Separation, purification and primary culture methods of intestinal macrophages in Ctenopharyngodon idella
A macrophage and separation method technology, applied in the field of fish cell culture, can solve the problems of cell death, decreased cell viability, unclear conditions of grass carp intestinal macrophages, etc., and achieves high purity and activity, strong operability, good repeatability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
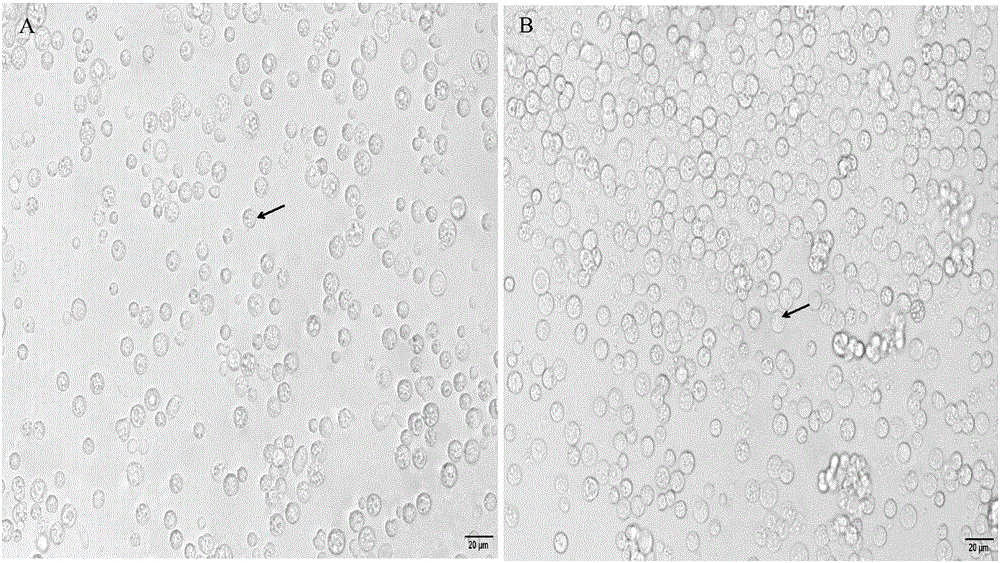
[0052] Example 1 Isolation of grass carp intestinal macrophages
[0053] 1.1 Removal of intestinal mucus and intestinal epithelial cell layer of grass carp
[0054] Select about 250g of healthy grass carp, rinse the body surface with tap water, beat the head to death, and quickly soak in 75% ethanol for 20s. Aseptically remove the middle and posterior intestinal tract on the ultra-clean workbench, put it in a petri dish containing pre-cooled sterile PBS buffer solution (0.01mol / L, pH 7.4), and remove extra-intestinal fat and mesentery with sterile elbow tweezers , dissect the intestine longitudinally and wash the feces. Afterwards, scrape the intestinal mucus and epithelial cell layer on the inner side of the intestinal wall repeatedly with sterile elbow tweezers until no mucus is scraped off (it takes 15 minutes), and then wash it with PBS buffer (0.01mol / L, pH 7.4) for 3 times with slight shaking. At this time, the intestinal mucus and epithelial cells can be seen to fall ...
example 2
[0059] Purification of example 2 grass carp intestinal macrophages
[0060] The isolated intestinal macrophage suspension was further purified by differential attachment method. That is, resuspend the isolated intestinal macrophages with RPMI1640 basal medium, and adjust the cell density to 3×10 6 cells / mL and spread in 96-well cell culture plate, 100 μL / well, 28°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in the incubator, change the medium for the first time after culturing 4h, discard the old nutrient solution when changing the medium, add fresh RPMI 1640 complete nutrient solution containing grass carp autologous serum (84% RPMI 1640 nutrient solution (Gibco product), 10% FBS, 5% grass carp autologous serum, 1% antimicrobial solution) continued to culture for 12 hours, changed the medium again, discarded the old culture medium, and added RPMI 1640 complete culture medium containing grass carp autologous serum to continue the culture. As a result, it was found that the macrophages began to adhe...
example 3
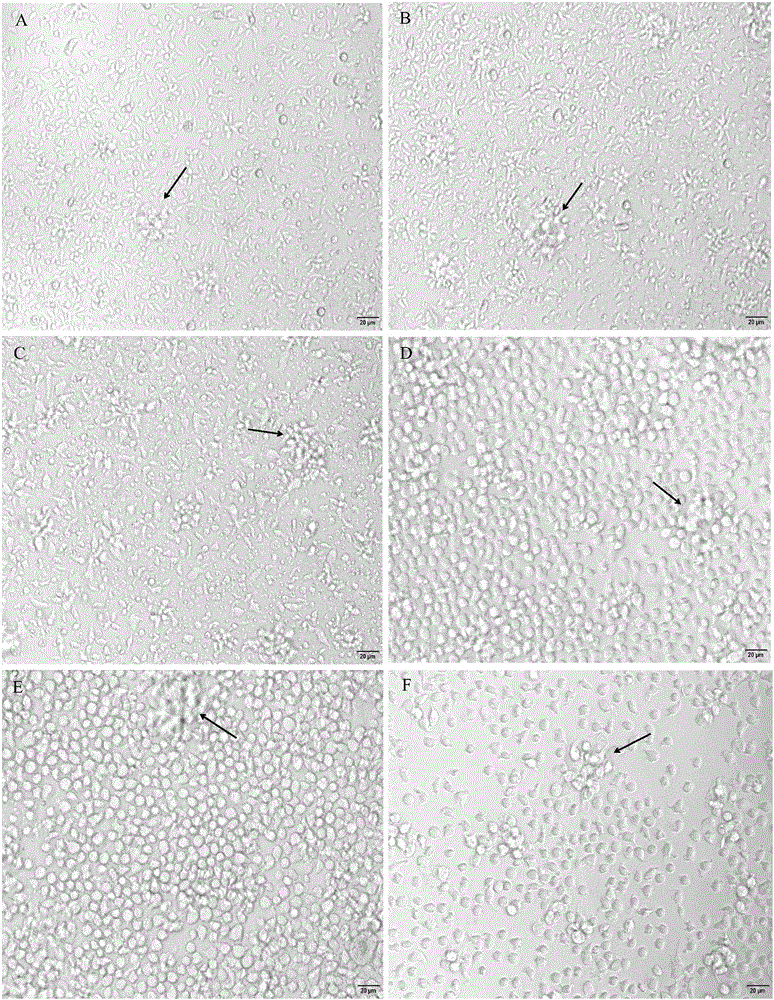
[0061] Primary culture of example 3 grass carp intestinal macrophages
[0062] The concentration of purified macrophages was adjusted to 3×10 with RPMI 1640 complete culture solution containing grass carp autologous serum (84% RPMI 1640 culture solution, 10% FBS, 5% grass carp serum, 1% antimicrobial solution). 6 cells / mL, inoculate 96-well cell culture plate, 100 μL / well, 28°C, 5% CO 2 Culture in an incubator. After the cells start to adhere to the wall, replace the medium with RPMI 1640 complete culture medium containing 20 μg / mL LPS, and then change the medium every 2 days. When changing the medium, suck out 500 μL of the old culture medium, and then add 500 μL of RPMI 1640 complete culture solution containing grass carp autologous serum was continued in the incubator. The results showed that after 1 day of culture, most macrophages began to stretch and grow, and a few cell clumps appeared ( figure 2 A); 2-3 days after culture, the cells continued to stretch and grow in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com