Method for purifying proteins and kit
A purification method and protein technology, applied in the fields of biochemistry and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of unsuitability for industrial production, low renaturation rate, and strict requirements on sample volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0132] Embodiment 1: the fermentation amplification of bacterial strain
[0133] The strain used is recombinant Escherichia coli GM221 capable of expressing thrombopoietin-mimetic peptide fusion protein, purchased from ATCC (strain preservation number 98957, plasmid preservation number 98113)), and the strain expresses the protein represented by formula A of the present invention.
[0134] Cultivate under conventional fermentation conditions to express the desired peptide. The medium used is LB medium, which can be prepared according to the "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide".
[0135] You can also follow the steps below:
[0136] Thaw the preserved strain, inoculate 50 μl into a 250ml Erlenmeyer flask containing 50ml LB medium for activation, and cultivate overnight at 30°C with a rotation speed of 150-300r / min, then transfer the bacterial solution into a triangle flask containing 2L LB medium In the bottle, 37°C, 250-400r / min, replenish the medium in time, cultivate ove...
Embodiment 2
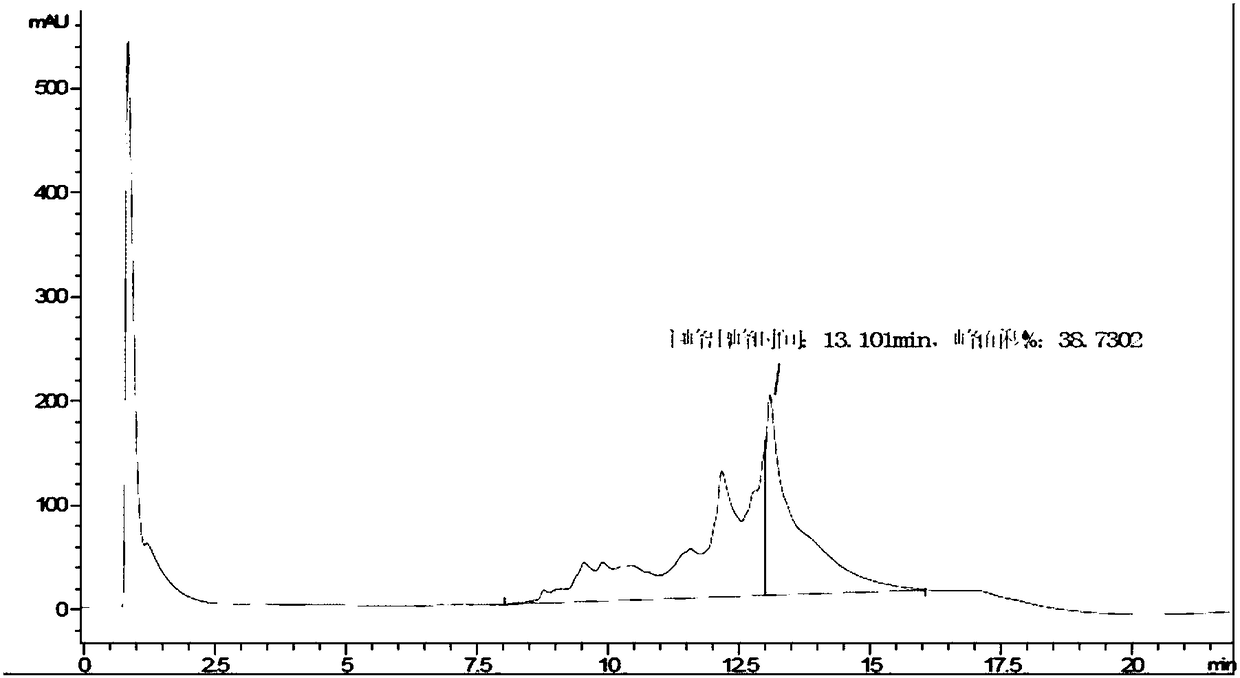
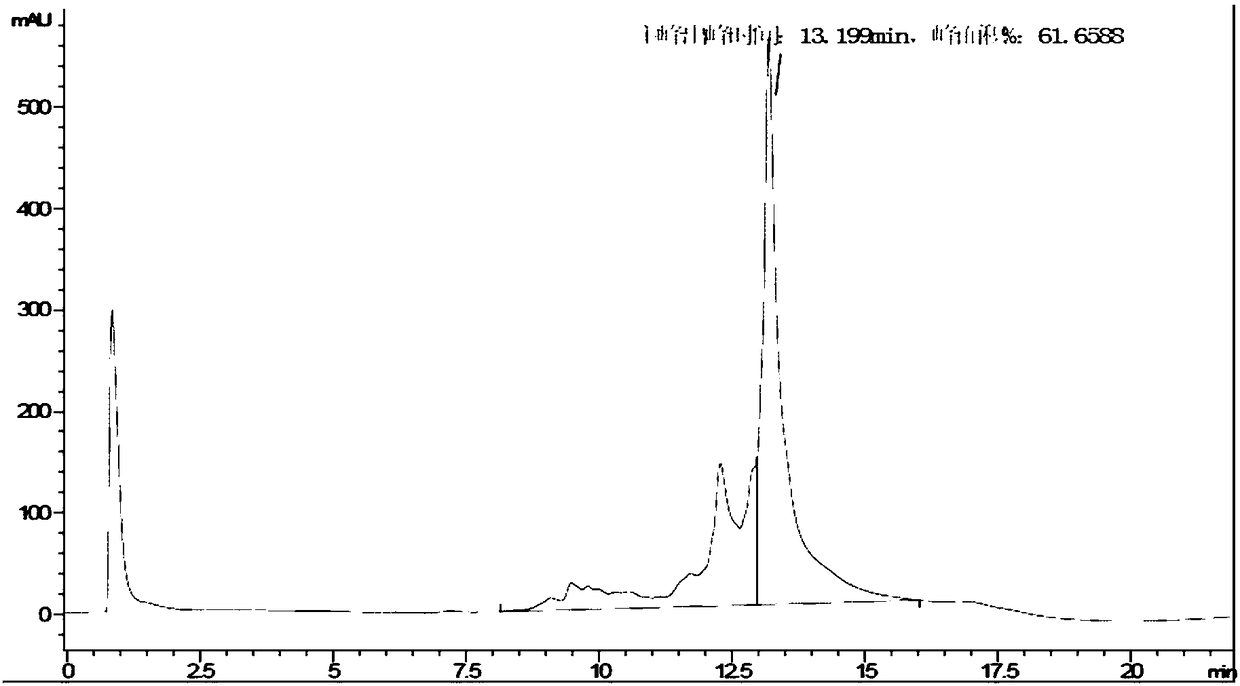
[0145] Example 2: Protein Purification
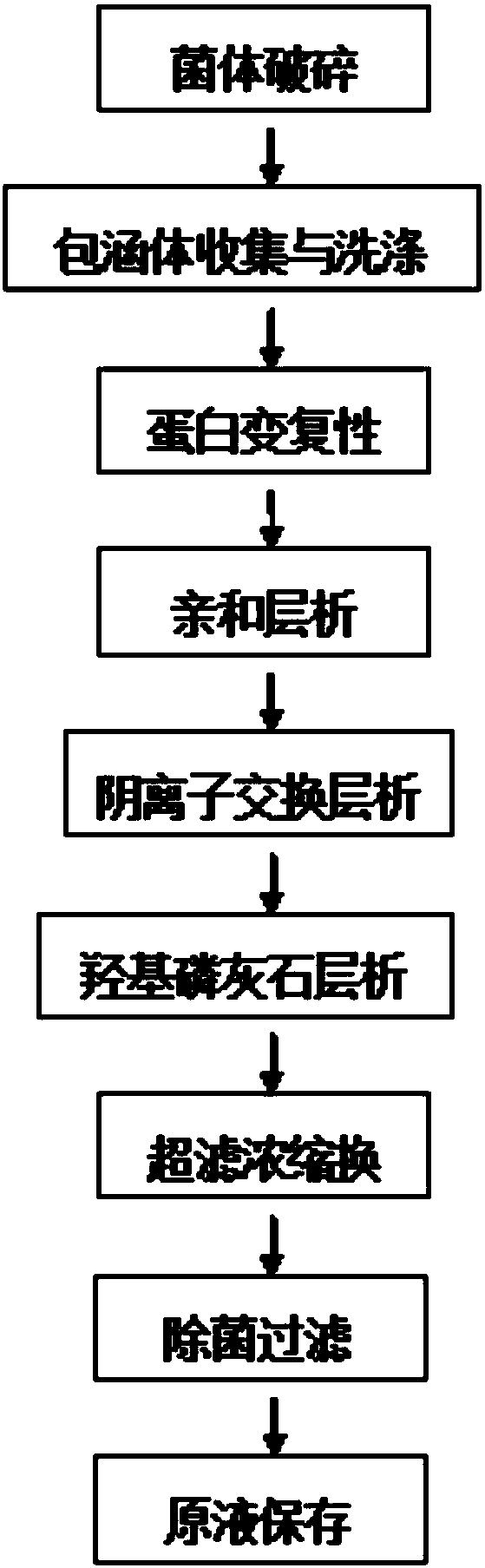
[0146] (1) Bacterial destruction: mix and stir the bacterium and the bacteriostasis solution 1:5 (w:v), the bacteriostasis solution is a solution with 20mM Tris, 10mM EDTA, and its pH is 8.0; Under the condition of 1000bar and 10°C, the bacteria were broken twice with a low-temperature ultra-high pressure continuous flow cell disruptor.
[0147] (2) Inclusion body collection and washing: centrifuge the sterilized solution in step (1) at 10°C at 9500rpm for 20min, collect the inclusion body precipitate, and then add the precipitate into washing buffer I at a ratio of 1:10 (w:v) and mix Stirring, the washing buffer I is a solution with 20mM Tris, 0.1%-0.2% Triton X-100, 0.1M NaCl, 1mM EDTA, 1M urea, its pH is 8.5, and the precipitate is collected by centrifugation; then the collected precipitate Washing buffer II was added at a ratio of 1:10 (w:v) for mixing and stirring. The washing buffer II was a solution with 20 mM Tris and 1 mM ED...
Embodiment 3
[0158] Example 3: Protein Purification
[0159] Steps (1)-(3) of Embodiment 3 With reference to steps (1)-(3) of Embodiment 2, steps (4)-(11) are as follows:
[0160] (4) Dialysis: dialyze the supernatant according to 1:30 (v:v) with the dialysate, and the dialysate is 30mM HCl solution;
[0161] (5) Oxidative derivatization: Then add an appropriate amount of urea to the dialysis harvest solution (retentate in the bag) so that the final concentration of urea is 10M, stir until the solution is clear, then add cystamine and 1g / L final concentration of 2.0g / L After stirring and dissolving the EDTA, adjust the pH to 8.5 with 2.5M Tirs, and let stand for oxidative derivatization for 4 hours;
[0162] (6) Refolding: Then dilute the protein solution with 10M urea solution to a concentration of 15g / L, then add the protein solution dropwise to the refolding solution at a ratio of 1:10 (v:v) to the refolding solution, so that the protein is finally The concentration is about 1.5g / L,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com