A method for removing mercury in the process of producing acid from lead-zinc smelting flue gas
A technology for smelting flue gas and lead-zinc, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, sulfur compounds, etc., can solve problems such as high operating costs, increased risk of equipment maintenance, difficult equipment maintenance, etc., to improve the effect of flocculation and sedimentation, Improve storage stability, ideal effect of sedimentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
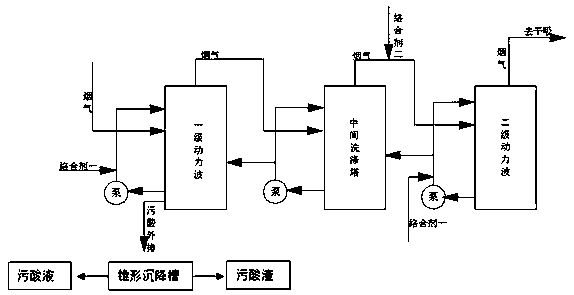
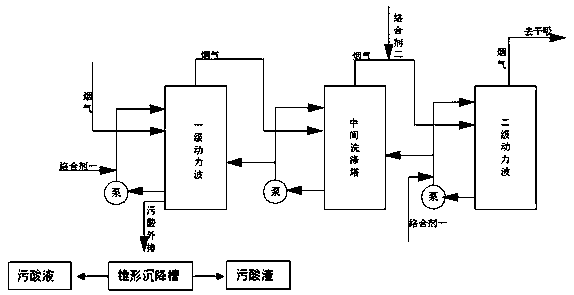
[0023] Add complexing agent 1 to the primary power wave and secondary power wave in the lead-zinc smelting flue gas acid production process, and add complexing agent 2 to the gas phase pipeline from the intermediate washing tower to the secondary power wave. Dosing method In order to set the feeding pipeline on the corresponding original pipeline, a metering pump is used to feed. Among them, the dosage of complexing agent 1 is 150mg / L at the primary dynamic wave, 80mg / L at the secondary dynamic wave, and 150mg / m of complexing agent 2 3 .
[0024] The complexing agent one is a mixture obtained by mixing the sodium dimethyl dithiocarbamate solution and the SRB bacterial liquid in a volume ratio of 7:1 generated by the modification of ammonium dimethyl dithiocarbamate potassium acid. Mixture two is a mixture of hypochlorite and fulvic acid salt, wherein the configuration method of the sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate solution is to mix dimethyldithiocarbamate with a mass concentra...
Embodiment 2
[0031]Add complexing agent 1 to the primary power wave and secondary power wave in the lead-zinc smelting flue gas acid production process, and add complexing agent 2 to the gas phase pipeline from the intermediate washing tower to the secondary power wave. Dosing method In order to set the feeding pipeline on the corresponding original pipeline, a metering pump is used to feed. Among them, the dosage of complexing agent 1 at the primary dynamic wave is 180mg / L, the dosage at the secondary dynamic wave is 100mg / L, and the dosage of complexing agent 2 is 220mg / m 3 .
[0032] The complexing agent one is the mixture obtained by mixing the sodium dimethyl dithiocarbamate solution and the SRB bacterial liquid in a volume ratio of 7.5:2.5 generated by the modification of ammonium dimethyl dithiocarbamate potassium acid. Mixture two is a mixture of hypochlorite and fulvic acid salt, wherein the configuration method of the sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate solution is to mix dimethyldit...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Add complexing agent 1 to the primary power wave and secondary power wave in the lead-zinc smelting flue gas acid production process, and add complexing agent 2 to the gas phase pipeline from the intermediate washing tower to the secondary power wave. Dosing method In order to set the feeding pipeline on the corresponding original pipeline, a metering pump is used to feed. Among them, the dosage of complexing agent 1 at the primary dynamic wave is 200mg / L, the dosage of complexing agent 2 at the secondary dynamic wave is 120mg / L, and the dosage of complexing agent 2 is 250mg / m 3 .
[0040] The complexing agent one is a mixture obtained by mixing the sodium dimethyl dithiocarbamate solution and the SRB bacterial liquid in a volume ratio of 9:3 generated by the modification of ammonium dimethyl dithiocarbamate potassium acid. Mixture two is a mixture of hypochlorite and fulvic acid salt, wherein the configuration method of the sodium dimethyldithiocarbamate solution is t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com