Poly-spirulina peptide biostimulant
A technology of biostimulants and spirulina peptides, applied in the directions of microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, and biological organic part treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low absorption and utilization rate of crops, affecting the nutrient content of fertilizers, and rapid nutrient loss, etc. Improve fertilizer utilization and soil enzyme activity, promote phosphorus absorption, and improve the effect of soil environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
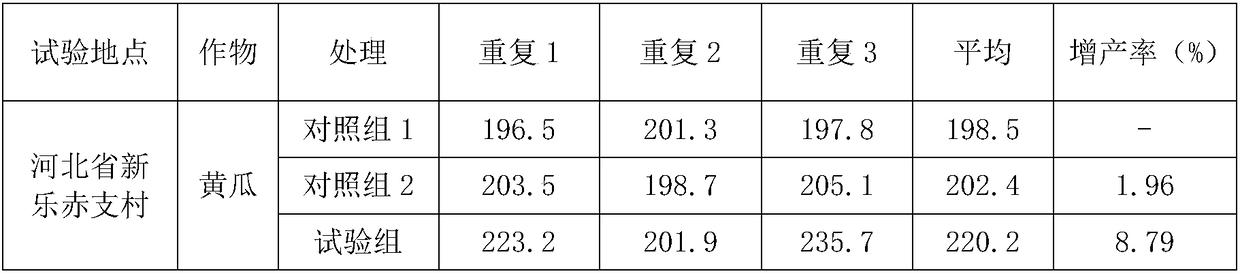
[0047] A polyspirulina peptide biostimulant is prepared by fermenting spirulina with domesticated and isolated Bacillus subtilis.
[0048] The water content of spirulina is 9.6%, and the mass percentage of each component is 17% of carbohydrates, 72% of protein, 1.2% of chlorophyll, 5.0% of amino acids and lysine, and 10% of total minerals. %.
[0049] The method for domestication and separation of fermentation strains is as follows:
[0050] A. Soak the unbroken dry spirulina in water for 20h and pull out and add sodium chloride and sucrose. The mass ratio of the added sodium chloride and sucrose to the unbroken dry spirulina is 1:2:18. Cook at 0.1MPa for 40min to obtain the primary culture medium;
[0051] B. Inoculate the fermentation strains on the primary selection medium, and after cultivating at a constant temperature at 36°C for 24 hours, select colonies that are brown, have wire drawing phenomenon, and have relatively obvious transparent circles and inoculate them in...
Embodiment 2
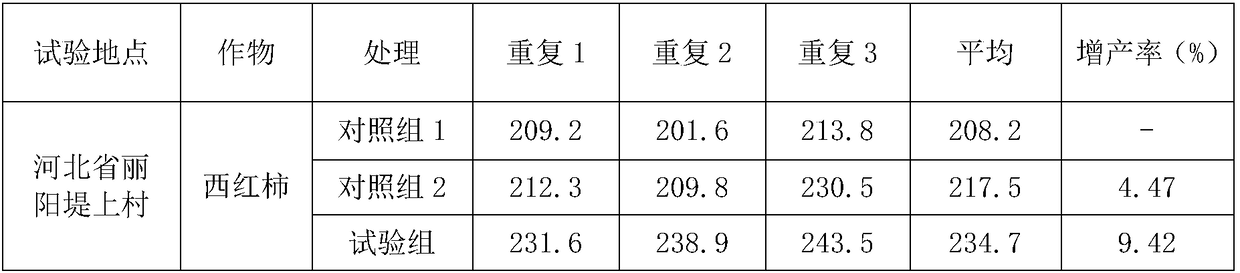
[0059] A polyspirulina peptide biostimulant is prepared by fermenting spirulina with domesticated and isolated bacillus licheniformis.
[0060] The water content of spirulina is 9.8%, and the mass percentage of each component is 16% of carbohydrates, 73% of protein, 1.3% of chlorophyll, 4.8% of amino acids and lysine, and 11% of total minerals. %.
[0061] The method for domestication and separation of fermentation strains is as follows:
[0062] A. Soak the unbroken dry spirulina in water for h and then pull it out and add sodium chloride and sucrose. The mass ratio of the added sodium chloride and sucrose to the unbroken dry spirulina is 1:3:22. Under 0.3MPa, cook for 55min to obtain primary culture medium;
[0063] B. Inoculate the fermentation strains on the primary selection medium, and after cultivating at a constant temperature at 38°C for 24 hours, select colonies that are brown, have wire drawing phenomenon, and have a relatively obvious transparent circle and inocu...
Embodiment 3
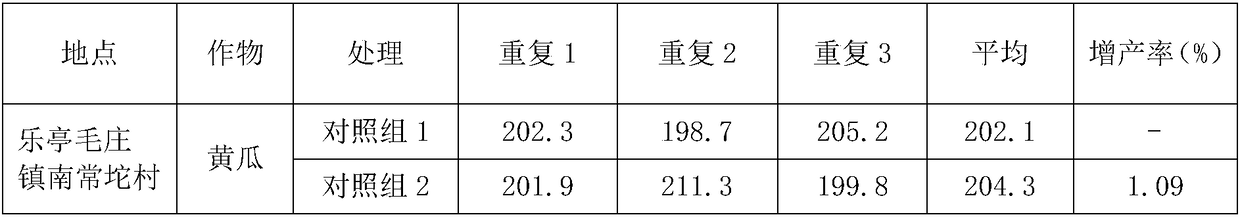
[0071] A polyspirulina peptide biostimulant is prepared by fermenting spirulina with domesticated and isolated bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
[0072] The water content of spirulina is 9.7%, and the mass percentage of each component is 18% of carbohydrates, 72% of protein, 1.4% of chlorophyll, 4.9% of amino acids and lysine, and 9% of total minerals. %.
[0073] The method for domestication and separation of fermentation strains is as follows:
[0074] A. After soaking the dry spirulina with unbroken walls in water for 24h, pull out and add sodium chloride and sucrose, the mass ratio of the added sodium chloride and sucrose to the dry spirulina with unbroken walls is 1:2:20. Cook at 0.2MPa for 50min to obtain the primary culture medium;
[0075] B. Inoculate the fermentation strains on the primary selection medium, and after cultivating at a constant temperature at 37°C for 24 hours, select colonies that are brown, have wire drawing phenomenon, and have relatively obvious trans...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com