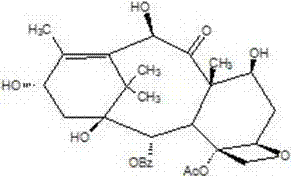
Method for extracting 10-deacetylbaccatin III from taxus chinensis
A technology for deacetylation and yew, applied in the field of extracting 10-deacetyl baccatine III from yew, can solve the problems of large influence, large cost input, obvious effect and the like, and achieves reduction of production cost and low production cost , the effect of high extraction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1: This industrialized method for extracting 10-DAB from the branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis, the specific operations are as follows:
[0033] (1) Add 1 kg of dried Yunnan yew branches and leaves with a 10-DAB content of about 4‰ in a 10L pot, add 5L of pure tap water, and drop 2.5 mL of glacial acetic acid at the same time, mix well and soak at 45-50°C for 4 hours , filter, soak the filter residue with an aqueous solution containing a stabilizer (volume concentration of 0.5‰ glacial acetic acid solution), soak twice, and combine the soaking solution; use 4L ethyl acetate to extract the soaking solution, keep stirring for 1 hour, and let it stand for separation layer, the ethyl acetate layer was taken out, the remaining liquid was extracted twice with ethyl acetate again, the three extracts were combined, and then concentrated and dried under reduced pressure at 60°C to obtain 25.86 g of a light yellow-green solid, which was tested for the content of 10...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: This industrialized method for extracting 10-DAB from the branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis, the specific operations are as follows:
[0037] (1) Add 10kg of dried Yunnan yew branches and leaves with a 10-DAB content of about 4‰ in a 50L pot, add 60L of pure tap water, and drop 48mL of glacial acetic acid at the same time, mix well and soak at 40-45°C for 5 hours, Filter, soak the filter residue with an aqueous solution containing a stabilizer (volume concentration of 0.8‰ glacial acetic acid aqueous solution), soak repeatedly 3 times, and combine the soaking solution; use 35L ethyl acetate to extract the soaking solution, keep stirring for 0.8h, and let stand to separate layer, the ethyl acetate layer was taken out, the remaining liquid was extracted 3 times again, the 4 extracts were combined, and then concentrated and dried under reduced pressure at 65°C to obtain 300.1 g of a light yellow-green solid, which was detected to have a 10-DAB content of ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3: This industrialized method for extracting 10-DAB from the branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis, the specific operations are as follows:
[0041] (1) Add 1 kg of dried Yunnan yew branches and leaves with a 10-DAB content of about 4‰ in a 10L pot, add 7L of pure tap water, and drop 7 mL of citric acid at the same time, mix well and soak at 45-50°C for 3 hours , filter, soak the filter residue with an aqueous solution containing a stabilizer (citric acid volume concentration is 1‰), soak twice, and combine the soaking solution; use 6L ethyl acetate to extract the soaking solution, keep stirring for 0.5h, and let stand to separate layer, the ethyl acetate layer was taken out, the remaining liquid was extracted 3 times again, the 4 extracts were combined, and then concentrated and dried under reduced pressure at 70°C to obtain 26.3 g of a light yellow-green solid, which was detected to have a 10-DAB content of 14.5%. The rate is about 95%;
[0042] (2) Disso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com