Molten salt electroforming preparation method of rhenium
A technology of molten salt and electroforming, which is applied in the direction of electroforming and electrolysis, which can solve problems such as difficulties, inability to heat process rhenium, complex processing, etc., and achieve the effects of convenient operation, good compactness, and good thickness uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
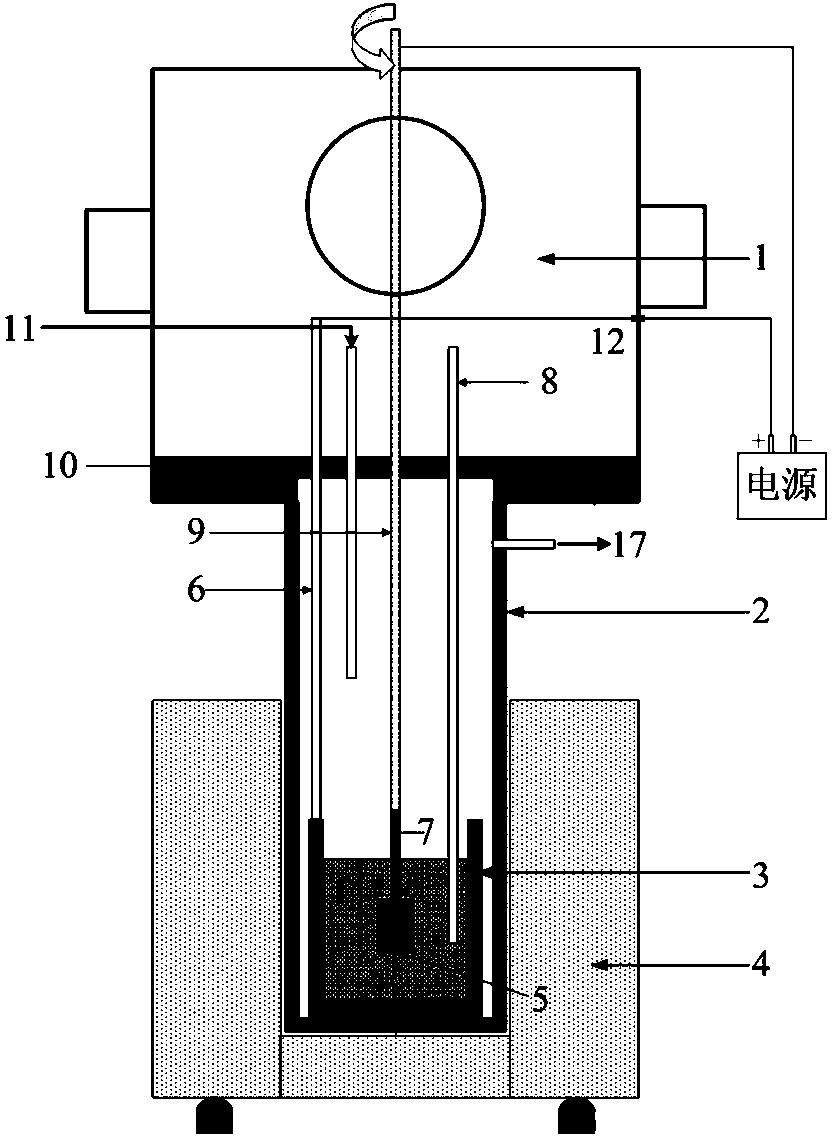
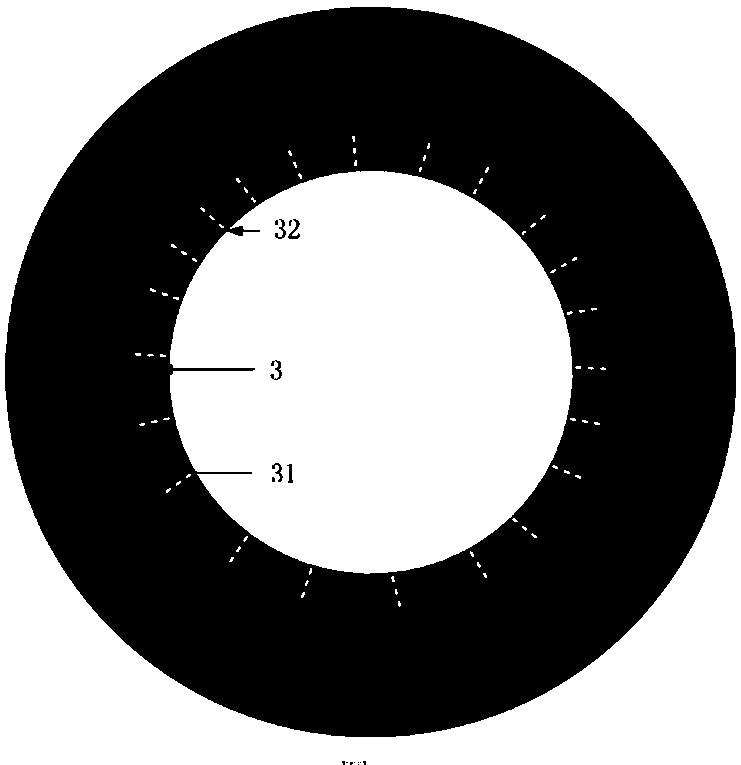
[0039] A kind of molten salt electroforming preparation method of rhenium, technological process is as follows image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0040] (1) Molten salt chlorination:
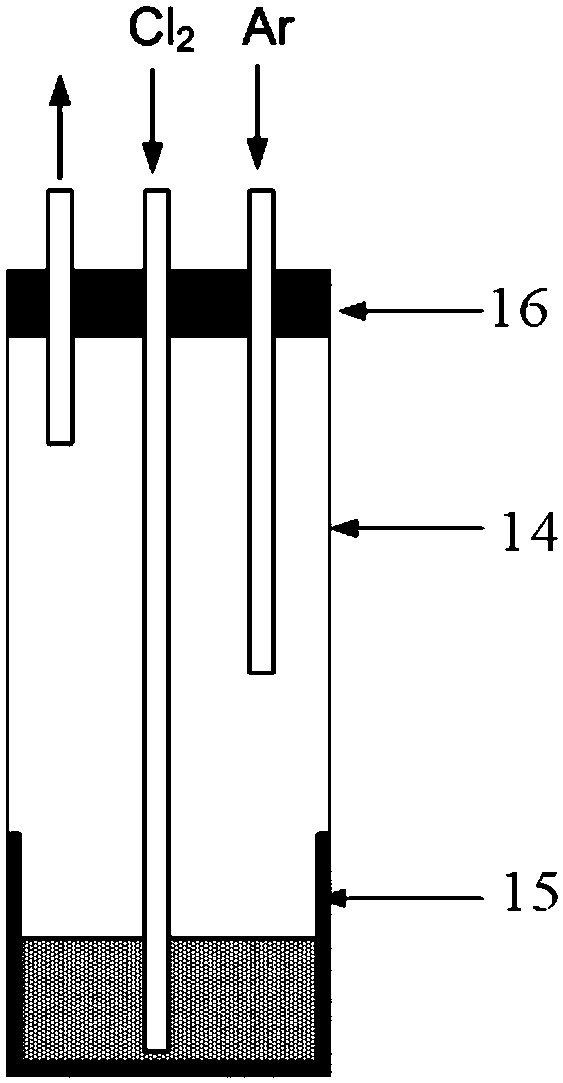
[0041] Weigh NaCl, KCl and CsCl respectively according to the raw material percentage of 34.7: 44.2: 21.1, then place the above raw materials in an oven at 200°C for 24 hours to remove crystal water, grind and mix them and put them in figure 1 In the quartz cup of the molten salt chlorination device shown, the device was purged with argon three times, and heated to 750°C under an argon protective atmosphere to melt. Stir the molten salt and add a certain amount of K to the molten salt 2 ReCl 6 , so that containing K 2 ReCl 6 The concentration of rhenium ions in the molten salt is 5wt.%, chlorine gas is passed into the molten salt for 30 minutes of chlorination, and finally cooled under the protection of argon to obtain the chlorinated molten salt.
[0042] (2) Yin and anodic ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A preparation method of molten salt electroforming of rhenium, the steps of which are basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference being that the electroforming time of step (3) is 12 hours.
[0052] Figure 7 The macrophotograph of the combustion chamber component of the 200N engine obtained in this example shows that the surface of the component is relatively smooth, silver-gray, and has nodules locally. Figure 8 The metallographic photograph of the cross-section of the component shows that there is no obvious hole in the cross-section of the component, and the compactness is good. The density measured by the drainage method is 99.4% of the theoretical density, the thickness of the component (that is, the rhenium layer) is about 600 μm, and the current efficiency is 94%.
Embodiment 3
[0054] A preparation method of molten salt electroforming of rhenium, the steps of which are basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that the cathode in step (2) is the mandrel of the combustion chamber of a 25N engine, and the contour shape of the inner wall of the anode basket is designed to be the same as that of the The profile of the mandrel is matched to form the pictorial anode; the electroforming time of step (3) is 22 hours.
[0055] Figure 9 The macrophotograph of the 25N engine combustion chamber component obtained for this embodiment, as can be seen from the figure, the surface of the component is silver-gray with nodules locally. Figure 10 It is a macroscopic photo of the component after EDM cutting and surface mechanical grinding. It can be seen that the surface of the component is bright and dense after being mechanically polished. After removing the graphite mandrel, the density of the rhenium component measured by the drainage method is 9...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com