Method for preparing water body sexavalent molybdate adsorbent based on waste iron-aluminum mud of water plants
A technology of hexavalent molybdate and iron-aluminum mud is applied in the preparation of molybdate sewage treatment adsorbent materials, the use of solid waste adsorbent materials and the field of investigation of molybdenum removal effect, which can solve the problems of high operation cost, difficult operation, Secondary pollution and other problems, to achieve the effect of low price, expanded application scope and strong adsorption capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
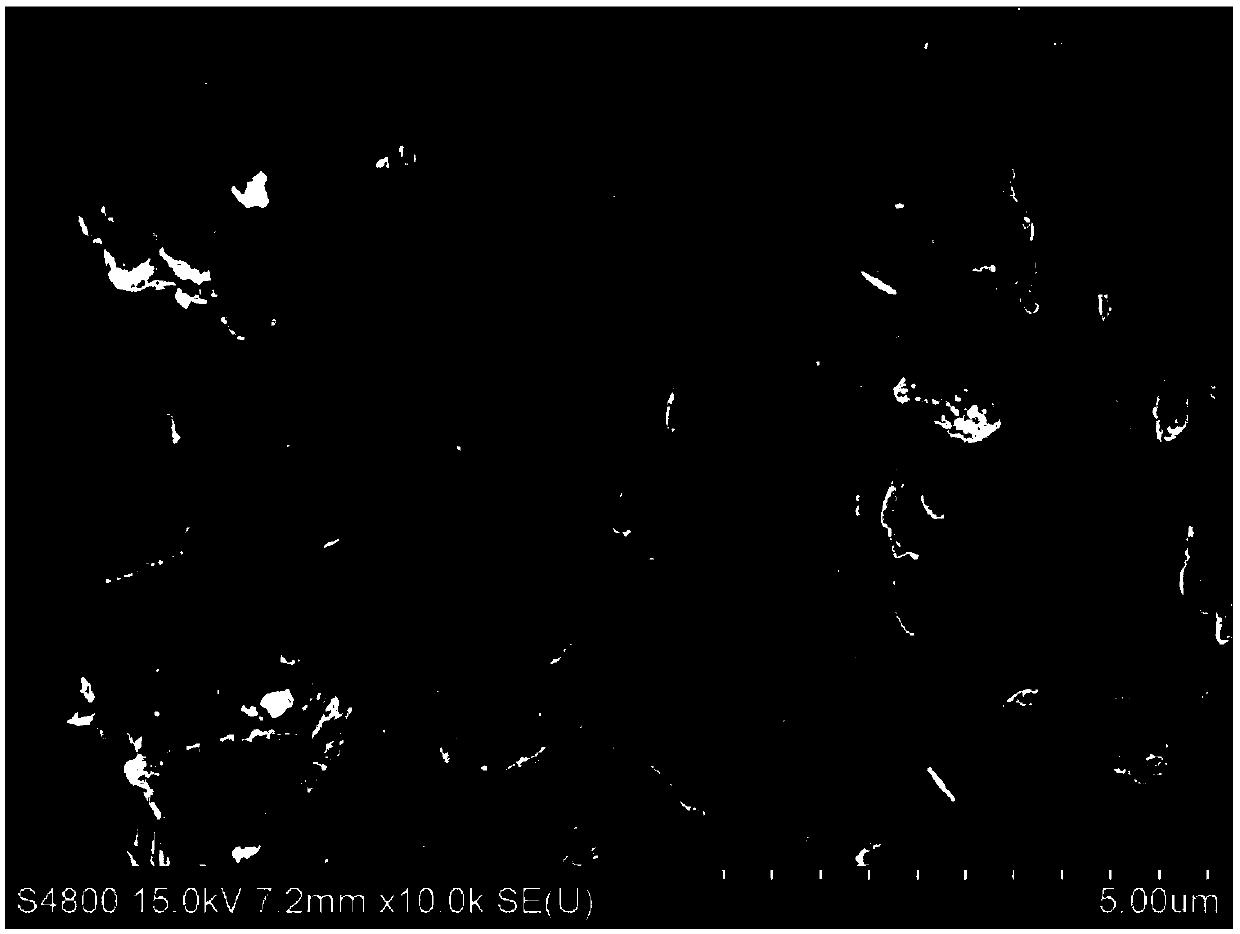
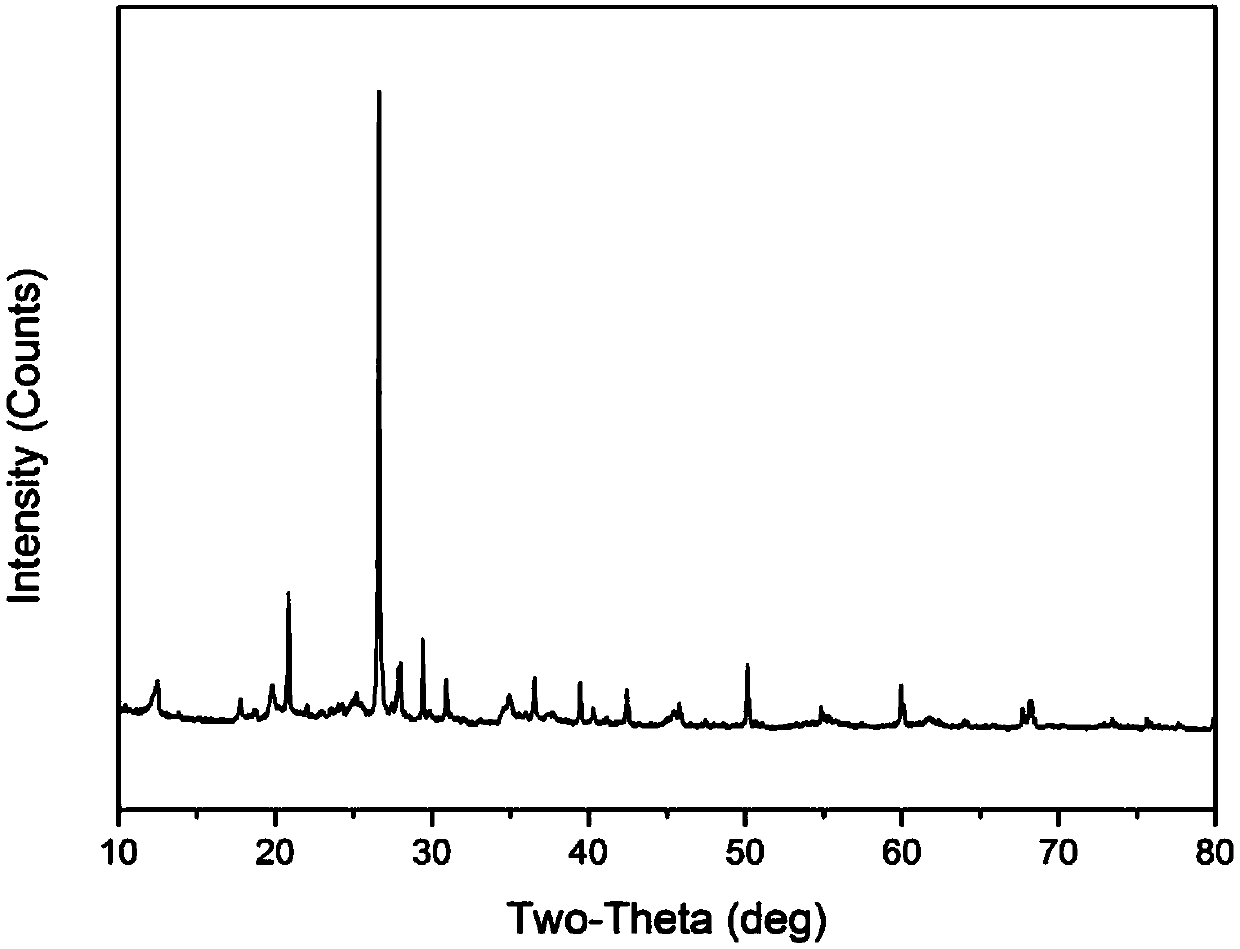
[0034] Rinse the iron-aluminum slime in clean water for 1 day, then dry and grind naturally, and screen to obtain iron-aluminum slime with a particle size below 0.15mm; place it in a quartz crucible, put it in a muffle furnace, and pyrolyze it at 600°C 4h. After cooling, add it to 1.0g L at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:1 -1 In the fulvic acid solution, shake for 4~5h, the vibration speed is 200r min -1 , and then dried at 50°C for later use. Scanning electron microscope pictures of iron-aluminum mud before and after modification figure 1 , figure 2 It can be seen from the above two figures that the surface structure of the ferro-aluminum slime before modification is relatively dispersed, while the surface structure of the material after modification is denser, and the inner and outer layer voids are relatively reduced. The XRD pattern of the modified iron-aluminum mud is as follows image 3 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the main crystalline substance of t...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Accurately weigh the 50mg example 1 sample in a centrifuge tube, and add a concentration of 50mg L -1 50mL of sodium molybdate solution, adjust the pH of the solution to 1-10 respectively, make 10 parallel samples, shake well and place at a speed of 150r min -1 Shake in a constant temperature shaker. After 12h, the sample was taken out, and the mixed solution was subjected to 8000r min -1 After centrifugation for 10 min, the concentration of molybdenum in the supernatant was determined by spectrophotometry. According to the difference between the initial solution and the concentration of Mo(VI) in the supernatant after centrifugation, the adsorption amount of the iron-aluminum slime to Mo(VI) was calculated, and the variation curve of the adsorption amount of the iron-aluminum slime to Mo(VI) with the pH of the solution was made ( Figure 4 ). It can be seen from the figure that acid-base conditions have a certain influence on the adsorption process, and the adsorpti...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Accurately weigh 50 mg of the sample of Example 1 in a centrifuge tube, and add a concentration gradient of 2 to 100 mg L -1 50mL of sodium molybdate solution, the pH of the solution is 2.3, after shaking well, place it at a speed of 150r min -1 Shake in a constant temperature shaker. After 12h, the sample was taken out, and the mixed solution was subjected to 8000r min -1 After centrifugation for 10 min, the concentration of Mo(VI) in the supernatant was measured by spectrophotometry. According to the difference between the concentration of Mo(VI) in the initial solution and the supernatant after centrifugation, the adsorption amount of Mo(VI) to the iron-aluminum slime was calculated, and the variation curve of the adsorption amount of the iron-aluminum slime to Mo(VI) with the concentration of molybdenum was made ( Figure 5 ). It can be seen from the figure that the amount of molybdenum adsorption tends to be stable with the increase of molybdenum concentration. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com