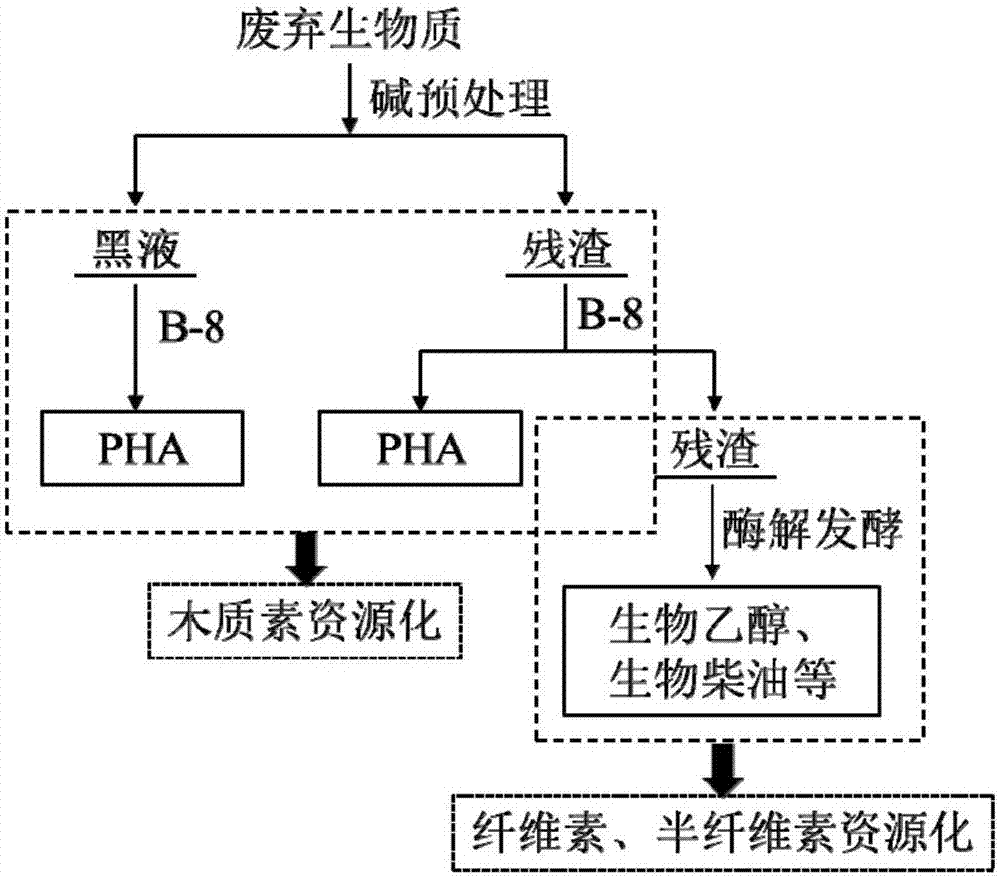
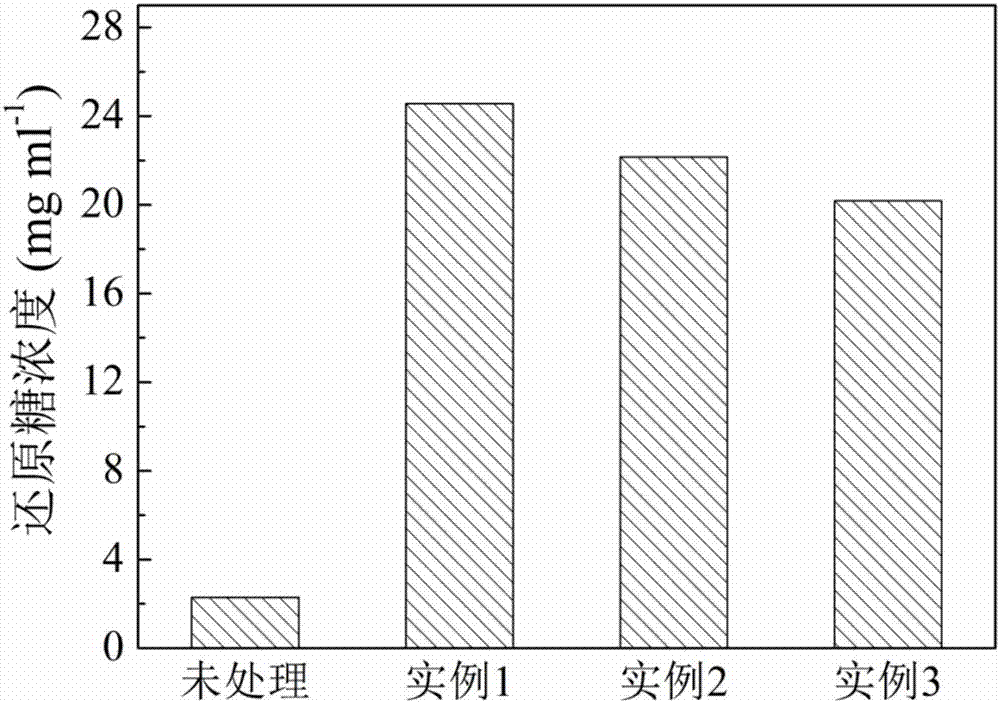
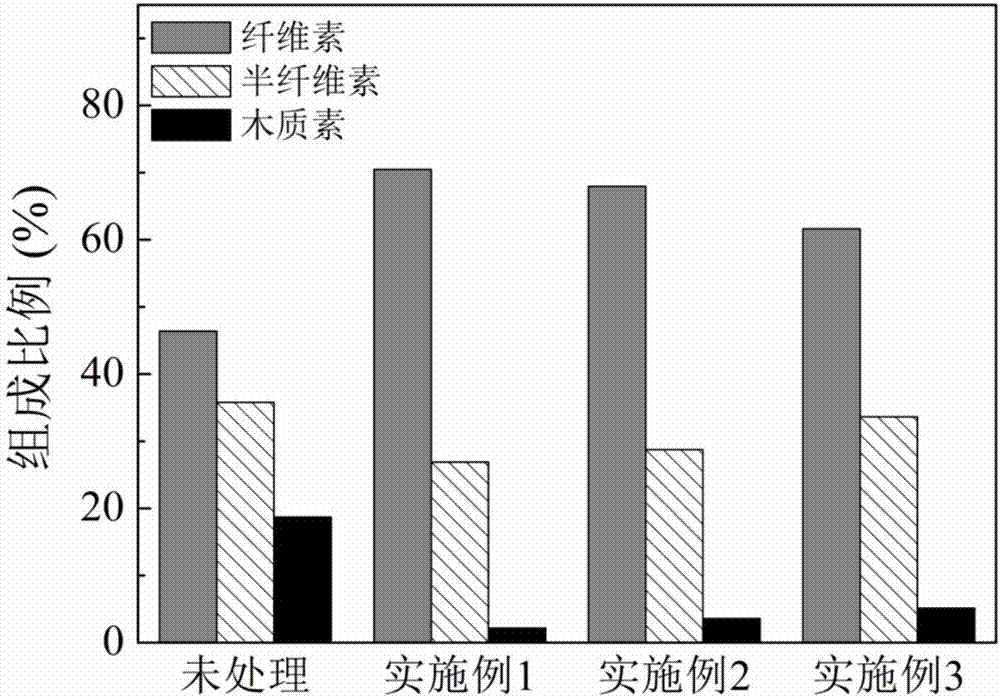
Waste biomass recycling method
A technology for waste biomass and recycling, which is applied in the field of waste biomass recycling technology, can solve problems such as waste of lignin resources, and achieve the effects of large dosage of chemicals, improved efficiency of enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification, and reduced strength.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0040] (2) Put the waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH solution with a concentration of 2% according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml), let it stand in a constant temperature environment of 121°C for 60 minutes, and then filter and separate to obtain Wet slag A1 and treated black liquor B.
[0041] (3) Rinse the wet residue A1 obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing solution is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue A2.
[0042] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 cells stored on the LB slope into LB liquid medium, and culture at 30°C for 18 hours (the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain the seeds of Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Liquid; wherein said LB liquid culture medium each composition ratio ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0053] (2) Put waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH solution with a concentration of 2% according to the solid-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml), let it stand in a constant temperature environment of 121°C for 15 minutes, and then filter and separate to obtain Wet slag A1 and treated black liquor B.
[0054] (3) Rinse the wet residue A1 obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing solution is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue A2.
[0055] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 bacteria stored on the LB slant into LB liquid medium, and cultivate at 30°C for 18 hours (that is, the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Seed liquid; wherein the distribution ratio of the components of the LB ...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (1) The rice straw was crushed and sieved with 60 meshes, washed twice with ultrapure water, and dried at 60°C until constant weight.
[0066] (2) Put waste biomass in a container of appropriate size, add NaOH solution with a concentration of 1% according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g / ml), let it stand in a constant temperature environment of 121°C for 30 minutes, and then filter and separate to obtain Wet slag A1 and treated black liquor B.
[0067] (3) Rinse the wet residue A1 obtained by filtering and separating with distilled water repeatedly until the pH of the washing solution is neutral, and dry at 60° C. to a constant weight to obtain dry residue A2.
[0068] (4) Inoculate the Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 bacteria stored on the LB slant into LB liquid medium, and cultivate at 30°C for 18 hours (that is, the optical density at 600nm reaches 0.8-1.0) to obtain Cupriavidus basilensis B-8 Seed liquid; wherein the distribution ratio of the components of the LB l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com