Genetic molecular marking combination for anti-disease stichopus japonicas breeding and application of genetic molecular marking combination
A technology of molecular markers and genetic markers, which is applied in the direction of resistance to vector-borne diseases, recombinant DNA technology, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problem of late development of sea cucumber selection and breeding, and achieve improved breeding survival rate and breeding Benefits, automatic procedural detection, clear target effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Acquisition of genetic molecular markers for breeding of disease-resistant sea cucumbers and their verification in the offspring of the family
[0024] A japonicus family was constructed, and the disease resistance of each family was evaluated through the challenge test. A japonicus family with moderate disease resistance was selected, and the 2 parents and 142 offspring of the family were used as the mapping group. With the help of a high-throughput sequencing platform , developed SLAF markers, and constructed a high-density genetic linkage map of A. japonicus using HighMap software. After high-throughput sequencing, a total of 264,810 SLAF tags were developed, including 112,322 polymorphic SLAF tags. The average sequencing depth of parents with SLAF tags was 23.67×, and the average sequencing depth of offspring was 5.44×. Through bioinformatics analysis, there are 50,905 tags that can be used for genetic map construction. After quality filtering, 4629 poly...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Verification of Apostichopus japonicus disease resistance-related SNP molecular markers in an expanded population
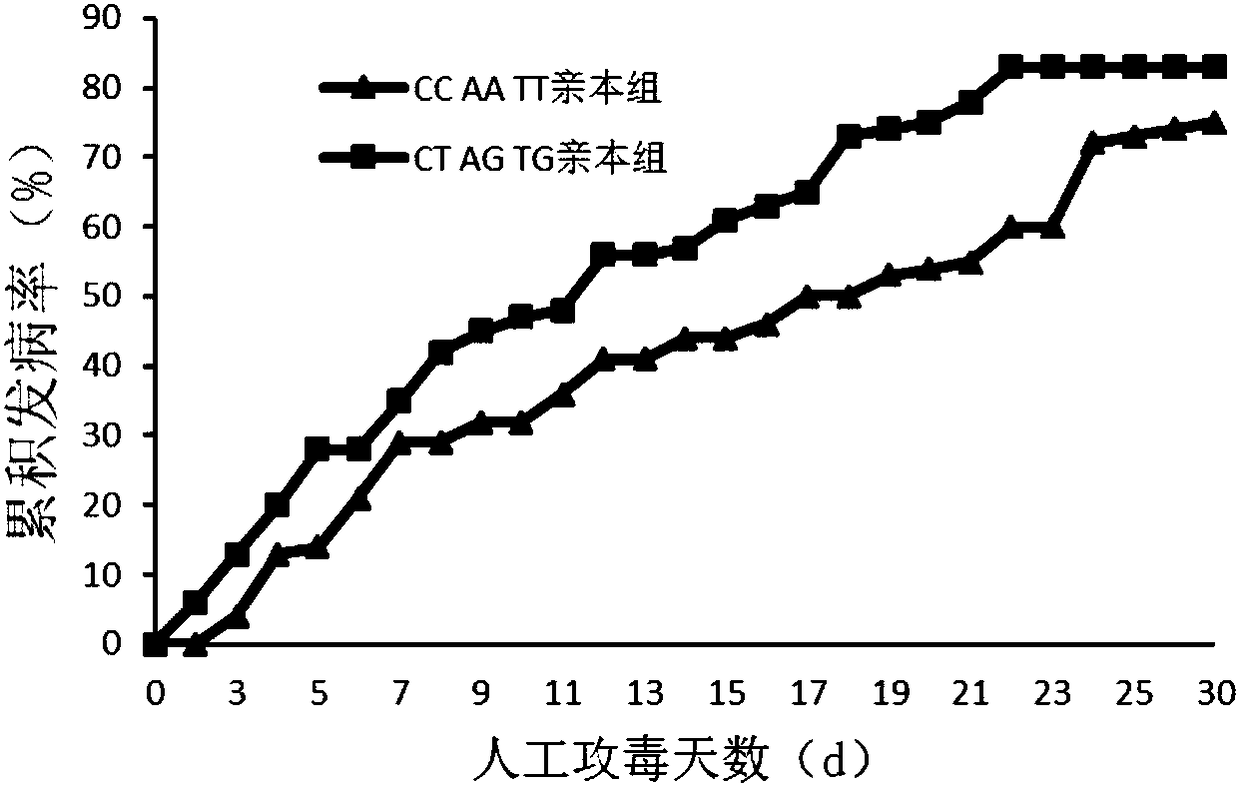
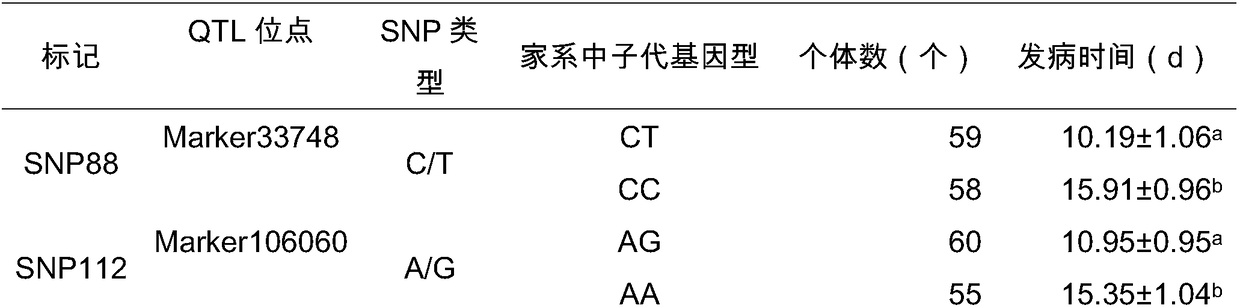
[0030]According to the flanking sequences on both sides of the three SNP sites obtained by high-throughput sequencing, primers for SNP site amplification detection were designed, and the corresponding primer sequences were SNP88F 5'-TTTTGTCCCCAGAGCATTATCCAA-3' and SNP88R 5'-TCCAGGAATGATATTTAGTGGTTGT-3' ; SNP112F 5'-ATTTTGGTTAGGGTTAAGAAGGCT-3' and SNP112R 5'-GTTTCCAAACAACATATGCACTCC-3'; SNP126F 5'-GGATTGATCGGGGACACACA-3' and SNP126R 5'-TGGGCTAAGTCACCAATCTGC-3'. The three SNP loci related to disease resistance of A. japonicus were typed by using the HRM small fragment method in the expanded population by using the corresponding sequences, and the QTL loci were verified in combination with the related trait data of the expanded population. The expanded population used was 8-month-old seedlings cultivated in the same batch of large-scale seedlings i...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Application of Genetic Molecular Marker Combination in the Breeding of Disease-resistant Apostichopus japonicus in the Production of Apostichopus japonicus
[0041] During the spring seedling period of A. japonicus, 100 parent references were randomly selected from the cultivated parent references, and the genotypes of 100 reference references at SNP88, SNP112, and SNP126 loci were genotyped using HRM technology. The primer sequences used were SNP88F 5′-TTTTGTCCCAGAGCATTATCCAA-3′ and SNP88R 5′-TCCAGGAATGATATTTAGTGGTTGT-3′; SNP112F 5′-ATTTTGGTTAGGGTTAAGAAGGCT-3′ and SNP112R 5′-GTTTCCAAACAACATATGCACTCC-3′ and SNP126FCATCG5′-GGGA '-TGGGCTAAGTCACCAATCTGC-3'. These three genetic marker amplification detection systems are: 1 μL (50 ng / μL) of DNA template, 4.5 μL 2×ES Taq Master Mix, 0.5 μL (10 μmol / L) of upstream and downstream primers, 3.5 μL ddH 2 O; PCR reaction program for 3 genetic marker typing: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com