Method and application for rapidly detecting nucleic acid based on electrochemical electric potential pretreatment technology
A technology of electrochemistry and pretreatment, which is applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, electrochemical variables of materials, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effect of simple and economical operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1. DNA-DNA hybrid system
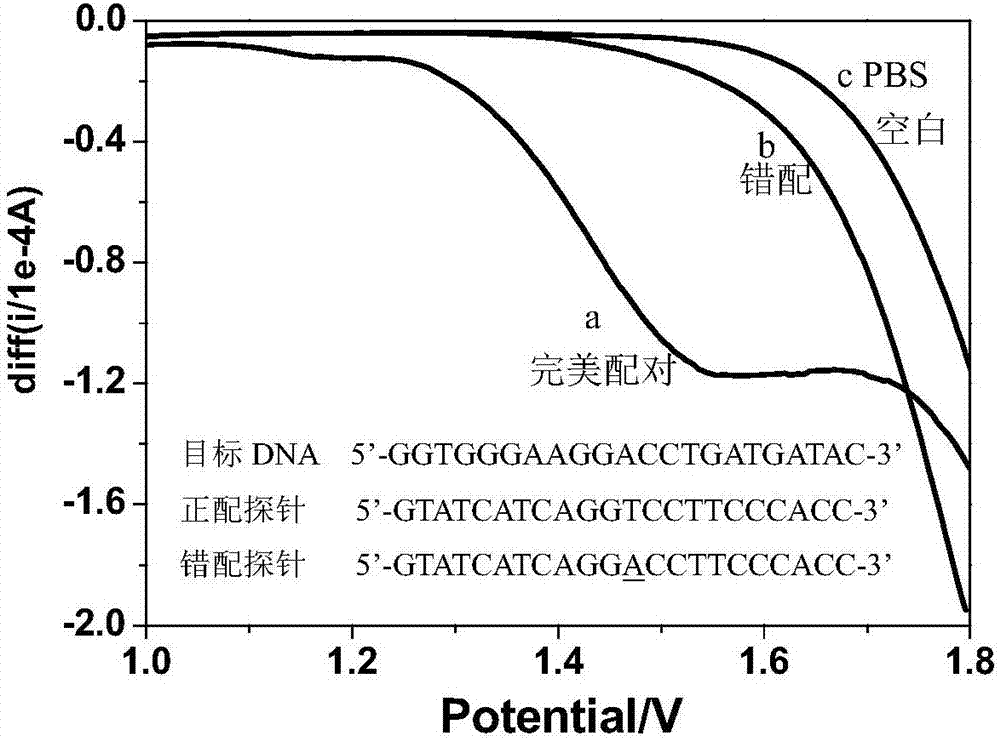
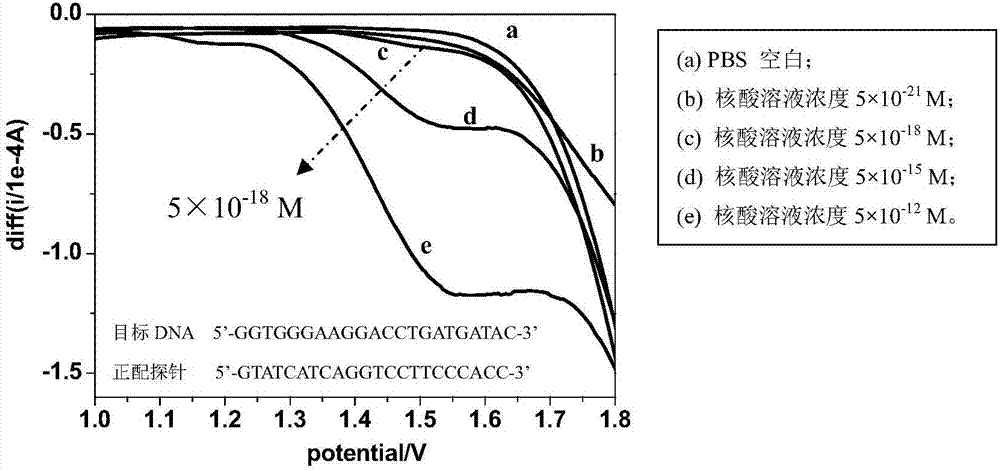
[0022] The artificially synthesized target DNA (5'-GGTGGGAAGGACCTGATGATAC-3') solution was dropped into equal volumes of 5pM positive match probe (5'-GTATCATCAGGTCCTTCCCCACC-3') solution and 5pM mismatch probe (5'-GTATCATCAGGACCTTCCCACC-3 ') solution, a positive hybridization solution and a mismatched hybridization solution are formed through the DNA-DNA hybridization reaction. The glassy carbon electrode is pretreated in the potential range of 1.8-2.7V, and then the simulated body fluid phosphate buffer solution (PBS buffer) with pH=7.4 is used as a blank comparison. The hybridization solution and the PBS blank solution were subjected to square wave voltammetry scanning, and the electrochemical sensing results were as attached figure 1 Shown: shoulder peak occurs in the square wave voltammetry curve of normal matching hybridization solution in the range of 1.0-1.8V, see figure 1 a, the square wave voltammetry curves of the mismat...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2. DNA-cDNA hybrid system
[0024] The cDNA (5'-TAACACTGTCTGGTAAAGATGG-3') solution of artificially synthesized prostate cancer characteristic marker miR-141 was dropped into 5pM positive matching probe (5'-CCATCTTTACCAGACAGTGTTA-3') solution and 5pM mismatching probe respectively in equal volumes. In the needle (5'-ACATCTTTACCAGACAGTGTTA-3') solution, a positive hybridization solution and a mismatched hybridization solution are formed through cDNA-DNA hybridization reaction. The glassy carbon electrode is pretreated in the potential range of 1.8-2.5V, and then the simulated body fluid phosphate buffer solution (PBS buffer) with pH=7.4 is used as a blank comparison. The hybridization solution and the PBS blank solution were scanned by square wave voltammetry, and the electrochemical sensing results were similar to those in the attached figure 1 , figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Embodiment 3.DNA-RNA hybrid system
[0026] The synthetic target RNA (5'-GGUGGGAAGGACCUGAUGAUAC-3') solution was dropped into 5pM positive matching probe (5'-GTATCATCAGGTCCTTCCCCACC-3') solution and 5pM mismatching probe (5'-GTTTCATCAGGTCCTTCCCACC-3 ') solution, a positive hybridization solution and a mismatched hybridization solution are formed through the DNA-RNA hybridization reaction. The glassy carbon electrode is pretreated in the potential range of 0-2.7V, and then the simulated body fluid phosphate buffer solution (PBS buffer) with pH=7.4 is used as a blank comparison. In the potential range of less than 1.8V, the positive hybridization solution and mismatch The hybridization solution and the PBS blank solution were scanned by square wave voltammetry, and the electrochemical sensing results were similar to those in the attached figure 1 , figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com