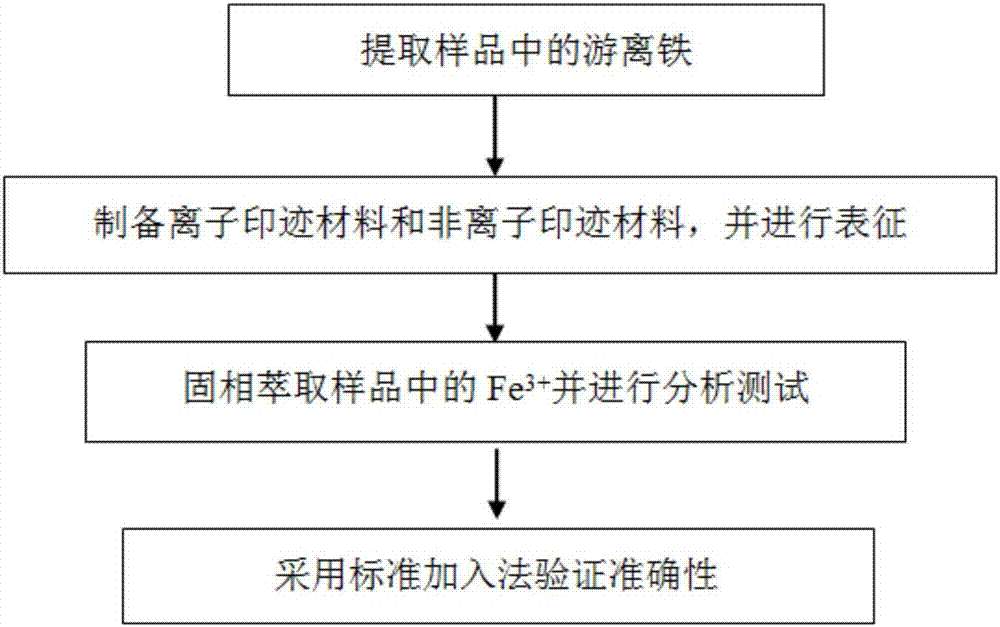
Method for quantitatively analyzing content of free ion in soil sediment sample
A quantitative analysis and sediment technology, applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis through optical means, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of salt accumulation, corrosion, instrument failure, high background of the instrument, etc., to achieve the elimination of interference, small error, The effect of high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
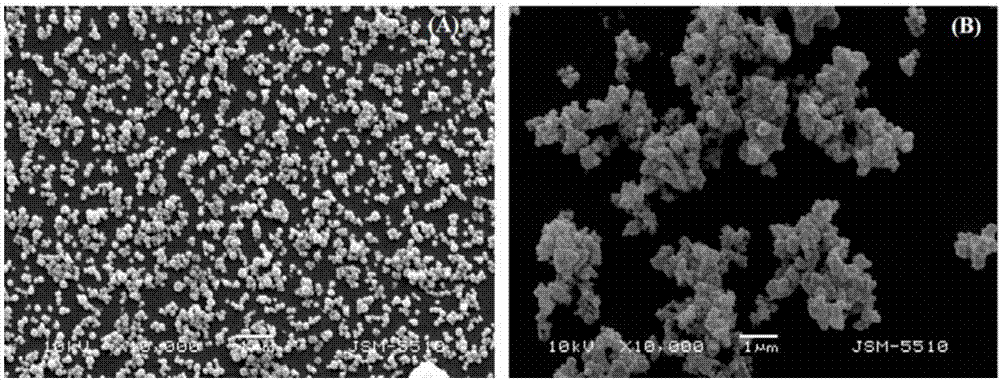
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Adopt the method of the present invention to analyze the Eocene gypsum rock sedimentary sample of Xining Basin, concrete method is as follows:
[0060] (1) Firstly, free iron was dissolved and extracted from the sample (Eocene gypsum rock sedimentary sample in Xining Basin). Grind the sample to 100 mesh in an agate mortar, accurately weigh 0.1 g of the sample and add 0.2 g of sodium dithionite powder reagent. Then add 10ml sodium citrate (0.3mol L -1 ) and sodium bicarbonate (0.1mol L -1 ) to mix the extracts. The above mixed solution was heated in a water bath at 75 °C for 15 min. The heated solution was centrifuged in a centrifuge for 5min (3600r / min), and 2.0mL of the supernatant was taken and diluted to 100mL for later use.
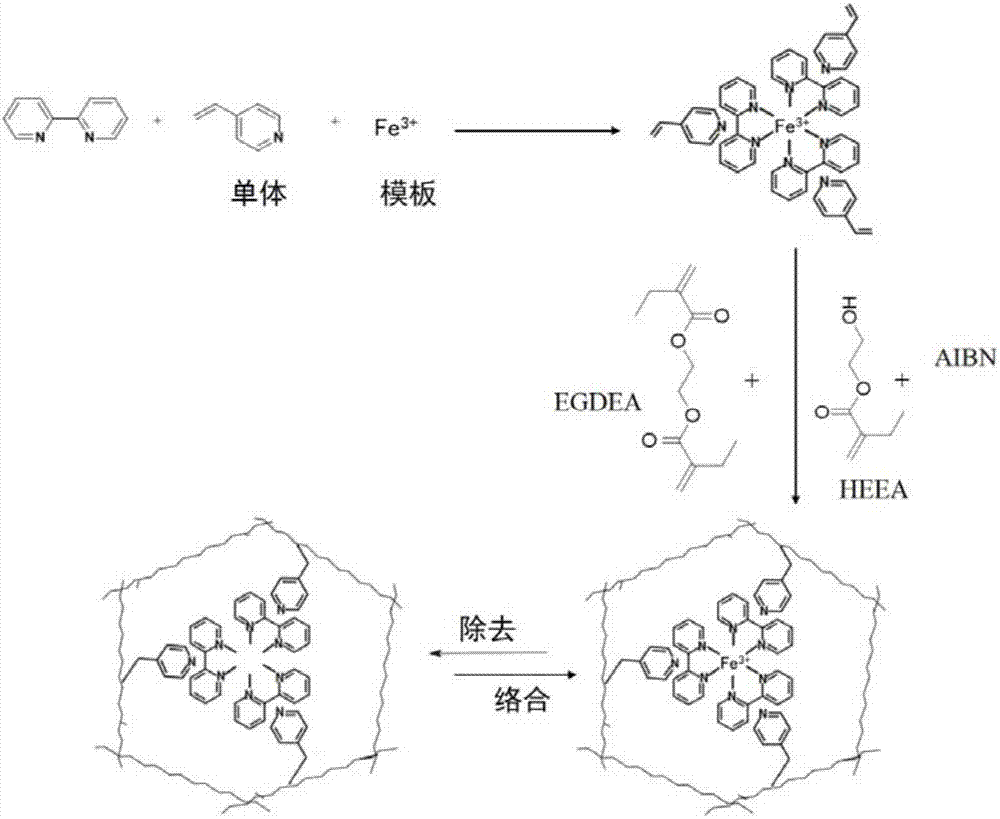
[0061] (2) Preparation of ion imprinted materials. 4-vinylpyridine (C 7 h 7 N) as a functional monomer, 2,2'-bipyridine (C 10 h 8 N 2 ) is a chelating agent, azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN, C 8 h 12 N 4 ) as an initiator, Fe 3+ As a...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Adopt the method of the present invention to analyze the silt grade loess sample in Gansu area, analysis process is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific method is as follows:
[0075] (1) Firstly, dissolving and extracting free iron from soil sediment samples (silt grade loess samples). Grind the sample in an agate mortar to below 100 mesh, and accurately weigh 0.15 g of the sample and add 0.25 g of sodium dithionite powder reagent. Then add 12ml sodium citrate (0.3mol L -1 ) and sodium bicarbonate (0.1molL -1 ) to mix the extracts. The above mixed solution was heated in a water bath at 75 °C for 15 min. The heated solution was centrifuged in a centrifuge for 5min (3600r / min), and 2.0mL of the supernatant was taken and diluted to 100mL for later use.
[0076] (2) Preparation of ion imprinted materials. 4-vinylpyridine (C 7 h 7 N) as a functional monomer, 2,2'-bipyridine (C 10 h 8 N 2 ) is a chelating agent, azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN, C 8 h 12 N 4 ...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Adopt the method of the present invention to analyze the sediment sample in the Jingbian area of the Loess Plateau, the specific method is as follows:
[0089] (1) Firstly, free iron was dissolved and extracted from soil sediment samples (sediment samples from the Jingbian area of the Loess Plateau). Grind the sample in an agate mortar to below 100 mesh, and accurately weigh 0.2 g of the sample and add 0.3 g of sodium dithionite powder reagent. Then add 15ml sodium citrate (0.3mol L -1 ) and sodium bicarbonate (0.1mol L -1 ) to mix the extracts. The above mixed solution was heated in a water bath at 75 °C for 15 min. The heated solution was centrifuged in a centrifuge for 5min (3600r / min), and 2.0mL of the supernatant was taken and diluted to 100mL for later use.
[0090] (2) Preparation of ion imprinted materials. 4-vinylpyridine (C 7 h 7 N) as a functional monomer, 2,2'-bipyridine (C 10 h 8 N 2 ) is a chelating agent, azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN, C 8 h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com