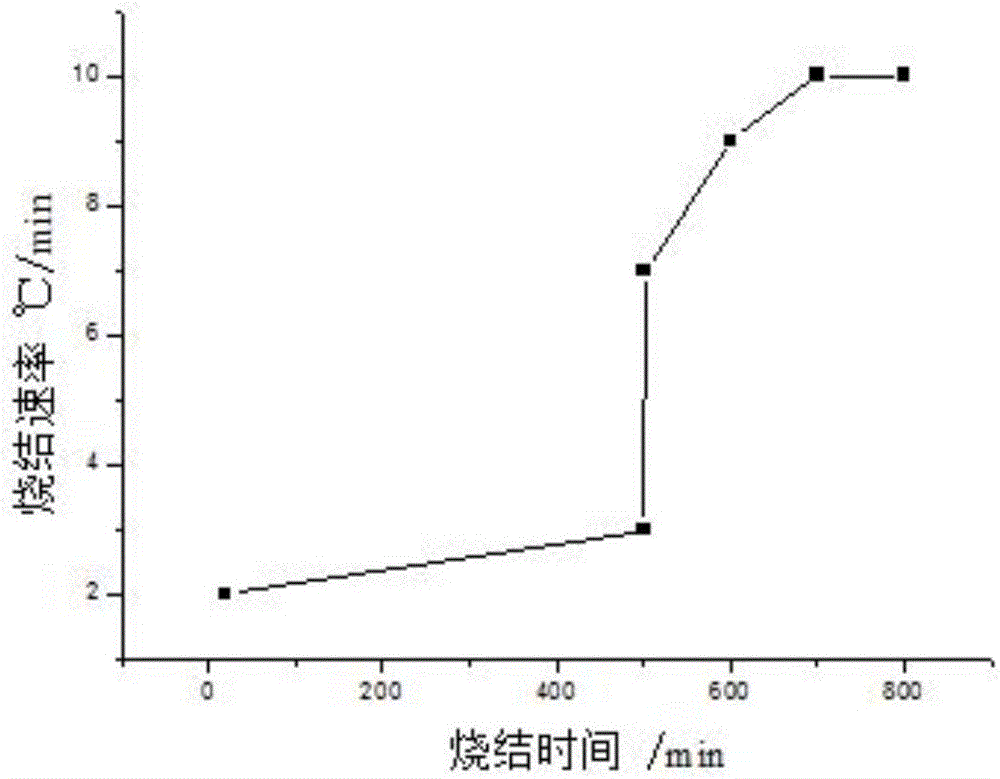
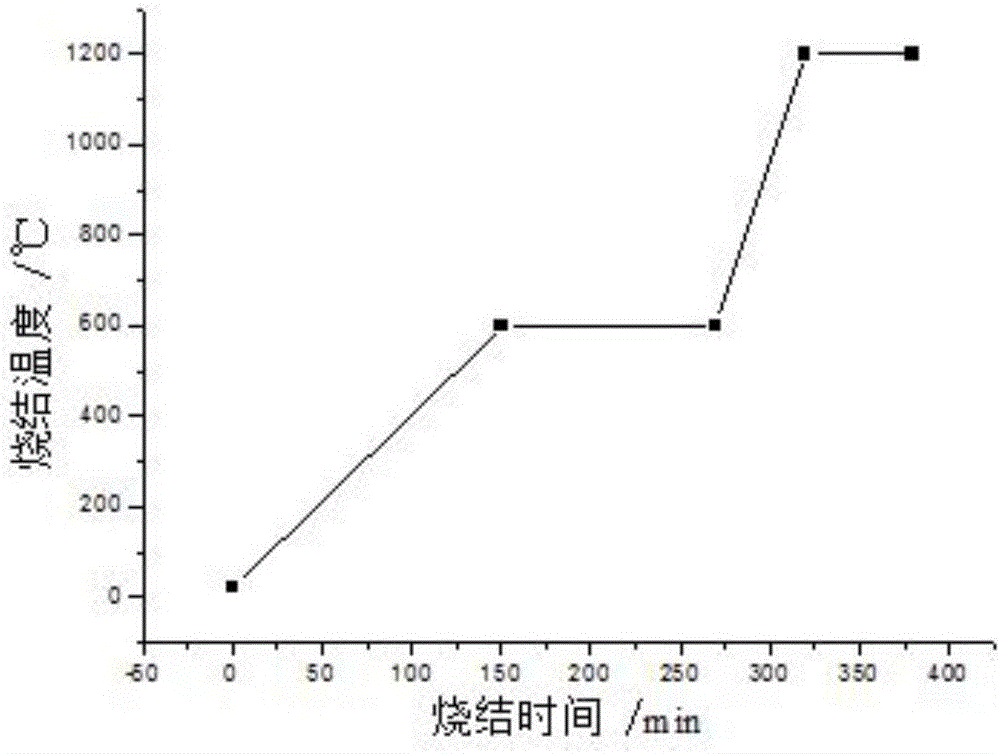
[0027] (1) Determination of the critical temperature of 3Y-TZP zirconia ceramics: Determine the critical temperature of 3Y-TZP zirconia ceramics through experiments, first place the 3Y-TZP zirconia ceramic samples in a microwave sintering experiment furnace and set the microwave sintering The power of the experimental furnace is 1000W, and the temperature is recorded every minute. After many experiments, the temperature change curve is as follows: figure 2 As shown in the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com