Method for producing carbon dioxide anionic free radicals and method for treating hexavalent-chromium-containing waste water
A carbon dioxide and anion technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, reduced water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of large power consumption and achieve low treatment cost, high commercial application value, and mild reaction system Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
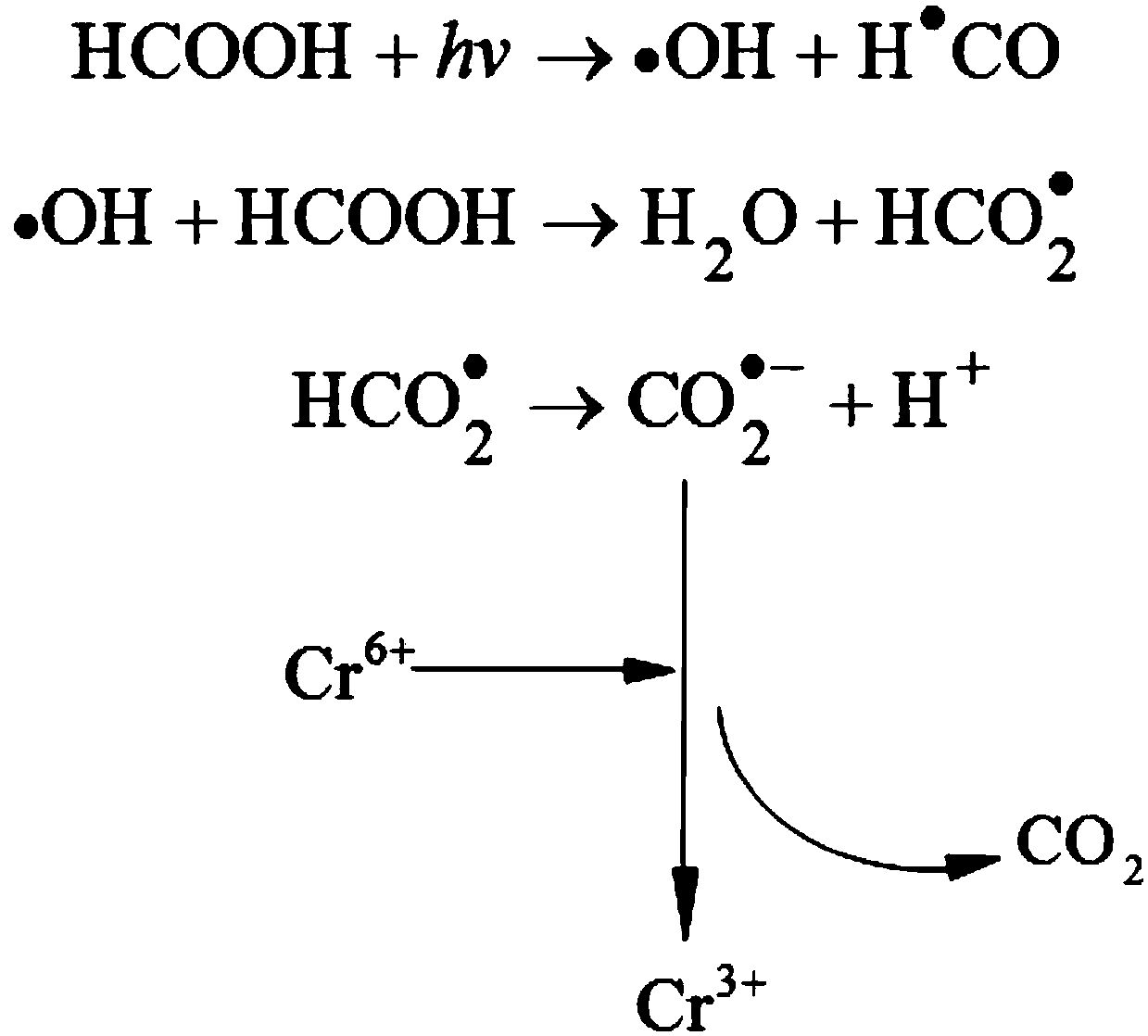
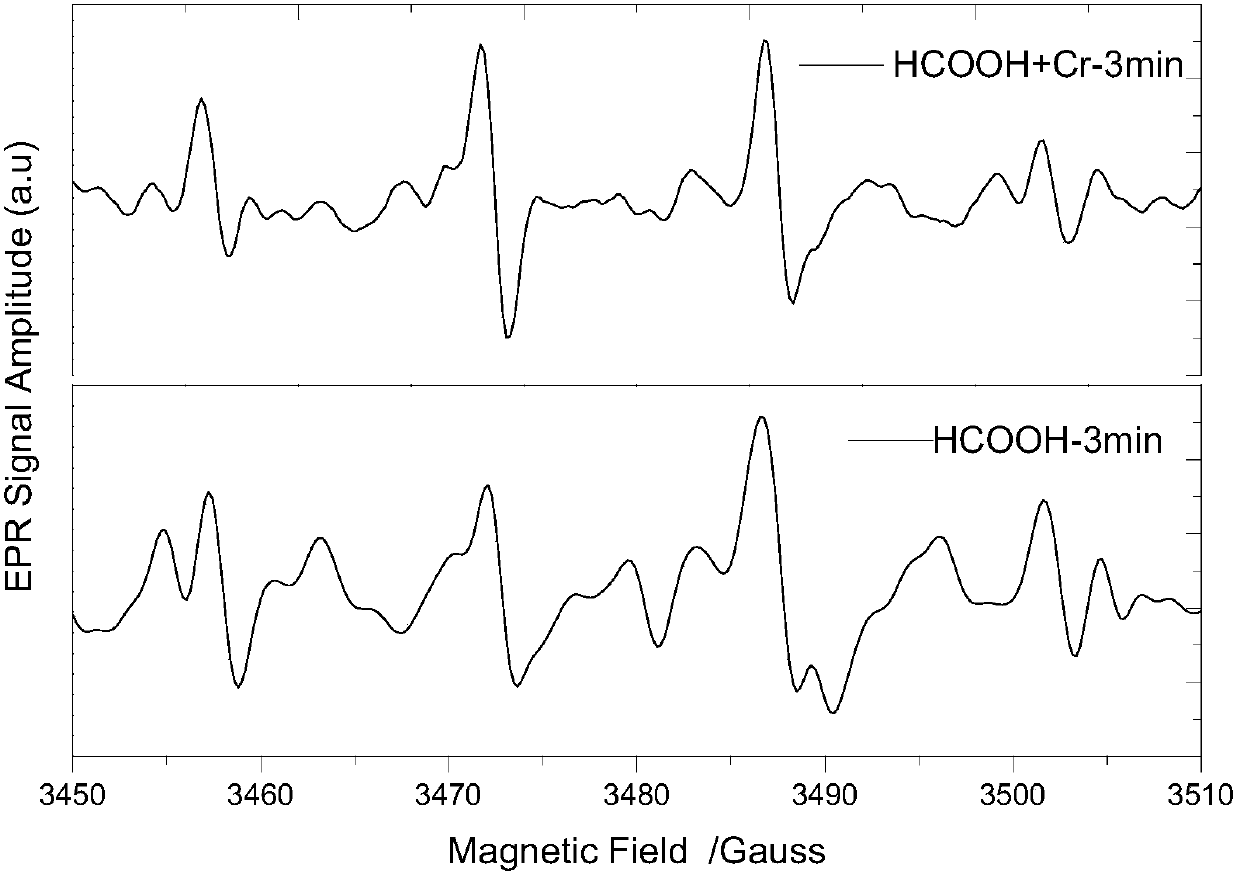
[0025] A method for producing carbon dioxide anion free radicals, the specific method is:
[0026] Put the formic acid in the quartz glass round-bottom test tube built in the photochemical reaction instrument, and turn on the ultraviolet light source.
[0027] A method for treating waste water containing hexavalent chromium, comprising the following steps:
[0028] Potassium dichromate (K 2 Cr 2 o 7 ) in advance at 120°C for 2 hours, then weigh 0.2829g of potassium dichromate and dissolve it in deionized water, transfer it into a 1000ml volumetric flask, dilute to the marked line, shake well, and prepare a Cr(VI) concentration of 1000mg / L chromium standard The stock solution was further configured with different initial concentrations of Cr(VI)-containing simulated wastewater.
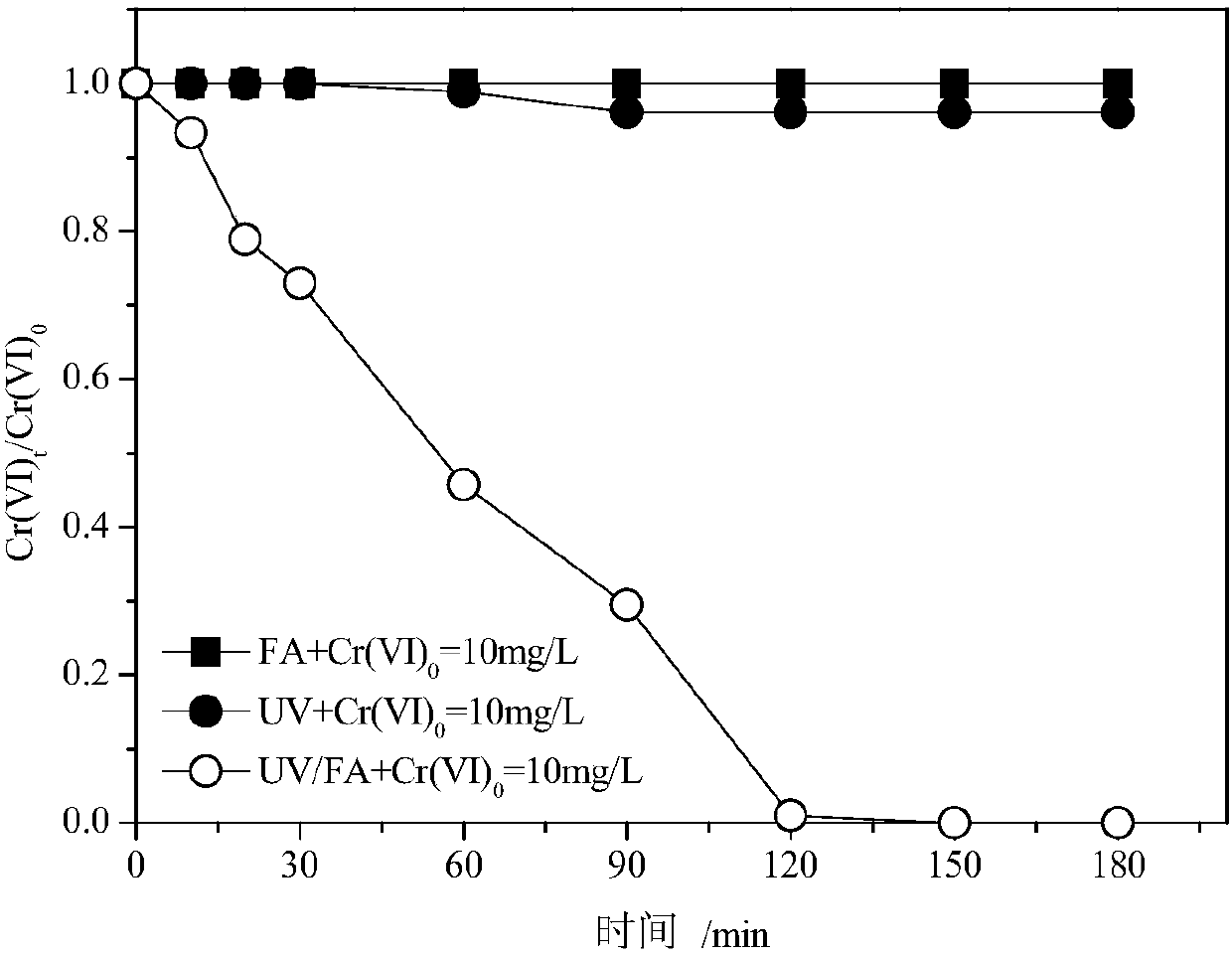
[0029] Take the prepared simulated wastewater with an initial concentration of Cr(VI) of 10mg / L, without adjusting the initial pH, directly add formic acid (HCOOH, referred to as FA), the dosage is...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The experimental process is the same as that in Example 1, with different initial Cr(VI) concentrations (1, 5 and 10 mg / L), different FA dosages (5, 10, 20, 30, 40 mM), and different time periods of 0-180 min for the reaction The concentration of Cr(VI) in the effluent is shown in Table 1. It can be seen that when the initial concentration of Cr(VI) is 10mg / L, the dosage of formic acid is 20M, and the initial pH is not adjusted, and the ultraviolet radiation reacts to 150min; when the initial concentration of Cr(VI) is 10mg / L, the dosage of formic acid The dosage is 30M, the initial pH is not adjusted, and the ultraviolet radiation reaction lasts for 120min; when the initial concentration of Cr(VI) is 10mg / L, the dosage of formic acid is 40M, the initial pH is not adjusted, and the ultraviolet radiation reaction lasts for 60min; when Cr(VI) VI) When the initial concentration is 5mg / L, the dosage of formic acid is 40M, the initial pH is not adjusted, and the ultraviolet ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com