Method for detecting staphylococcus aureus by synthesizing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) enzyme through magnetic separation RCA (rolling circle amplification)
A staphylococcus, DNA enzyme technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of low sensitivity, high detection limit, complicated operation, etc., to improve sensitivity, accuracy and specificity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
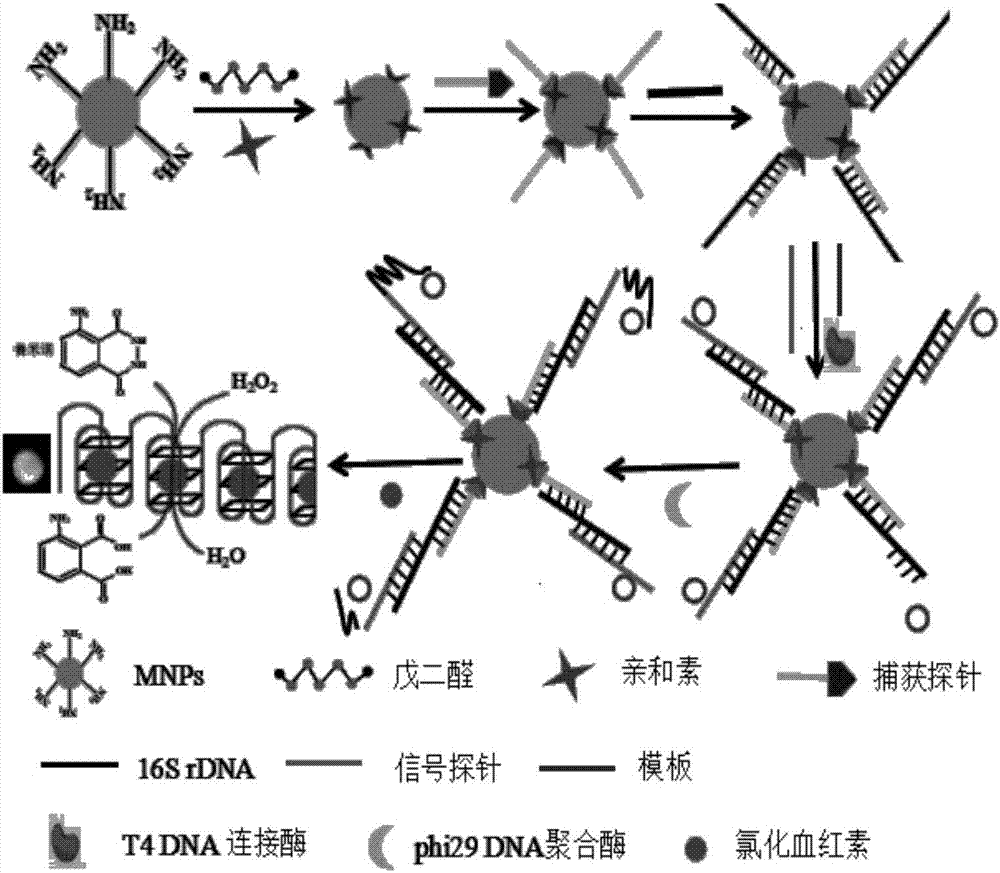
[0054] (1) Preparation of magnetic nanoparticles functionalized with capture probes
[0055] Add 500 μL of aminated magnetic nanoparticles to 150 μ glutaraldehyde and 1350 μ L PBS solution, mix well, react in the dark for 2 hours, wash with PBS buffer for 3 times, then add 500 μL of a certain concentration of avidin, shake and react in the dark for 6 hours, PBS buffer Wash 3 times to obtain avidin-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Then 240 μL of synthesized avidin-modified magnetic nanoparticles and 10 μL of capture probe were mixed, incubated at room temperature for 30 min, and washed with TE buffer three times to obtain capture probe functionalized magnetic nanoparticles.
[0056] (2) Sandwich structure generated by 16S rDNA sequence and probe
[0057] Take 30 μL of capture probe-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles, add the test solution containing 16S rDNA sequence (that is, target DNA), incubate at room temperature for 30 min, wash with TE buffer for 3 times, then add 3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2: Specific analysis of target DNA (tDNA)
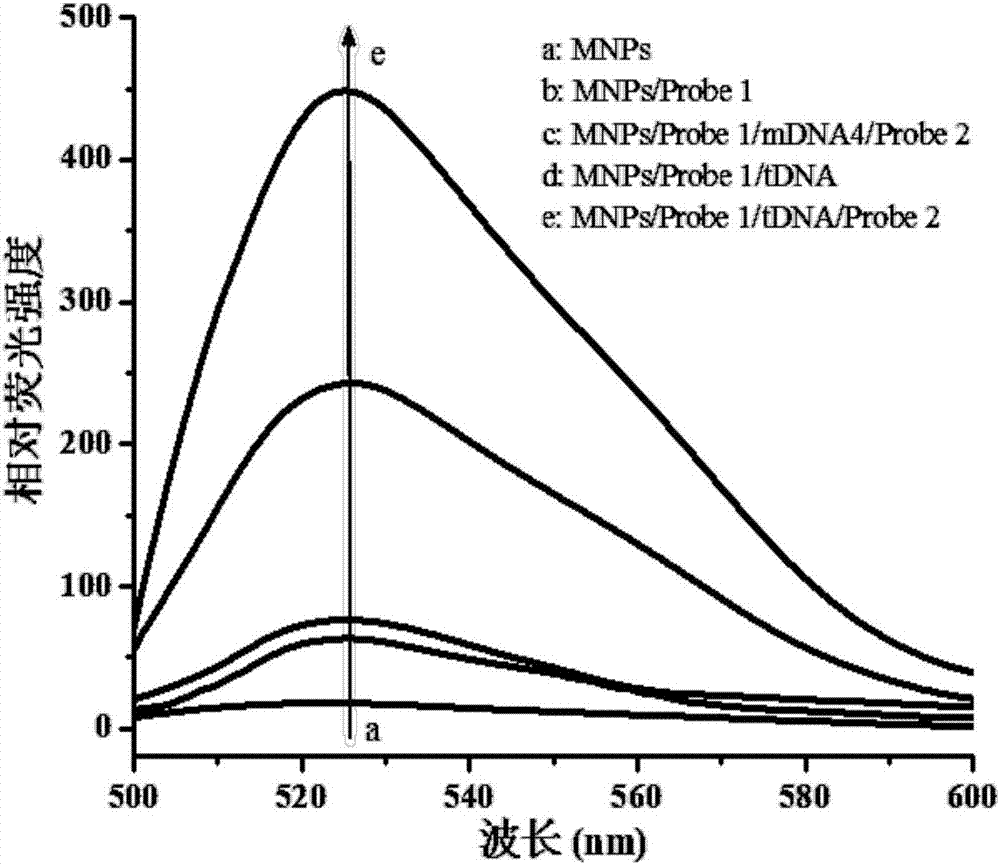
[0068] The specificity is established based on the principle of sandwich hybridization, that is, the specific complementary pairing between the probe and the target sequence.
[0069] Under the condition that the concentration of magnetic nanoparticles is 1.0 mg / mL, the concentration of capture probe is 100 nmol / L, the amplification time is 50 min, and the connection time is 50 min, equal volume and concentration of tDNA (sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 ) and base-mismatched DNA sequences (mDNA1, mDNA2, mDNA3, and mDNA4, compared with tDNA, one-base mismatch DNA, two-base mismatch DNA, three-base mismatch DNA, random sequence DNA ; The sequences are shown in SEQ ID NO:6~SEQ ID NO:9, respectively,) as the detection object for evaluating the specificity of this experiment.
[0070] Such as Figure 4 As shown, different relative luminescence values were obtained by detecting different DNA sequences, from which it can...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Example 3: Specific analysis of Staphylococcus aureus
[0072] Based on the principle of specific complementary pairing of nucleic acid probes with 16S rDNA of Staphylococcus aureus.
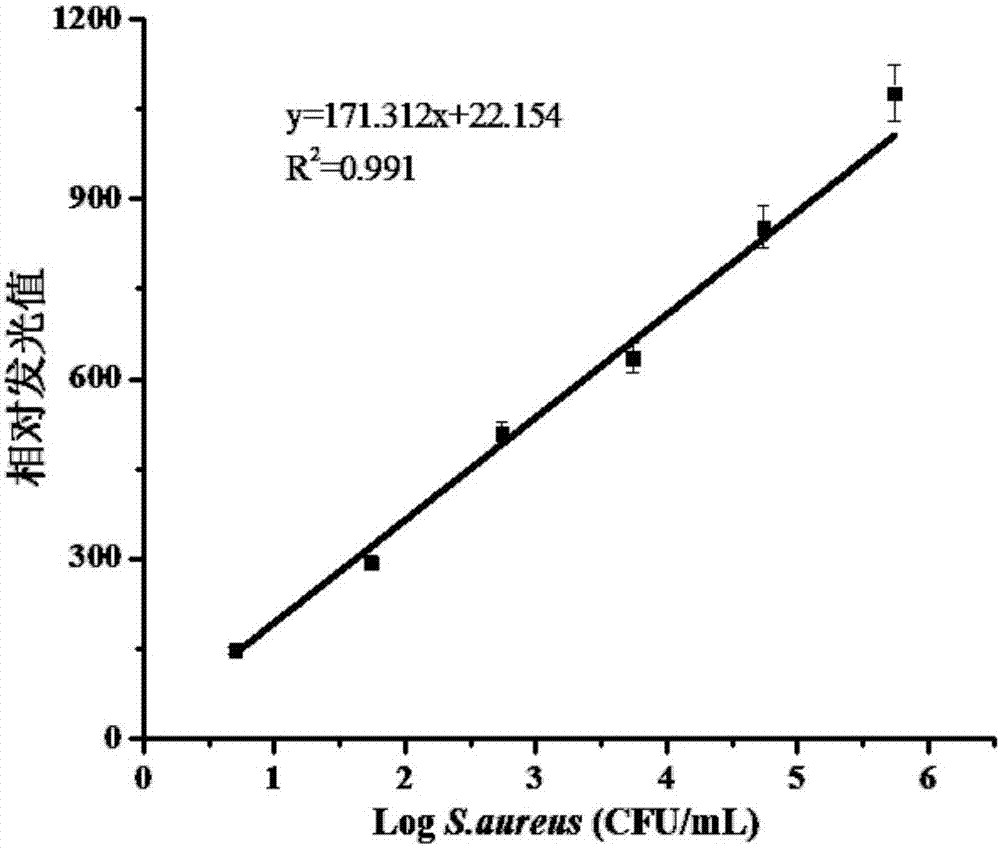
[0073] Using Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus and Shigella dysenteriae as samples to be tested, the method in Example 1 was used to investigate and compare the detection effects, and TE buffer was used as a blank control.
[0074] Depend on Figure 5 It can be seen that the relative luminescence value of Staphylococcus aureus is much higher than that of Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Bacillus cereus and Shigella dysenteriae, indicating that the method in Example 1 has good specificity for Staphylococcus aureus.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com