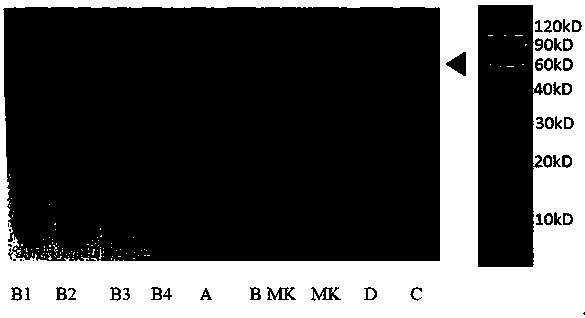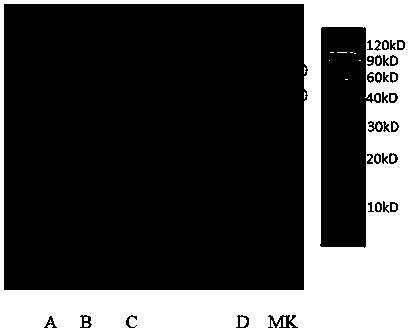Transposase-antibody binding protein fusion protein and preparation and application thereof
A fusion protein, transposase technology, applied in transferase, fusion polypeptide, antibody mimic/scaffold, etc., can solve the problems of complicated operation, loss of sequencing information, and many steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] Example 1 Preparation of fusion protein of transposase-antibody binding protein
[0108] 1. Fusion protein structure
[0109] The structure of the fusion protein of this embodiment includes a first domain with a transposition function and a second domain with a function of binding to the Fc fragment of an antibody. The transposition function refers to the function of inserting gene sequence by transposition. The function of binding to the Fc segment of an antibody refers to binding to the function of the Fc segment of an IgG molecule. The first structural domain and the second structural domain are connected by a connecting fragment, ie Linker. Further, the first domain may be a transposase protein, and the second domain may be an antibody binding protein.
[0110] The specific construction scheme of the fusion protein is: the linking fragment between the transposase protein and the antibody binding protein, that is, the structural formula is (GS) a (GGS) b (GGGS) ...
Embodiment 2
[0197] Example 2 Functional detection of the fusion protein of transposase-antibody binding protein
[0198] 1. To detect the function of the fusion protein of the transposase-antibody binding protein obtained in Example 1, firstly verify the randomly interrupted genome of the fusion protein, insert a tag sequence, and construct a sequencing library function after PCR.
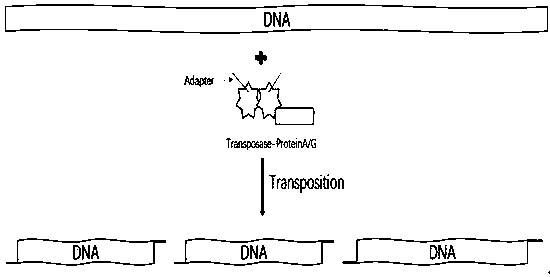
[0199] The principle and schematic diagram of random insertion of fusion protein are as follows: Figure 11 Shown: Transposomes formed by fusion proteins and adapters can fragment double-stranded DNA and add adapters to both ends of the fragmented DNA.
[0200]We used fusion proteins 1-5 (i.e. Tn5-ProteinA-1, Tn5-ProteinG-2, Tn10-ProteinA-3, Tn10-ProteinG-4, Tn5-ProteinA-5) and Tn5 transposase (positive control) respectively When dealing with human genomic DNA, fragmented short DNAs of different sizes and lengths are expected to be obtained, and linker sequences are connected to both ends of these fragmented ...
Embodiment 3
[0275] Example 3 The fusion protein of transposase-antibody binding protein brings a new method for studying protein-DNA interaction: ChT-Seq
[0276] The principle of the traditional ChIP-Seq method is to first specifically enrich the DNA fragments bound by the target protein through chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), then purify these fragments and construct a library, and then perform high-throughput sequencing on them. The experimental procedure is as follows:
[0277] (1) Formaldehyde cross-links the entire cell line (tissue), linking the target protein with chromatin;
[0278] (2) Separating genomic DNA and breaking it into small fragments of a certain length with ultrasound;
[0279] (3) Add a specific antibody that binds to the target protein, and the antibody forms an immunoprecipitation immunobinding complex with the target protein;
[0280] (4) Remove cross-linking and purify DNA to obtain DNA samples of chromatin immunoprecipitation;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com