Method for detecting neutralizing antibody in coxsackievirus A6 (CV-A6), and recombinant virus applied in method
A technology of Coxsackie virus, group A, applied in the direction of virus/phage, biochemical equipment and method, virus, etc., can solve the problems of long time, large impact, cumbersome operation, etc., and achieve simple cost and easy operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1, detection of enterovirus CV-A6 neutralizing antibody detection
[0053] 1. Construction of CV-A6 nucleocapsid protein expression plasmid and CV-A16 replicon plasmid
[0054] (1) Construct CV-A6 nucleocapsid protein expression plasmid
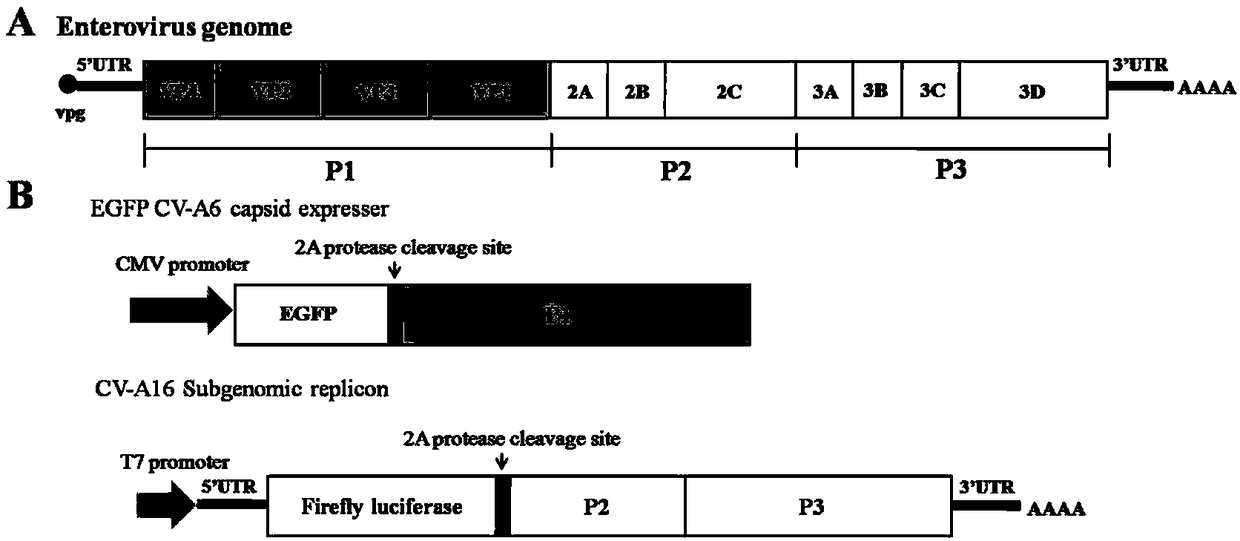
[0055] Using the full-length infectious cloning plasmid of CV-A6 as a template, the structural protein coding segment of CV-A6 (including VP4, VP2, VP3, VP1) was obtained by PCR amplification, and green fluorescent protein (GFP) was inserted into the N-terminal of the viral genome structural protein ( EGFP) gene. The gene sequence of EGFP was spliced with the gene sequence of all structural proteins of CV-A6, and the restriction site of 2A protease was inserted into the C-terminus of the EGFP gene, and spliced to obtain the fusion gene ( figure 1 B), its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.2, wherein the 1st to 717th is the coding gene of green fluorescent protein (the amino acid sequence of green fluorescent pro...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment two, check the consistency of the method of the present invention and classical live virus neutralization test
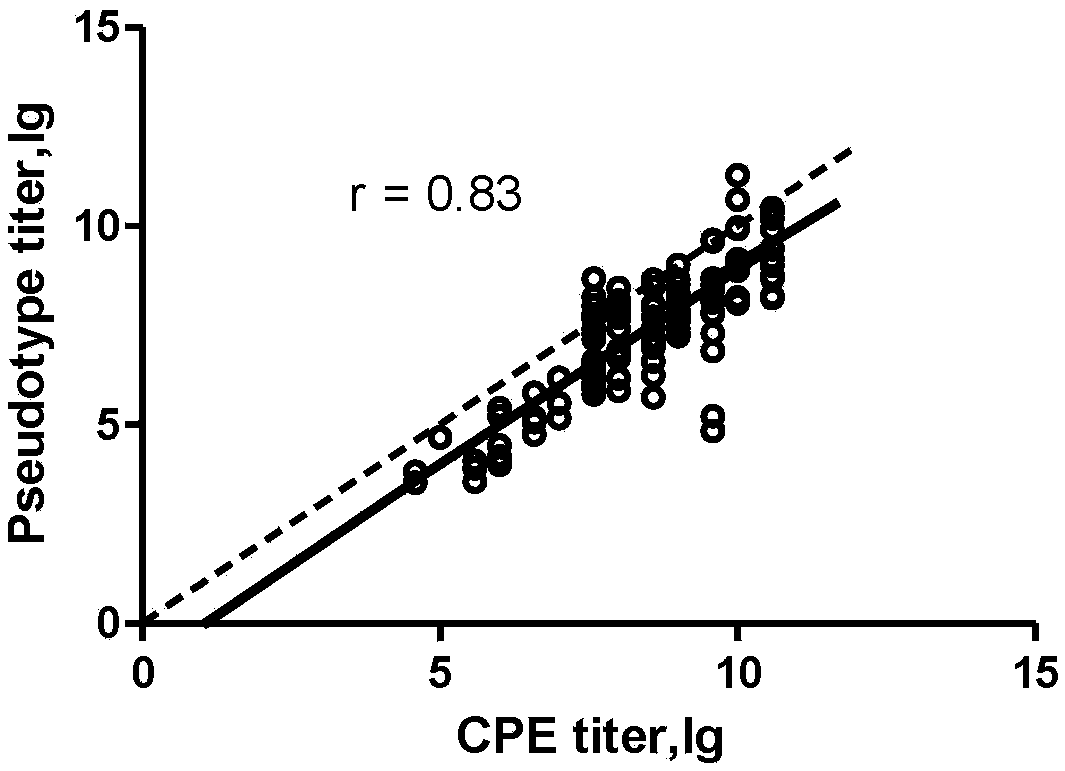
[0082] In parallel, the neutralizing antibody titer of a group of human plasma samples was tested with the wild-type CV-A6 live virus and the CV-A6 pseudovirus of the present invention. The wild-type CV-A6 virus strain is CV-A6-2014-XM, and the test sample comes from the phase III clinical serum sample of EV-A71 vaccine (from the China Institute for Food and Drug Control). Correlation analysis was performed on the two groups of test results, such as figure 2 As shown, the results show that the pseudovirus system of the present invention has good consistency with the classic live virus neutralization test when detecting serum neutralizing antibodies.
Embodiment 3
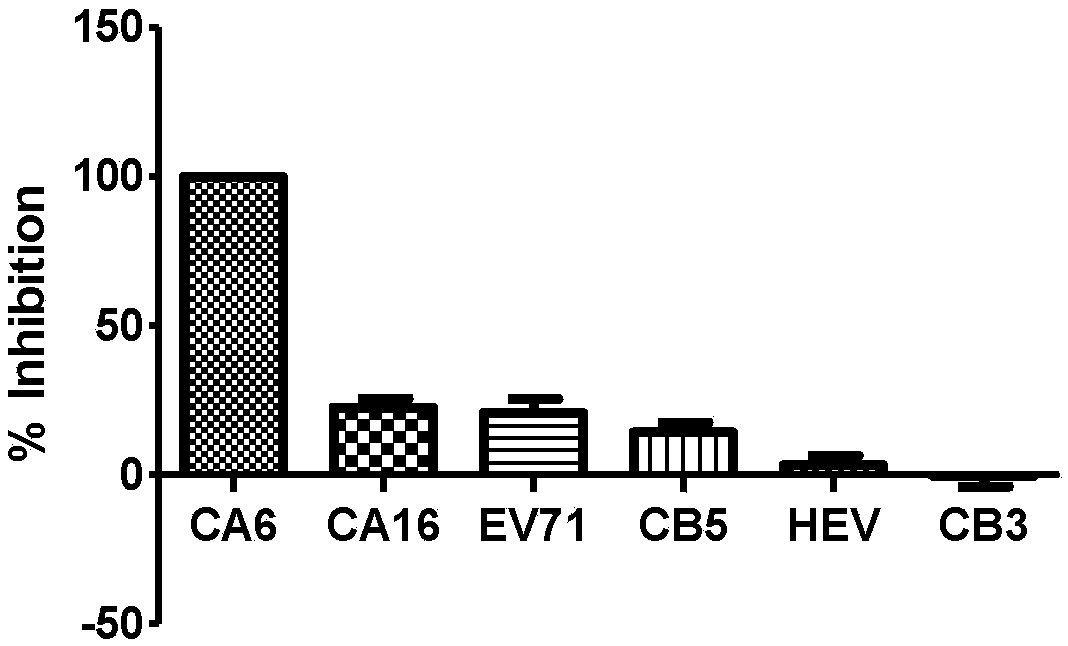
[0083] Embodiment three, test the specificity of CV-A6 pseudovirus system
[0084] In order to test the specificity of the CV-A6 pseudovirus system, a mouse-derived specific antiserum against CV-A6 (serum from SPF grade BALB / c mice immunized with CV-A6(XM) inactivated virus ), mouse-derived specific antiserum against EV-A71 (FY) (from the serum of SPF grade BALB / c mice immunized with EV-A71 (FY) inactivated virus), mouse-derived specific antiserum against CV -B3(112)-specific antiserum (serum from SPF-grade BALB / c mice immunized with CV-B3(112) inactivated virus), mouse-derived specific for CV-A16(G10) Antiserum (from SPF grade BALB / c mice immunized with CV-A16(G10) inactivated virus), mouse-derived specific antiserum against CV-B5(417) (from CV-B5 (417) The serum of SPF level BALB / c mice immunized with inactivated virus) and mouse-derived specific antiserum against hepatitis E HEV (from the hepatitis E vaccine immunized with the Hepatitis E vaccine produced by Wantai Canghai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com