Heavy metal lead-cadmium polluted soil biological remediation method based on plants
A cadmium-contaminated soil and bioremediation technology is applied in the field of plant-based bioremediation of heavy metal lead and cadmium contaminated soil. robust effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A plant-based bioremediation method for heavy metal lead and cadmium contaminated soil, comprising the following steps:
[0035] Step 1, Prepare the Cultivation Substrate
[0036] Step 1.1, take by weight the following raw materials: 80 parts of dead leaves, 80 parts of peat, 30 parts of birch bark, 15 parts of animal excrement, 5 parts of silkworm sand, 1 part of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 6 parts of urea;
[0037] In step 1.2, the dead leaves weighed in step 1.1 are mixed with animal feces to obtain a mixture, and water of the same quality as the mixture is added to the mixture, and the mixture is continuously stirred in the process of adding water, and the mixture is allowed to stand after adding water. 12h, then add anaerobic fermentation bacterial agent to it, ferment at 60°C for 12 days, after the fermentation is completed, the fermentation product is dried to a moisture content of 2%, then pulverized, and passed through a 40-mesh sieve to obtain organic fert...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The implementation steps of Example 2 are the same as those in Example 1, except that the cultivation substrate is prepared from the following components by weight in Example 2: 85 parts of dead leaves, 70 parts of peat, 25 parts of birch bark, 18 parts of Animal manure, 8 parts of silkworm sand, 0.5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 5 parts of urea;
[0052] In step 4, the number of effective viable bacteria of the young set of sacculus fungus is 1×10 9 pcs / g;
[0053] In step 4, the fertilizer is composed of the following components by weight: 45 parts of ammonium nitrate, 15 parts of ammonium polyphosphate, 15 parts of potassium fulvic acid, 1 part of chitosan, 2 parts of EDTA-Mg, 2 parts of citric acid, 1 part lecithin, 0.1 part gibberellin.
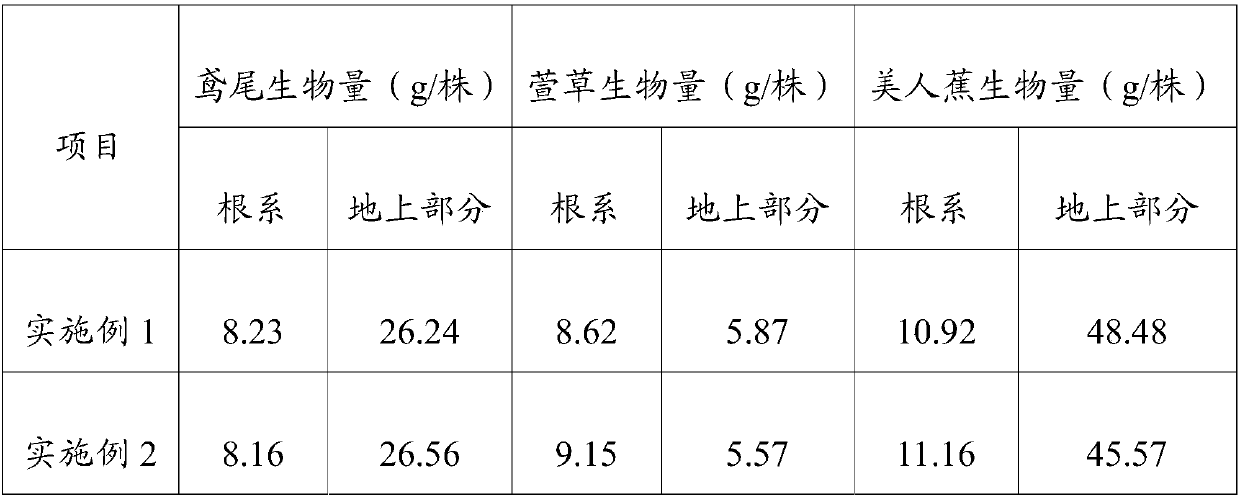
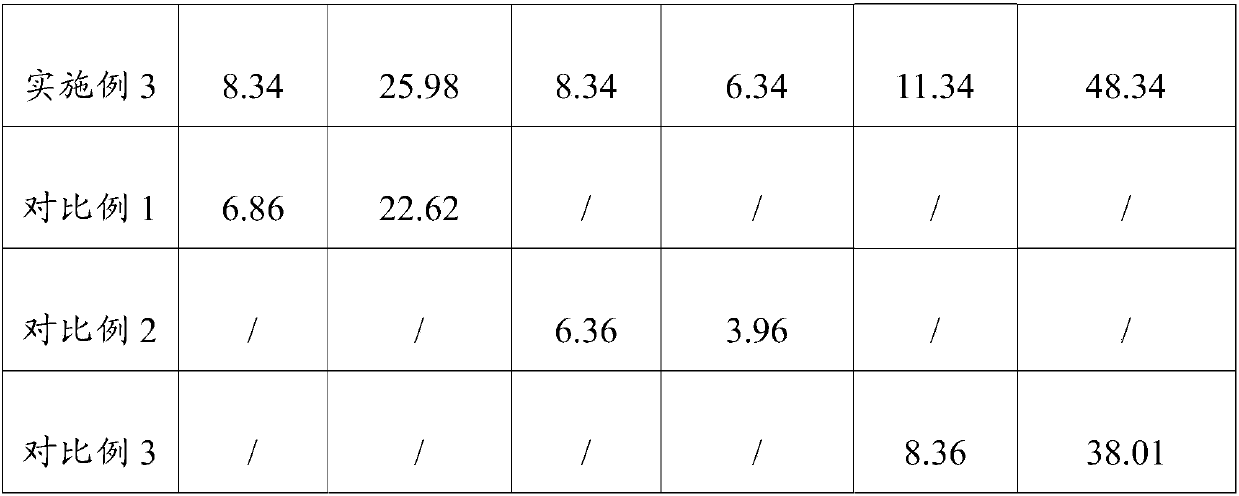
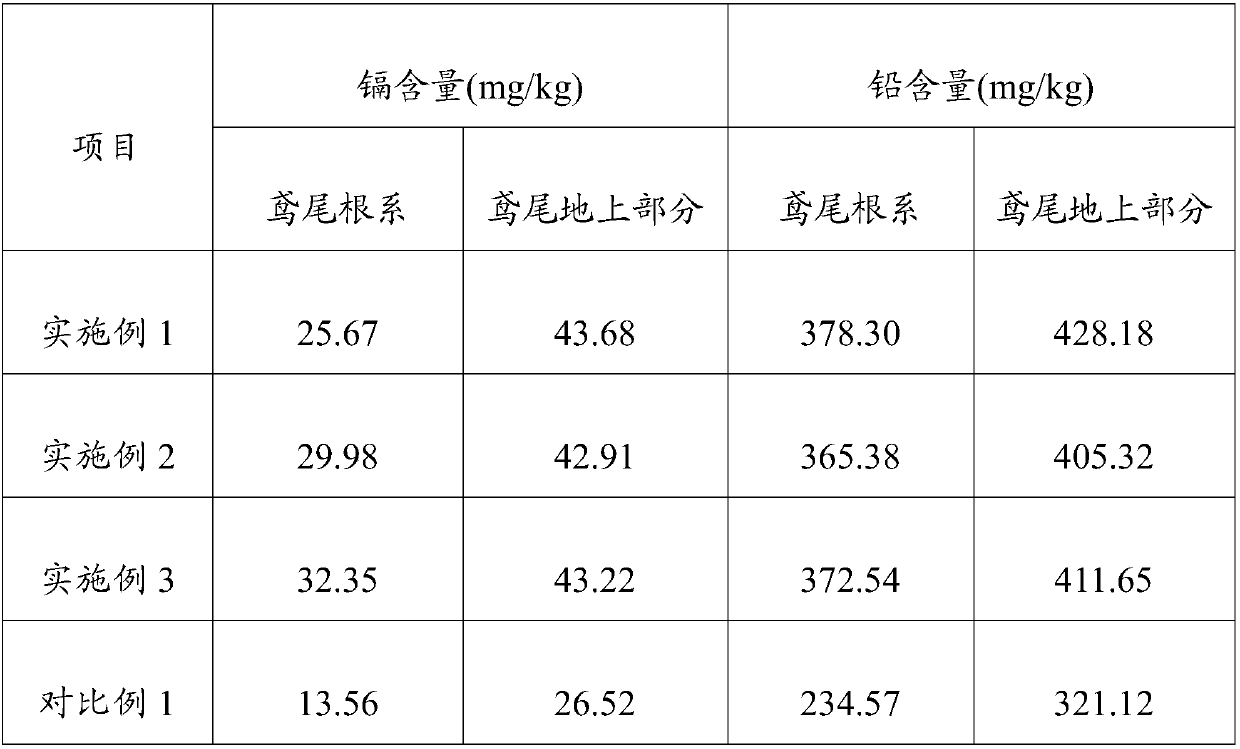
[0054] Example 2 After repeated planting 4 times, it was detected that the concentration of lead in the soil was 102 mg / kg and the concentration of cadmium was 0.16 mg / kg, which reached the secondary standard of soil ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The implementation steps of Example 3 are the same as those of Example 1, except that the cultivation substrate in Example 3 is prepared from the following components by weight: 90 parts of dead leaves, 60 parts of peat, 20 parts of birch bark, 20 parts of Animal manure, 10 parts of silkworm sand, 0.8 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3 parts of urea;
[0057] In step 4, the number of effective viable bacteria of the young set of sacculus fungus inoculum is 5×10 8 pcs / g;
[0058] In step 4, the fertilizer is made up of the following components by weight: 50 parts of ammonium nitrate, 10 parts of ammonium polyphosphate, 20 parts of potassium fulvic acid, 5 parts of chitosan, 1 part of EDTA-Zn, 3 parts of citric acid, 0.5 part lecithin, 0.1 part naphthalene acetic acid.
[0059] Example 3 After repeated planting 4 times, it was detected that the concentration of lead in the soil was 92 mg / kg and the concentration of cadmium was 0.18 mg / kg, which reached the secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com