Construction and application of infectious clone expression vector of watermelon mosaic virus
A watermelon mosaic virus and expression vector technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reduced infectivity, instability, loss, etc., and achieve the effects of high-efficiency expression of foreign proteins, increased error rate, and reduced error rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
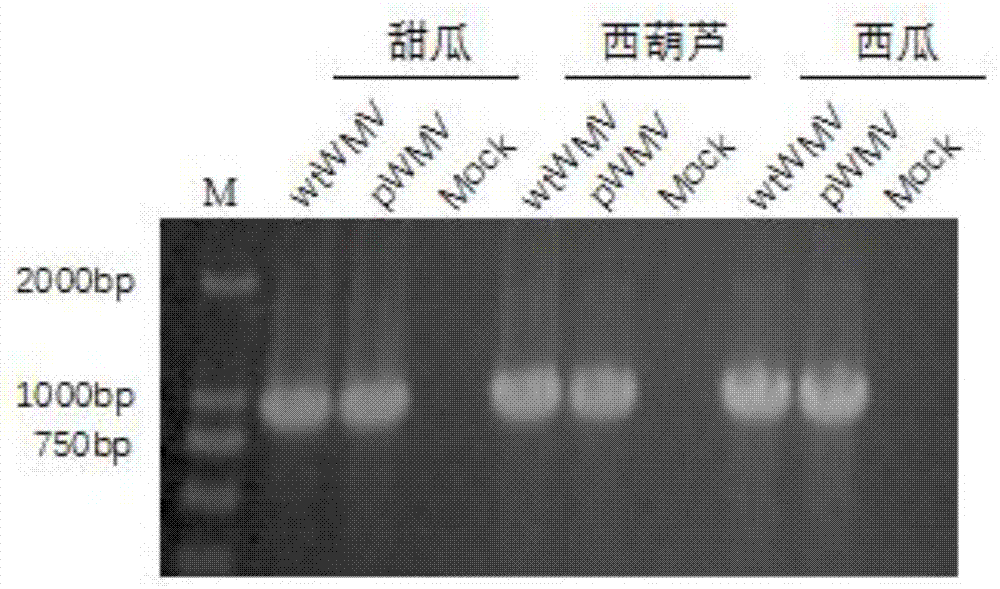
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1: the purification of watermelon mosaic virus virion virus RNA
[0054] Take 20g of zucchini diseased leaves infected by watermelon mosaic virus, grind them with liquid nitrogen, add 60mL of extraction buffer, mix well and put them on ice. Filter through magic filter cloth, transfer the supernatant to a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 15000g, 4°C for 20min. After the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μM membrane, it was ultracentrifuged at 40,000 g for 1.5 h at 4°C. Discard the supernatant, add 1.5mL 0.02M phosphate buffer (pH7.0) to dissolve the precipitate.
[0055] Take 300 μL of virus particles and add an equal amount of lysate (40 mM Tris-HCl, pH=9.0; 2 mM EDTA; 2% SDS), and vortex to mix. Add 100U RNase inhibitor and an equal volume of water-saturated phenol, vortex and mix well, and incubate at 60°C for 1min. Let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 13000g for 5 minutes at 4°C. Transfer the supernatant to a new 1.5mL centrif...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2: Construction of watermelon mosaic virus infectious clone
[0057] Using the viral RNA obtained in Example 1 as a template, reverse transcription was performed with random primers and Oligo dT. The reverse transcription reaction procedure is as follows:
[0058]
[0059] Incubate at 65°C for 5 minutes, quickly place on ice to cool for 2 minutes, and spin off.
[0060]
[0061] 25°C, 5min: 50°C, 45min: 85°C, 5min to terminate the reaction.
[0062] Using the obtained reverse transcription product as a template, use Phusion high-fidelity polymerase for PCR amplification. The PCR reaction system is as follows:
[0063]
[0064] Reaction procedure:
[0065]
[0066] The PCR product was subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and the gel was cut and recovered for later use to obtain the whole genome PCR product of WMV.
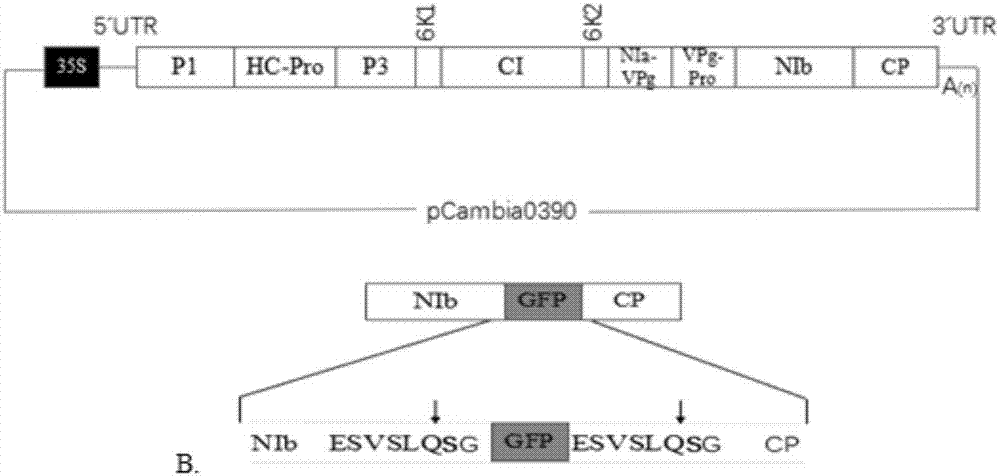
[0067] The 35S promoter gene amplified by PCR and the pCambia0390 plasmid were ligated by Xma I and Pst I after double dig...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Watermelon Mosaic Virus Infectious Cloning and Expression of Foreign Protein Vector Construction
[0069] Using Phusion high-fidelity polymerase PCR amplification to obtain GFP, the sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.10, and the reaction system is as follows:
[0070]
[0071] Reaction procedure:
[0072]
[0073]
[0074] The PCR product was subjected to 1% agarose gel electrophoresis, and after gel cutting and recovery, it was connected to the vector pCaWMV by homologous recombination, and the invasive expression vector was named pCaWMV-GFP ( figure 1 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com