Double-layer composite structure ceramic, preparation method of the ceramic, self-adsorption lithium-air battery and preparation method of the battery
A lithium-air battery, double-layer composite technology, which is applied to fuel cell type half cells and secondary battery type half cells, battery electrodes, structural parts, etc. The method is simple and the effect of improving the discharge capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
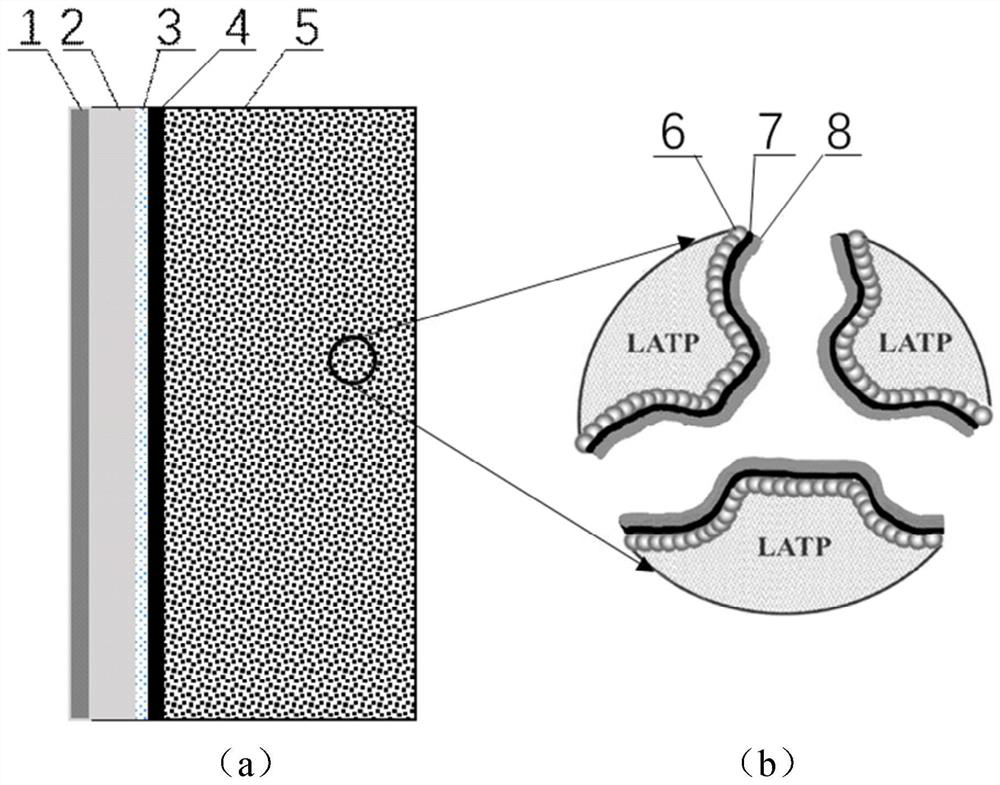
[0039] Specific Embodiment 1: The double-layer composite structure ceramic described in this embodiment includes a porous layer and a dense layer sequentially stacked from bottom to top, and the material of the double-layer composite structure ceramic is:
[0040] Li 1+x m x Ti 2-x (PO 4 ) 3 , 0≤x≤0.5, M is Al, Ga, In or Sc;
[0041] Or, Li 1+x al x Ge 2-x (PO 4 ) 3 , 0≤x≤1.2;
[0042] Or, Li 7-x La 3 Zr 2-x N x o 12 , 0≤x≤1.2, N is Al or Ta;
[0043]On the inner pore wall of the porous layer, an electronic conductive layer, a catalyst layer and a water vapor adsorption layer are uniformly deposited in sequence.
[0044] In this embodiment, the material of the electronically conductive layer is: nano-carbon powder, graphene, mesoporous carbon, carbon nanotube, amorphous carbon, multilayer graphite, conductive macromolecular material, conductive metal, conductive polymer or electronically conductive Sexual functional ceramics, such as: ABO 3 , wherein, A is La...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of the double-layer composite structure ceramic described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the material of the water vapor adsorption layer is deliquescent salt or superabsorbent resin.
[0050] Superabsorbent resin is a synthetic resin with hydrophilic groups, which can absorb a large amount of water and swell and keep water from flowing out, such as starch grafted acrylate, grafted acrylamide, high degree of substitution cross-linked carboxymethyl fiber Elements, cross-linked methyl cellulose grafted with acrylamide, cross-linked light ethyl cellulose grafted with acrylamide polymer, etc.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0051] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is a further description of the double-layer composite structure ceramics described in specific embodiment one. In this embodiment,
[0052] The density of the dense layer is greater than 90%, and the thickness of the dense layer is 10 μm to 50 μm.
[0053] The porosity of the porous layer is greater than 50%, and the thickness of the porous layer is 200 μm˜1000 μm.
[0054] In this embodiment, the higher the density of the dense layer, the better, and the thinner the dense layer, the better. The pores in the porous layer increase sequentially along the direction away from the dense layer. Preferably, a gradually changing gradient pore structure is formed in the porous layer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com