Method for screening algal toxin degrading bacterium from viscera of hemibarbus maculatus in Lake Taihu
A technology for degrading bacteria and algal toxins, which is applied in the field of microbiology for the degradation of algal toxins, can solve the problems of large energy consumption, achieve low extraction costs, significant degradation effects, and simple and feasible methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
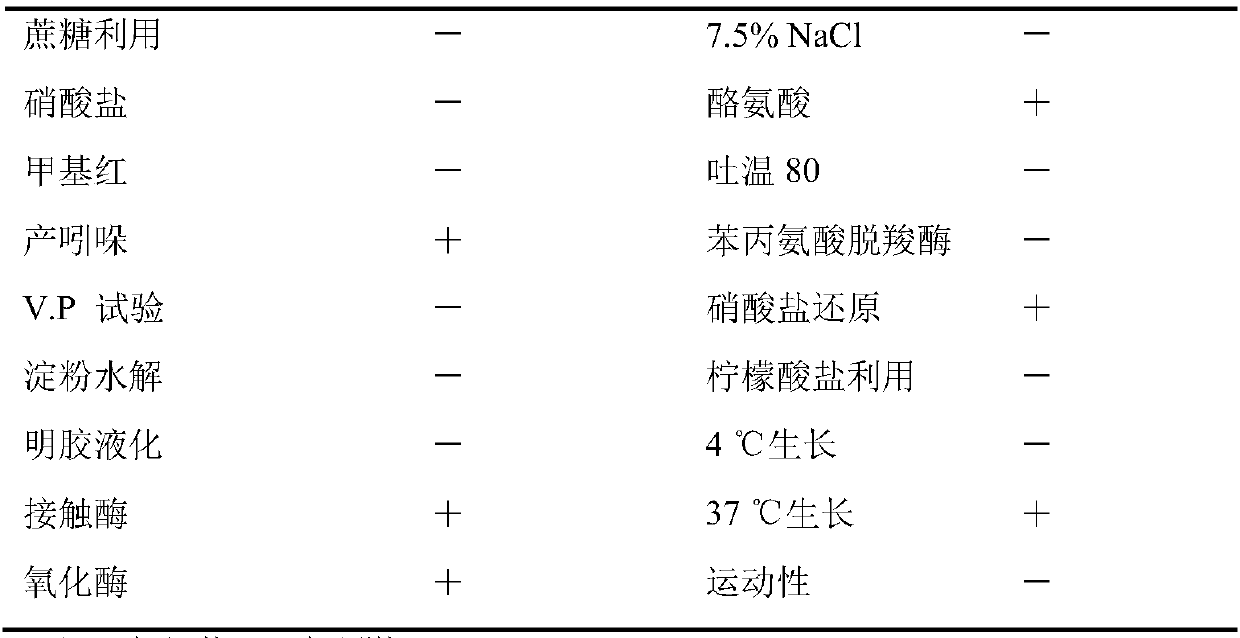
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Inoculate the bacterial solution into an Erlenmeyer flask containing 20mL of M9 liquid medium supplemented with MC-LR as a substrate, the pH is 7-7.4, the inoculation amount is 3%, 30°C, 150r min -1 Shake the culture at constant temperature, take samples every 24 hours, use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure the content of MC-LR, and investigate the degradation effect of the strain for 7 days. The degradation results showed that within 7 days the strain could convert the initial concentration of 13.98 μg L -1 MC-LR was degraded to 1.43 μg L-1 , the degradation rate is 89.72%, and the degradation effect is remarkable.
Embodiment 2
[0035] Inoculate the bacterial solution in a conical flask containing 20 mL of M9 liquid medium supplemented with MC-LR as a substrate, the inoculum amount is 3%, the pH is 5.5, 7.0, 8.5, 30°C, 150r min -1 Shake culture at constant temperature, and after 5 days, use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure MC-LR content. The degradation results showed that when the pH was 5.5, 7.0 and 8.5, the initial concentration of 13.98 μg L -1 MC-LR was degraded to 9.25 μg L -1 , 6.24 μg L -1 , 7.34 μg L -1 , the degradation rates were 33.8%, 55.36%, and 47.50%, respectively, and the degradation effect was the best when the pH was 7.0.
Embodiment 3
[0037] The bacterial solution was inoculated in a conical flask equipped with 20 mL of M9 liquid medium supplemented with MC-LR as a substrate, the pH was 7-7.4, the inoculum size was 3%, and the amount of MC-LR added was 5 μg L -1 , 10 μg L -1 , 20 μg L -1 , 30 μg L -1 , 30℃, 150rmin -1 Shake culture at constant temperature, and after 5 days, use enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to measure the content of MC-LR. The degradation results showed that after 5 days, the remaining MC-LR content in the mixture was 0.21 μg L -1 , 1.56 μg L -1 , 5.67 μg L -1 , 13.21 μg L -1 , the degradation rates were 95.8%, 84.40%, 71.65%, and 55.97%, respectively. It can be seen that the amount of MC-LR added was 20 μg L -1 The degradation efficiency is higher when it is below.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com