Method For Separating Hydrolyzed Product Of Biomass
A technology of hydrolysate and separation method, applied in the field of separation, can solve problems such as failure to achieve good separation of biomass hydrolysate and divalent metal salts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
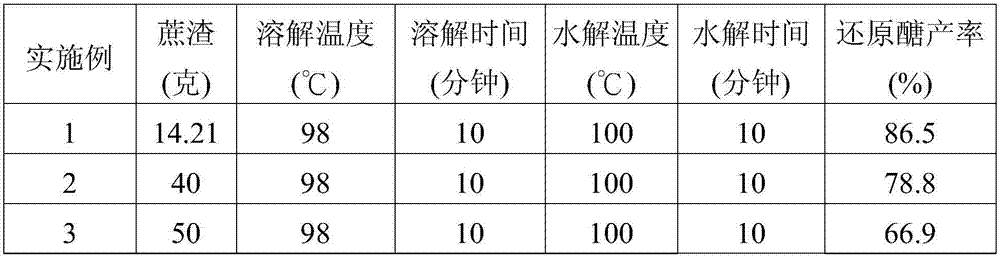
[0025] Mixed hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride (ZnCl 2 ) and stirred at room temperature and normal pressure to form a mixed solution (hydrochloric acid 2wt%, zinc chloride 257 grams). Add bagasse to 100 g of the mixture (14.21 g of bagasse) to carry out a dissolution reaction (temperature 98° C., time 10 minutes). After the bagasse dissolves, a reddish-brown homogeneous liquid is obtained. Afterwards, 100 g of hydrochloric acid (2 wt %) aqueous solution was added into the reddish-brown homogeneous liquid (temperature 100° C., time 10 minutes). The pH of the mixed solution is measured to be 1-2, and a concentrated solution (containing biomass hydrolyzate) and a filtrate (containing divalent metal salts) are obtained through solid-liquid separation. Next, measure the total weight of reducing sugars with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC method), and calculate the yield of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars may include glucose, xylose, mannose, arabinose and oligosa...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Mixed hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride (ZnCl 2 ) and stirred at room temperature and normal pressure to form a mixed solution (hydrochloric acid 2wt%, zinc chloride 257 grams). Add bagasse to 100 g of the mixed solution (40 g of bagasse) to carry out a dissolution reaction (temperature 98° C., time 10 minutes). After the bagasse dissolves, a reddish-brown homogeneous liquid is obtained. Afterwards, 100 g of hydrochloric acid (2 wt %) aqueous solution was added into the reddish-brown homogeneous liquid (temperature 100° C., time 10 minutes). The pH of the mixed solution is measured to be 1-2, and a concentrated solution (containing biomass hydrolyzate) and a filtrate (containing divalent metal salts) are obtained through solid-liquid separation. Next, measure the total weight of reducing sugars with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC method), and calculate the yield of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars may include glucose, xylose, mannose, arabinose and oli...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Mixed hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride (ZnCl 2 ) and stirred at room temperature and normal pressure to form a mixed solution (hydrochloric acid 2wt%, zinc chloride 257 grams). Add bagasse to 100 g of the mixture (50 g of bagasse) to carry out a dissolution reaction (temperature 98° C., time 10 minutes). After the bagasse dissolves, a reddish-brown homogeneous liquid is obtained. Afterwards, 100 g of hydrochloric acid (2 wt %) aqueous solution was added into the reddish-brown homogeneous liquid (temperature 100° C., time 10 minutes). The pH of the mixed solution is measured to be 1-2, and a concentrated solution (containing biomass hydrolyzate) and a filtrate (containing divalent metal salts) are obtained through solid-liquid separation. Next, measure the total weight of reducing sugars with high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC method), and calculate the yield of reducing sugars. Reducing sugars may include glucose, xylose, mannose, arabinose and oligosacch...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com