Acetylcholin esterase marked engineering phage for rapidly detecting microorganisms
A technology of acetylcholinesterase and bacteriophage, which can be applied in the direction of bacteriophage, microorganism, virus/phage, etc., can solve the problems of complicated operation steps and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Detection of sulfate-reducing bacteria:
[0018] The microorganisms used in the experiment were cultured in suspension in lysed broth (1% peptone, 1% sodium chloride, 0.5% yeast extract, 100 mL water), and a single colony was cultured overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm on a shaking table at 4500 rpm. / Centrifuge for ten minutes, and dilute to different concentrations with PBS buffer solution.
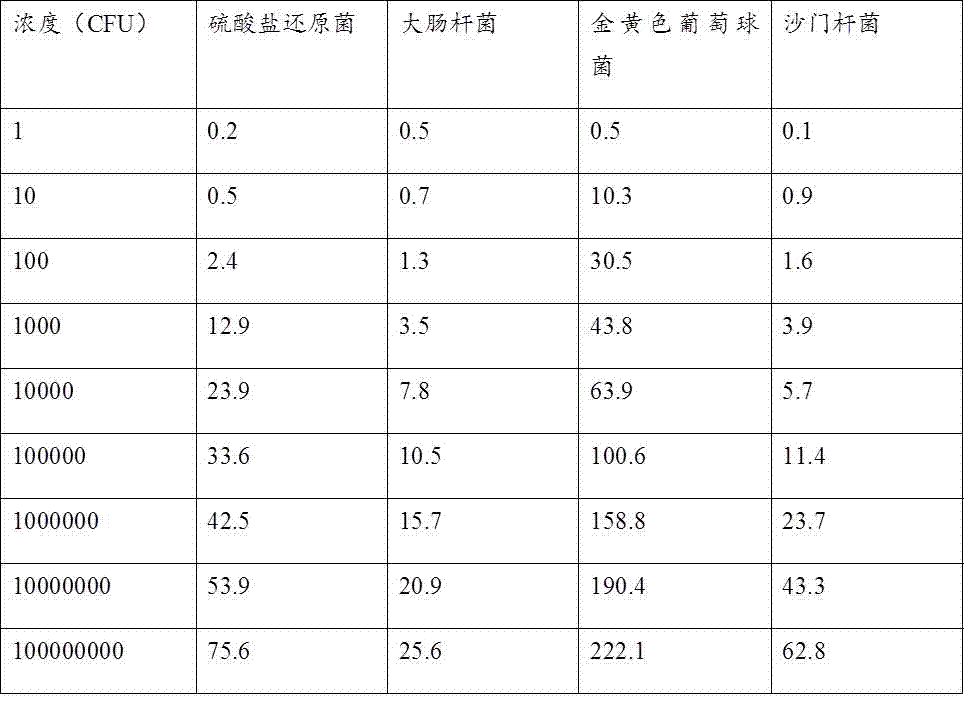
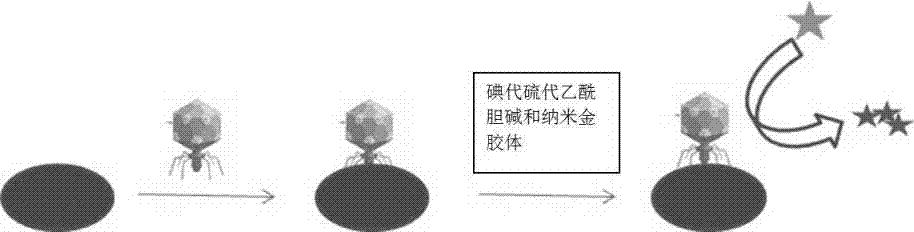
[0019] 100 µL concentration (10 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to the disposable medium, and reacted at 37 °C for 8 hours. Add acetylcholinesterase-responsive iodothioacetylcholine and nano-gold colloids, incubate for 30 minutes, use the excitation light source of the microbial diagnostic instrument to excite the sensor platform to generate light signals, and measure the microbial signals at this concentration.
[0020] 100 µL concentration (10 2 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to th...
Embodiment 2
[0029] E. coli detection
[0030] The microorganisms used in the experiment were cultured in suspension in lysed broth (1% peptone, 1% sodium chloride, 0.5% yeast extract, 100 mL water), and a single colony was cultured overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm on a shaking table at 4500 rpm. / Centrifuge for ten minutes, and dilute to different concentrations with PBS buffer solution.
[0031] 100 µL concentration (10 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to the disposable medium, and reacted at 37 °C for 8 hours. Add acetylcholinesterase-responsive iodothioacetylcholine and nano-gold colloids, incubate for 30 minutes, use the excitation light source of the microbial diagnostic instrument to excite the sensor platform to generate light signals, and measure the microbial signals at this concentration.
[0032] 100 µL concentration (10 2 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to the disposable medium, a...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Staphylococcus aureus detection
[0042] The microorganisms used in the experiment were cultured in suspension in lysed broth (1% peptone, 1% sodium chloride, 0.5% yeast extract, 100 mL water), and a single colony was cultured overnight at 30°C and 200 rpm on a shaking table at 4500 rpm. / Centrifuge for ten minutes, and dilute to different concentrations with PBS buffer solution.
[0043] 100 µL concentration (10 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to the disposable medium, and reacted at 37 °C for 8 hours. Add acetylcholinesterase-responsive iodothioacetylcholine and nano-gold colloids, incubate for 30 minutes, use the excitation light source of the microbial diagnostic instrument to excite the sensor platform to generate light signals, and measure the microbial signals at this concentration.
[0044] 100 µL concentration (10 2 cfu ml -1 ) bacteria solution and acetylcholinesterase-labeled phage were added to the dispos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com