Stent material used for cell storage proliferation
A scaffold material and cell technology, applied in medical science, non-woven fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problem of inconvenient cutting shape, achieve convenient control of size and shape, improve degradation or dissolution speed, and use convenient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
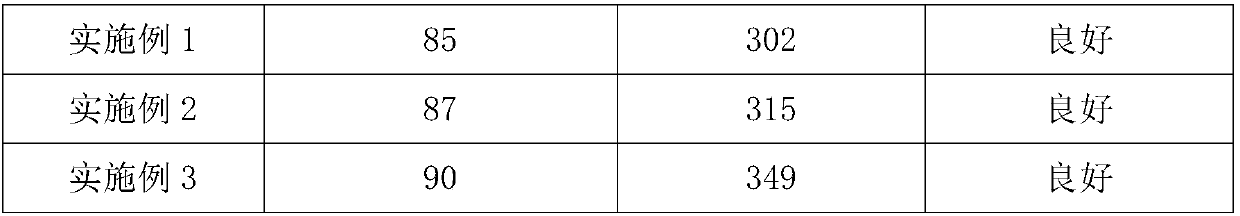
Embodiment 1
[0029] A scaffold material for cell storage and proliferation, characterized in that: the preparation method of the scaffold material follows the steps below:
[0030] Step 1, adding ureidopyrimidone and carbodiimide to the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecule, and using a conventional ring-forming click reaction to obtain a PEG supramolecule;
[0031] Step 2, dissolving PEG supramolecules in hexafluoroisopropanol, then adding gelatin, stirring at room temperature overnight to obtain a mixed solution;
[0032] Step 3, adding the mixed solution into an electrospinning machine for electrospinning to obtain a fiber film;
[0033] In step 4, the fiber film is vacuum-dried overnight to obtain a scaffold material.
[0034] The molecular weight of the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecule in the step 1 is 3000.
[0035] The molar ratio of the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecules, ureidopyrimidinone and carbodiimide in the step 1 is 1:2:2.
[0036] The conventional ring-forming click reacti...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A scaffold material for cell storage and proliferation, characterized in that: the preparation method of the scaffold material follows the steps below:
[0045] Step 1, adding ureidopyrimidone and carbodiimide to the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecule, and using a conventional ring-forming click reaction to obtain a PEG supramolecule;
[0046] Step 2, dissolving PEG supramolecules in hexafluoroisopropanol, then adding gelatin, stirring at room temperature overnight to obtain a mixed solution;
[0047] Step 3, adding the mixed solution into an electrospinning machine for electrospinning to obtain a fiber film;
[0048] In step 4, the fiber film is vacuum-dried overnight to obtain a scaffold material.
[0049] The molecular weight of the dihydroxyl-terminated PEG molecule in the step 1 is 15,000.
[0050] The molar ratio of the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecules, ureidopyrimidinone and carbodiimide in the step 1 is 1:2:2.
[0051] The conventional ring-forming click rea...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A scaffold material for cell storage and proliferation, characterized in that: the preparation method of the scaffold material follows the steps below:
[0060] Step 1, adding ureidopyrimidone and carbodiimide to the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecule, and using a conventional ring-forming click reaction to obtain a PEG supramolecule;
[0061] Step 2, dissolving PEG supramolecules in hexafluoroisopropanol, then adding gelatin, stirring at room temperature overnight to obtain a mixed solution;
[0062] Step 3, adding the mixed solution into an electrospinning machine for electrospinning to obtain a fiber film;
[0063] In step 4, the fiber film is vacuum-dried overnight to obtain a scaffold material.
[0064] The molecular weight of the dihydroxyl-terminated PEG molecule in the step 1 is 8000.
[0065] The molar ratio of the dihydroxy-terminated PEG molecules, ureidopyrimidinone and carbodiimide in the step 1 is 1:2:2.
[0066] The conventional ring-forming click react...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com