A class of fat-soluble 5-aminolevulinic acid derivatives and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of aminolevulinic acid and derivatives, which is applied in the field of fat-soluble 5-aminolevulinic acid derivatives and their preparation, can solve the problems of high hydrophilicity, restricted cell absorption, etc., and achieves easy preparation and strong photodynamic activity. , the effect of enhancing fat solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
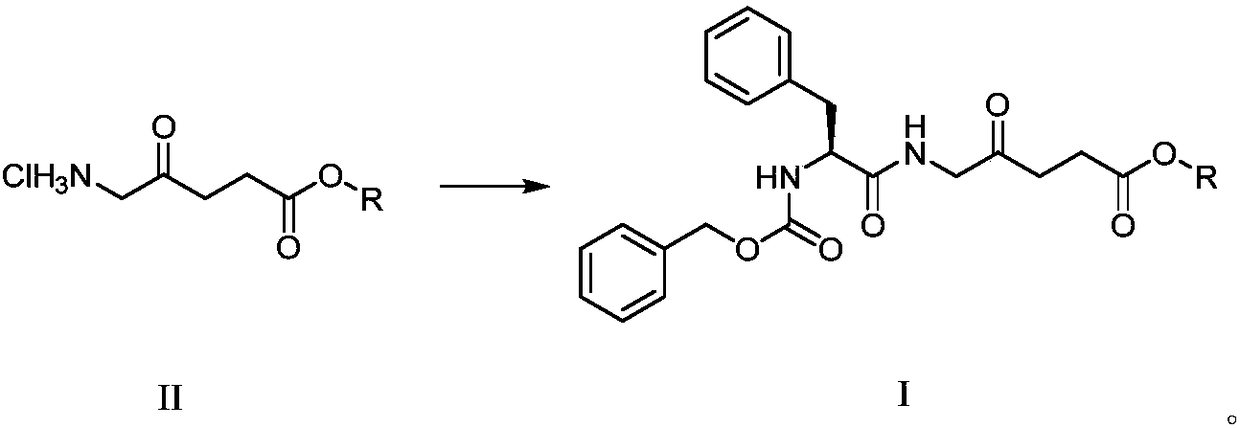
[0022] Preparation of 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L-phenylpropionyl)amino-4-oxopentanoic acid methyl ester:
[0023]
[0024] In a 50mL round bottom flask, 5-aminolevulinic acid methyl ester hydrochloride (1.0g, 5.5mmol), Cbz-L-phenylalanine (1.64g, 5.5mmol) and HBTU (1.7g, 4.49 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (10 mL), and DIPEA (2.0 mL, 11.5 mmol) was added, and stirred at 24° C. for 6 h. Concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, separated by silica gel column chromatography, the eluent was dichloromethane:methanol (v / v=50:1), to obtain a white solid 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L- Phenylpropionyl) amino-4-oxopentanoic acid methyl ester 1.95g, yield 83.2%. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δppm: 7.34 (s, 3H), 7.38–7.27 (m, 2H), 7.19 (s, 5H), 6.73 (s, 1H), 6.24 (s, 1H), 5.87 (d, J = 12.3Hz, 1H ), 5.19(t, J=7.0Hz, 1H), 4.62(d, J=12.4Hz, 1H), 4.23(d, J=12.4Hz, 1H), 3.75–3.62(m, 2H), 3.63(s ,3H),3.31(dd,J=12.4,7.0Hz,1H),3.06–2.91(m,2H),2.46–2.37(m,1H),2.32(dt,J=12....
Embodiment 2
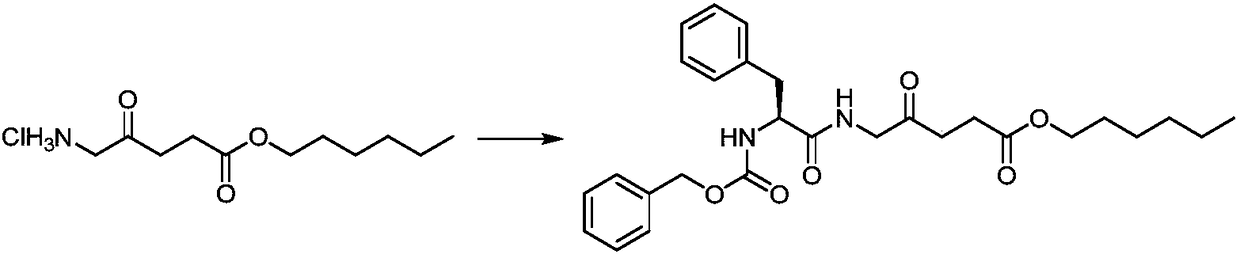
[0026] Preparation of 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L-phenylpropionyl)amino-4-oxopentanoic acid n-hexyl ester:
[0027]
[0028] In a 50mL round bottom flask, 5-aminolevulinic acid n-hexyl hydrochloride (1.0g, 3.97mmol), Cbz-L-phenylalanine (1.19g, 3.97mmol) and HBTU (1.7g, 4.49 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (10 mL), and DIPEA (1.5 mL, 8.6 mmol) was added, and stirred at 24° C. for 6 h. Concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, separated by silica gel column chromatography, the eluent was dichloromethane:methanol (v / v=100:1), to obtain a white solid 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L- phenylpropionyl)amino-4-oxopentanoic acid n-hexyl 1.60g, yield 81.3%. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3)δppm: 7.34 (s, 3H), 7.37–7.29 (m, 2H), 7.19 (s, 5H), 6.36 (d, J = 12.3Hz, 1H), 6.24 (s, 1H), 5.63 (d, J =12.4Hz,1H),5.52(t,J=7.0Hz,1H),4.77(d,J=12.2Hz,1H),4.08(td,J=12.4,2.3Hz,1H),4.01–3.91(m ,1H),3.64(ddd,J=12.3,9.8,2.1Hz,1H),3.42(d,J=12.4Hz,1H),3.17(dd,J=12.4,6.9Hz,1H),2.99–2.87( (...
Embodiment 3
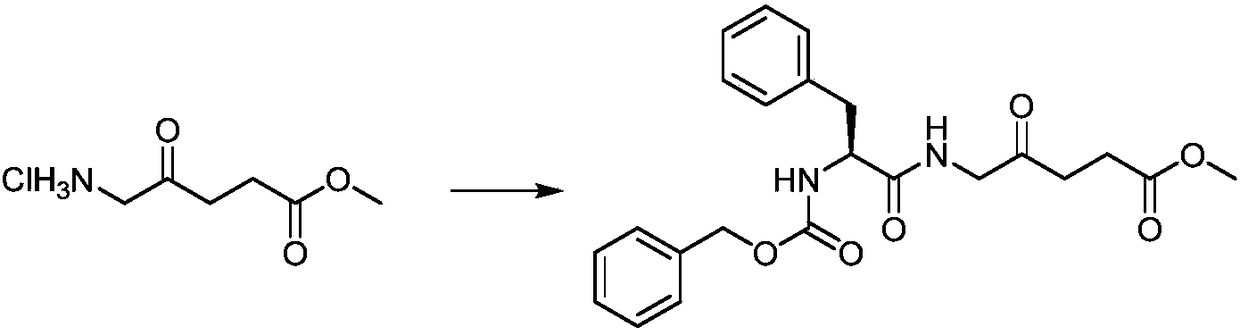
[0030] Preparation of 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L-phenylpropionyl)amino-4-oxopentanoic acid benzyl ester:
[0031]
[0032] In a 50 mL round bottom flask, 5-aminolevulinic acid benzyl hydrochloride (1.0 g, 3.88 mmol), Cbz-L-phenylalanine (1.16 g, 3.88 mmol) and HBTU (1.7 g, 4.49 mmol) was dissolved in DMF (10 mL), and DIPEA (2.0 mL, 11.5 mmol) was added, and stirred at 25° C. for 6 h. Concentrated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, separated by silica gel column chromatography, the eluent was dichloromethane:methanol (v / v=100:1), to obtain a white solid 5-((2'-benzyloxycarbonylamino)-L- Benzylpropionyl)amino-4-oxopentanoic acid benzyl ester 1.53g, yield 78.6%. 1 H NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δppm: 7.38–7.27(m,10H),7.19(s,5H),6.73(s,1H),6.40(d,J=12.4Hz,1H),6.24(s,1H),5.53(d,J =12.4Hz,1H),5.41(t,J=7.0Hz,1H),4.82(dd,J=30.4,12.4Hz,2H),4.40(d,J=12.5Hz,1H),3.55(d,J =12.3Hz,1H),3.47(dd,J=12.4,7.0Hz,1H),3.36(ddd,J=12.5,3.9,2.2Hz,1H),3.12(dd,J=12.4,7.0Hz,1H) ,2.68(ddd,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com