Method for obtaining high-purity tellurium from arsenic-containing alkaline leaching liquid
A high-purity tellurium and immersion solution technology, which is applied in the field of obtaining high-purity tellurium, can solve the problems of low tellurium recovery rate and complicated process flow, and achieve the effects of wide range of raw materials, high resource utilization rate, and high resource comprehensive utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
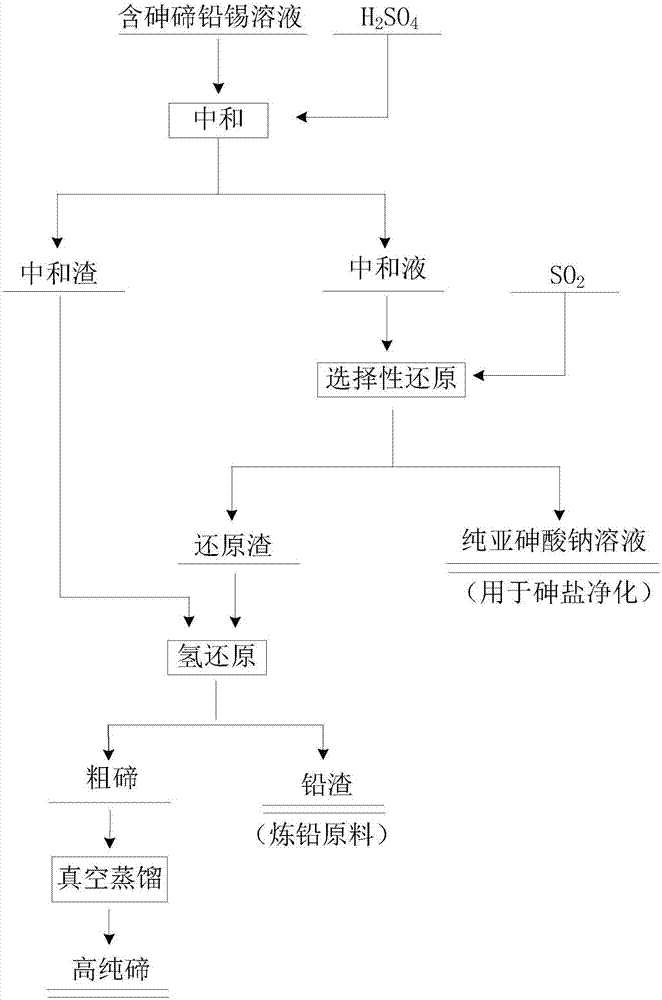
[0038] Taking the alkaline immersion solution in the experiment as an example, the concentration of main elements in it is Pb 706.67ppm, Sn 29.02ppm, Te134.56ppm, As 28.29g / L, and the following steps are used for treatment:
[0039] (1) Neutralization: Add H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the alkaline immersion solution to 5, and separate the liquid and solid to obtain neutralization liquid and neutralization slag; the obtained neutralization slag enters the subsequent hydrogen reduction process;
[0040] (2) Selective reduction: the neutralized liquid obtained in step (1) enters the selective reduction process, and SO is introduced into the neutralized liquid 2 , the control conditions are that the gas flow rate is 2L / min, the temperature is 60°C, and the aeration time is 2h. Obtain sodium arsenite solution and reduction slag after reduction finishes;
[0041] After testing: the content of each element in the reducing solution is: Pb 2.86ppm, Sn 0.79ppm, Te 1.08ppm, As27.01g / L. ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Take the alkaline immersion solution in the experiment as an example, in which the main element concentrations are Pb 647.26ppm, Sn 68.59ppm, Te238.45ppm, As 38.46g / L, and the following steps are used for treatment:
[0045] (1) Neutralization: Add H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the alkaline immersion solution to 4, and separate the liquid and solid to obtain neutralization liquid and neutralization slag; the obtained neutralization slag enters the subsequent hydrogen reduction process;
[0046] (2) Selective reduction: the neutralization solution obtained in step (1) enters the reduction process, and SO is introduced into the neutralization solution 2 , the control conditions are that the gas flow rate is 3L / min, the temperature is 90°C, and the aeration time is 3h. Obtain sodium arsenite solution and reduction slag after reduction finishes;
[0047] After testing: the content of each element in the reducing solution is: Pb 2.43ppm, Sn 0.98ppm, Te 1.45ppm, As37.89g / L. T...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Taking the alkaline immersion solution in the experiment as an example, the concentration of main elements in it is Pb 547.85ppm, Sn 67.43ppm, Te164.27ppm, As 19.44g / L, and the following steps are used for treatment:
[0051] (1) Neutralization: Add H 2 SO 4 Adjust the pH of the alkaline immersion solution to 5, and separate the liquid and solid to obtain neutralization liquid and neutralization slag; the obtained neutralization slag enters the subsequent hydrogen reduction process;
[0052] (2) Selective reduction: the neutralized liquid obtained in step (1) enters the reduction process, and the neutralized slag enters the hydrogen reduction process. Introduce SO into the neutralizing solution 2 , the control conditions are that the gas flow rate is 5L / min, the temperature is 70°C, and the aeration time is 0.5h. Obtain sodium arsenite solution and reduction slag after reduction finishes;
[0053] After testing: the content of each element in the reducing solution i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com