A kind of molten salt electrodeposition method of niobium coating
An electrodeposition and molten salt technology, applied in electrolytic components, electrolytic processes, cells, etc., can solve the problems of low stability of complexes, weak reverse polarization, low working temperature, etc., and achieve convenient operation, convenient concentration, fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
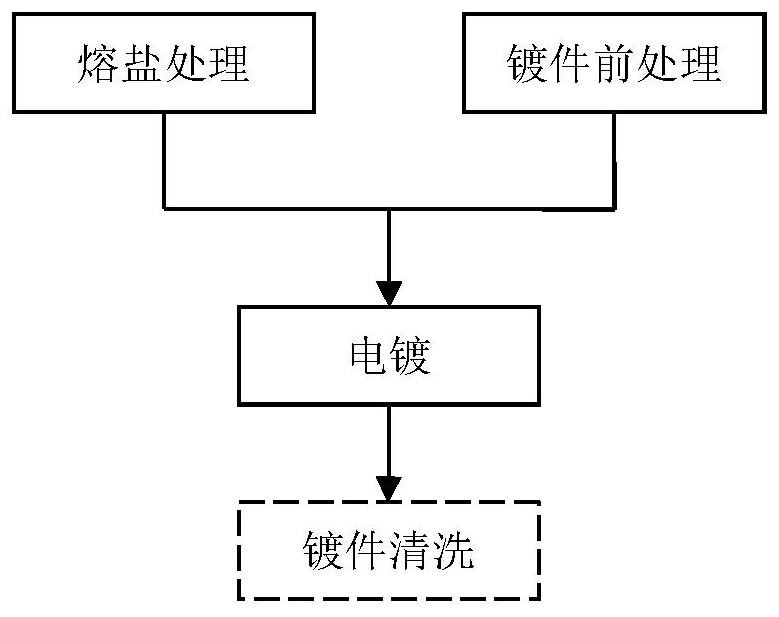
[0054] A molten salt electrodeposition method for niobium coating, comprising the following steps:
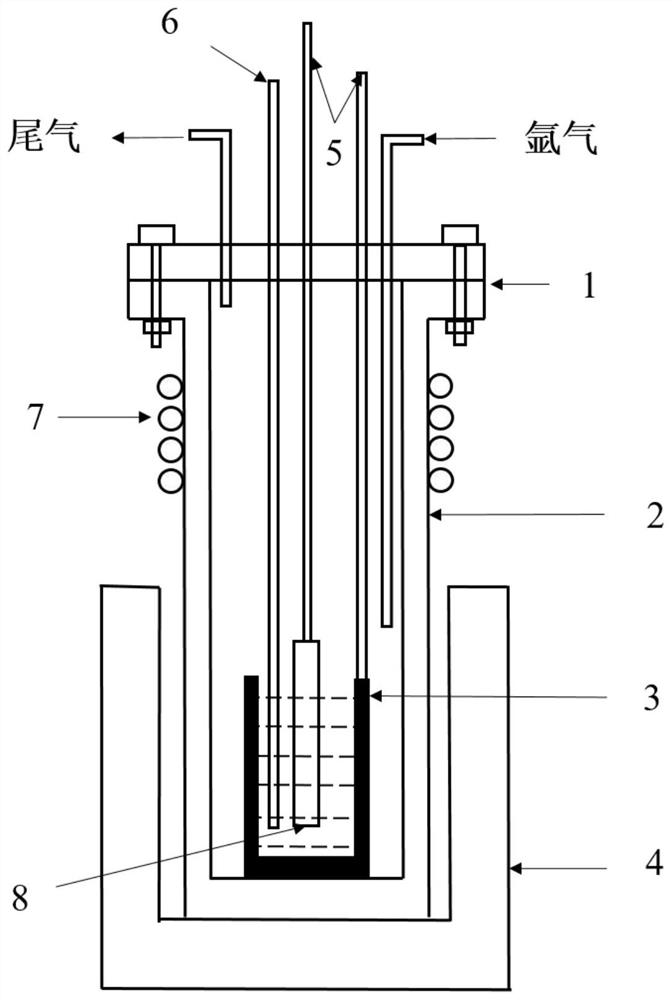
[0055] 1. Preparation of molten salt: Weigh NaCl, KCl and CsCl respectively according to the ratio of raw material mass ratio of 1:1.28:3.41, put NaCl, KCl and CsCl in a 200 ℃ oven for drying treatment for 8h to remove crystal water, and then NaCl, KCl and CsCl , KCl and CsCl were ground and mixed in a quartz cup, the device was purged with argon gas three times, and heated to 750°C under an argon gas protective atmosphere to melt. Chlorine was introduced into the molten salt for 10 minutes, then argon was bubbled for 15 minutes, and finally cooled under argon protection. will K 2 NbF 7 After drying for 8 hours in a vacuum drying oven at 120°C and a vacuum degree of 100Pa, it was added to the supporting electrolyte to make the K containing 2 NbF 7 The niobium ion concentration in the molten salt was 2.4 wt.%.
[0056] 2. Pre-treatment of plating parts and crucible plating....
Embodiment 2
[0061] The steps are basically the same as those in Example 1, except that the temperature in Step 3 is adjusted to 800°C.
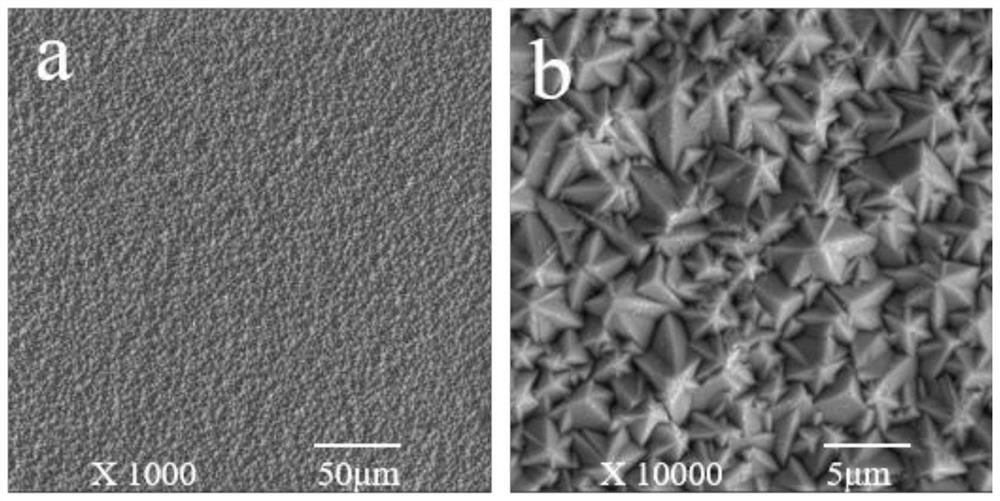
[0062] Figure 5 It is the SEM picture of the coating surface obtained in Example 2. It can be seen that the coating surface is uniform and undulating, and the crystal grains are in the shape of shells. Image 6 From the SEM picture of the coating section obtained in this example, it can be seen that the coating section has no obvious holes, good compactness, coarse grains, and the thickness of the niobium layer is about 26 μm.
Embodiment 3
[0064] The steps are basically the same as those in Example 1, except that the steady-state current in Step 3 is adjusted to pulse current, and the average current density is 50mA / cm 2 , the duty cycle is 50%, and the frequency is 0.5Hz.
[0065] Figure 7 For the SEM picture of the coating surface obtained in Example 3, it can be seen that the coating surface is uniform and the crystal grains are irregular polygonal. Figure 8 From the SEM picture of the coating section obtained in this example, it can be seen that the coating section has no obvious holes, good compactness, fine columnar crystals, and the thickness of the niobium layer is about 50 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com