A method of grafting and modifying thin films by electron beam curing
A technology of electron beam curing and graft modification, which is applied in the field of graft modification of thin films by electron beam curing, can solve the problems of complicated operation and poor durability, achieve strong penetration, uniform distribution, and reduce formula Product Cost Effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
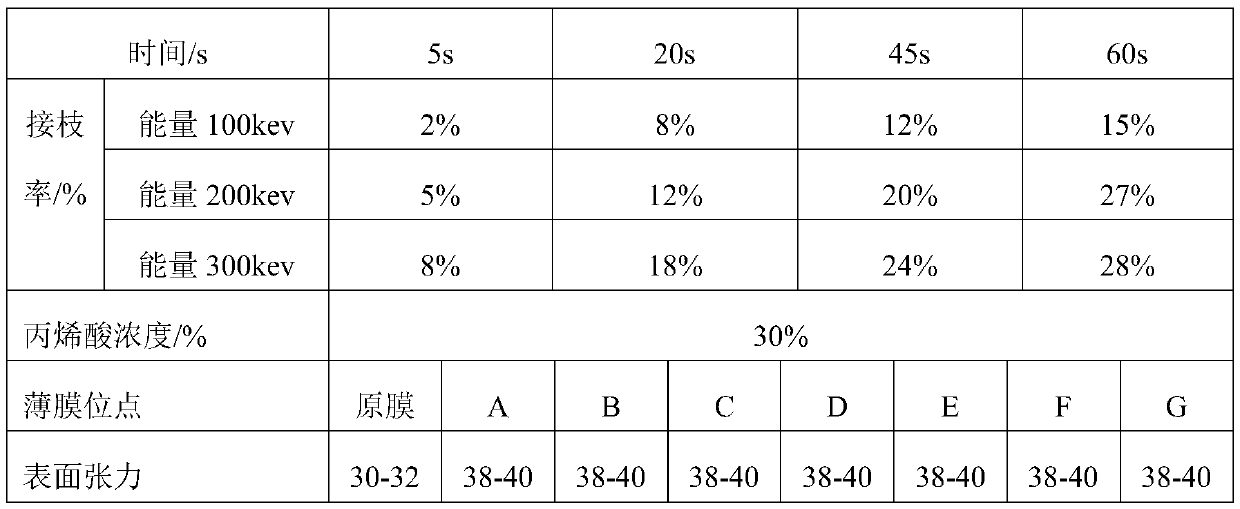
[0035] Example 1: Polyethylene film electron beam curing grafted acrylic acid
[0036] The polyethylene film is placed in a quartz glass container filled with acrylic acid (containing 0.15% polymerization inhibitor) solution (the polyethylene film is 60 parts by weight, the acrylic acid is 30 parts by weight, and the solvent is 100 parts) , compacted with a glass sheet, open the nitrogen valve, fill the nitrogen for a period of time, then turn on the electron accelerator, and act for a certain period of time (5-60s) under the action of energy 100-300kev and power 20kw. After completion, wash with warm water, and then wash away unreacted acrylic acid monomers on the surface of the polymer with chloroform, and dry to constant weight. The polyethylene grafted acrylic acid was obtained, and the specific grafting rate is shown in Table 1. The surface tension shown in Table 1 is the result obtained by measuring the polyethylene grafted acrylic acid obtained under the action of ener...
Embodiment 2
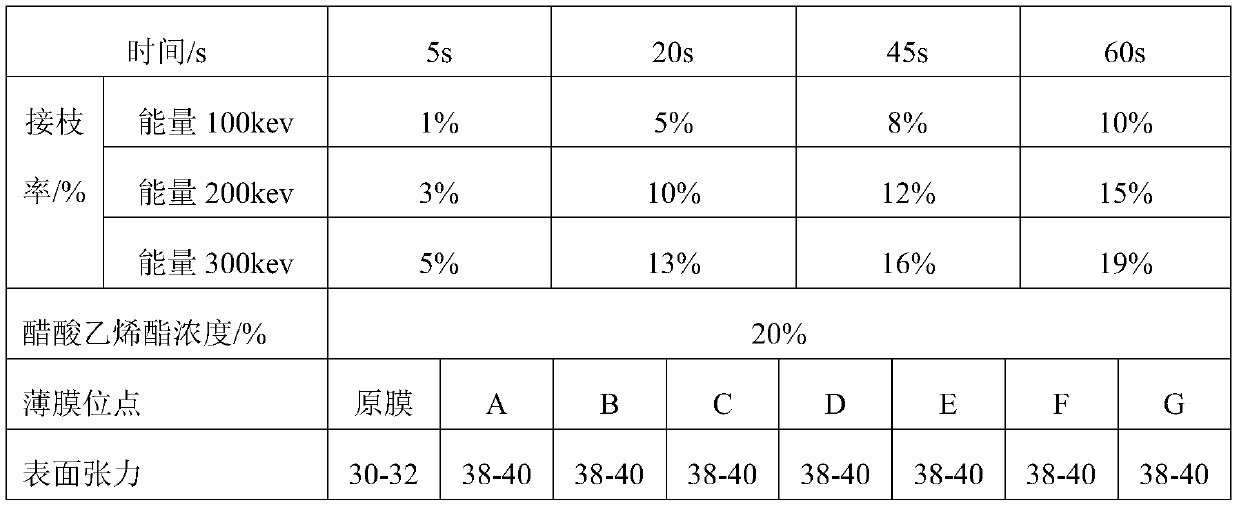
[0039] Example 2: Electron Beam Curing of Low Density Polyethylene Grafted Vinyl Acetate
[0040] Take two low-density polyethylene films, inject 20% vinyl acetate solution (pre-filled with nitrogen to remove oxygen) into the middle of the two films with a micro-syringe, gently press the film to spread the reaction solution evenly, and place it on a quartz glass plate , use an electron beam accelerator at a predetermined temperature (10-50°C) to irradiate with a certain energy. After the reaction, take out the film, dry it to remove unreacted monomers, dry the film and weigh it. Obtained low-density polyethylene grafted vinyl acetate, the specific grafting rate is shown in Table 2, the surface tension shown in Table 2 is the result measured by polyethylene grafted acrylic acid obtained under the action of energy 300kev for 60s.
[0041] Table 2
[0042]
Embodiment 3
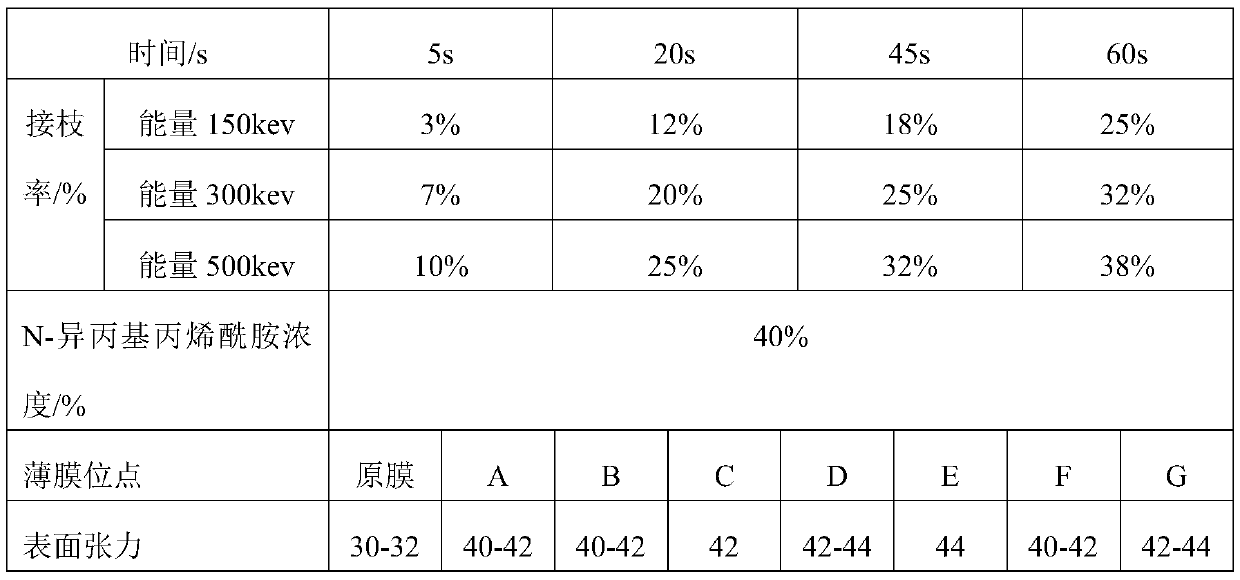
[0043] Example 3: Polypropylene electron beam curing grafted N-isopropylacrylamide
[0044] Between the two polypropylene films to be grafted, inject a certain concentration of N-isopropylacrylamide solution (pre-filled with nitrogen to remove oxygen) and inject it into the middle of the two films and lightly press the film to spread the reaction solution evenly. The quartz glass sheet is irradiated with an electron beam accelerator at a predetermined temperature and a certain energy. After the reaction is completed, the film is taken out, dried to remove unreacted monomers, and the film is dried and weighed. The polypropylene grafted N-isopropylacrylamide was obtained, and the specific grafting rate is shown in Table 3. The surface tension shown in Table 3 is the result obtained by measuring the polyethylene grafted acrylic acid under the action of energy 300kev for 60s.
[0045] table 3
[0046]
[0047] In summary, the grafting rate of the grafted film prepared in this ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com