A lead high-salt-resistant nucleic acid sensor and its application
A salt nucleic acid and sensor technology, which is applied in the field of lead high-salt-resistant nucleic acid sensors, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, limitation, and poor repeatability, and achieve high specificity and sensitivity, rapid detection, and rapid response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
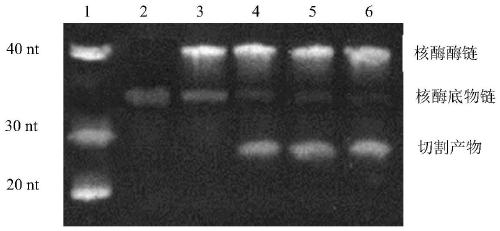
[0069] The preparation of embodiment 1 lead ion deoxyribozyme and the generation of cleavage product
[0070] The substrate chain, enzyme chain and DNAzyme cleavage products of the DNAzyme designed for lead ions are as follows:
[0071]
[0072]
[0073] Note: GACTC in the amplified template D is the Nt.BstNBI nicking endonuclease recognition sequence, and the first four base pairs of the sequence (between C and A) are the synthetic strand cleavage sites; DNAzyme cleavage products C and The amplification product F is completely complementary to the amplification template D; the TTGGGGGGT sequence at the end of the DNAzyme substrate chain A is added to increase the Tm value of the template binding; the lead ion cleavage site is at the rA of the DNAzyme substrate chain A after.
[0074] The preparation method of lead ion deoxyribozyme:
[0075] Mix 4 μL of 10 μM DNAzyme substrate chain stock solution with 4 μL of 10 μM DNAzyme enzyme chain stock buffer (final concentrati...
Embodiment 2
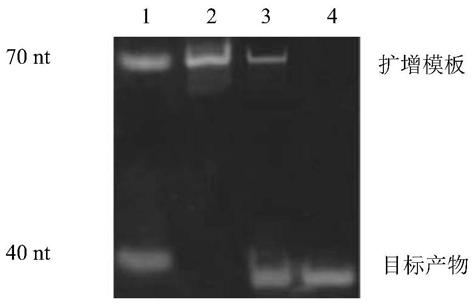
[0077] The amplification of embodiment 2 lead ion deoxyribozyme cleavage products
[0078] The system for isothermal amplification reaction consists of two parts (system A and system B). Amplification reaction system composition: 30 μL system.
[0079] Part A system composition: 24.2μL system
[0080] Amplification template (1μM stock solution): 6μL (final concentration 0.2μM)
[0081] dNTPs (2.5mM stock solution): 3μL
[0082] Cutting product of lead ion DNAzyme (1 μM): 6 μL, final concentration 0.2 μM
[0083] Ultrapure water: 9.2μL
[0084] Part B system composition: 5.8 μL
[0085] Bst DNA polymerase (8U / μL stock solution): 0.1μL (final concentration 0.02U / μL)
[0086] Polymerase reaction buffer solution (10x stock solution): 3 μL (final concentration 1x)
[0087] Nt.BstNBI nicking endonuclease (10U / μL stock solution): 1.2μL (final concentration 0.37U / μL)
[0088] Nt.BstNBI nicking endonuclease reaction buffer solution (10x stock solution): 1.5 μL (final concentrat...
Embodiment 3
[0092] Example 3 Preparation of G-quadruplex functional nucleic acid chromogenic sensor
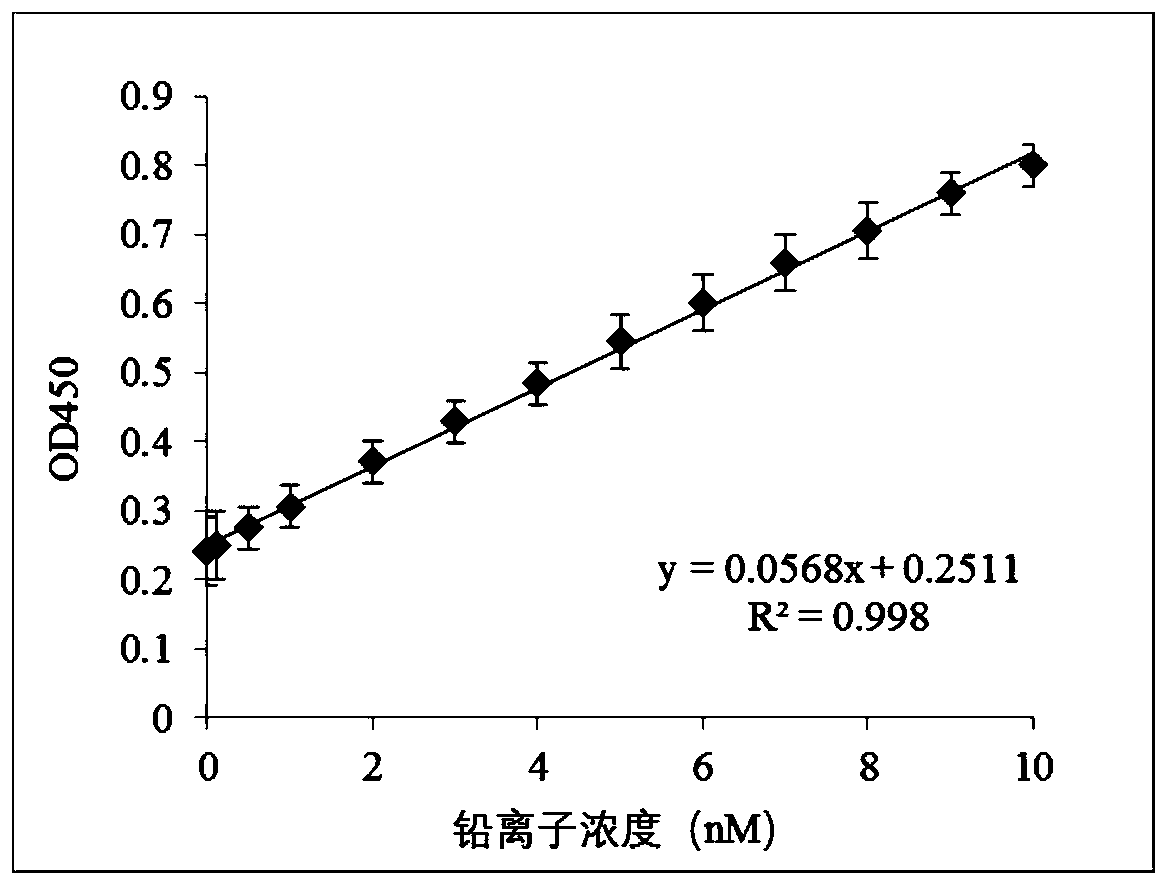
[0093] 80 μL enzyme activity buffer (100mM Tris, 120mM NaCl, 10mM MgCl 2 , 100mM KCl, pH8.4), 10μL hemin dilution solution (2μL hemin stock solution (10μM) mixed with 1mL enzyme activity buffer) mixed with 10μL of the material to be developed (i.e. the amplified target product), mixed After homogenization, react at 37°C for 30 minutes to make the amplified target product F combine with hemin to form a G-quadruplex structure, add 50 μL TMB chromogenic solution, mix well, react at 37°C for 10 minutes, add 50 μL 2M H 2 SO4, mix well to obtain a color-developed product, and obtain a G-quadruplex functional nucleic acid color sensor.
[0094] Then carry out microplate reader to measure OD 450 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com