Grid composite fiber
A composite fiber and grid technology, applied in the direction of electrode carrier/current collector, electrical components, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the service life of lead-acid batteries, failure of lead-acid batteries, heavy metal lead pollution, etc., and reduce heavy metal pollution. , Good structural strength and dimensional stability, the effect of improving the service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
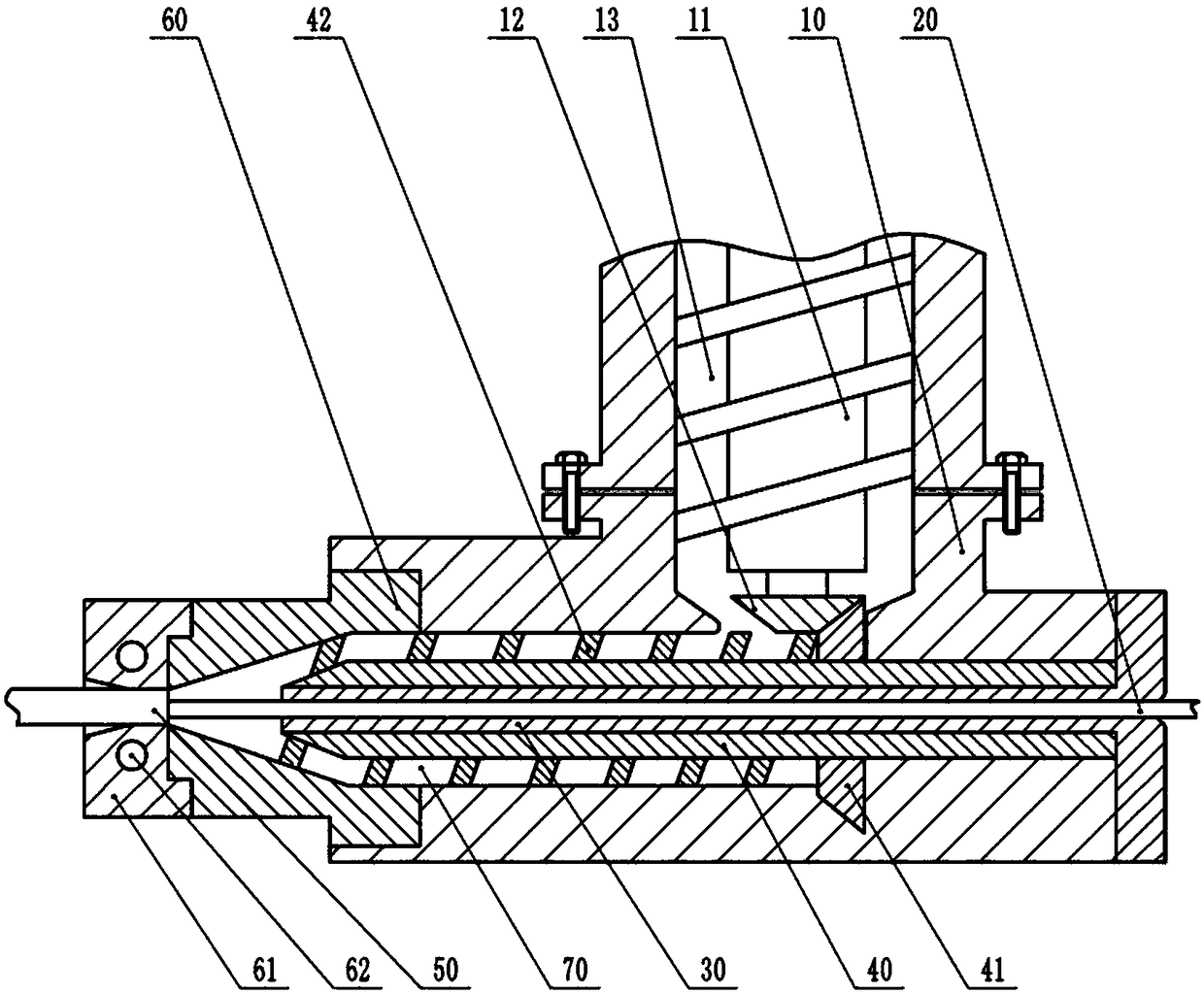
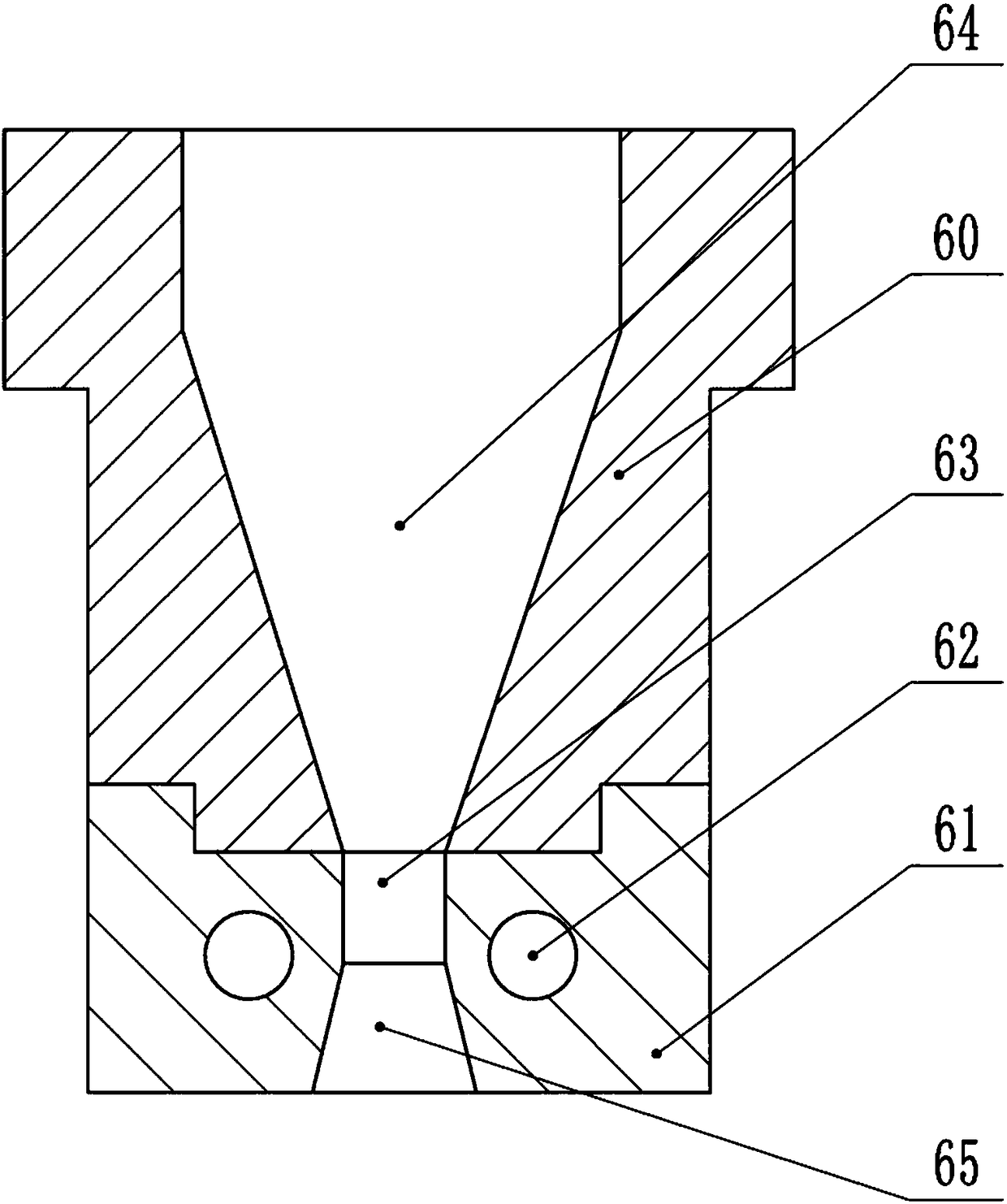
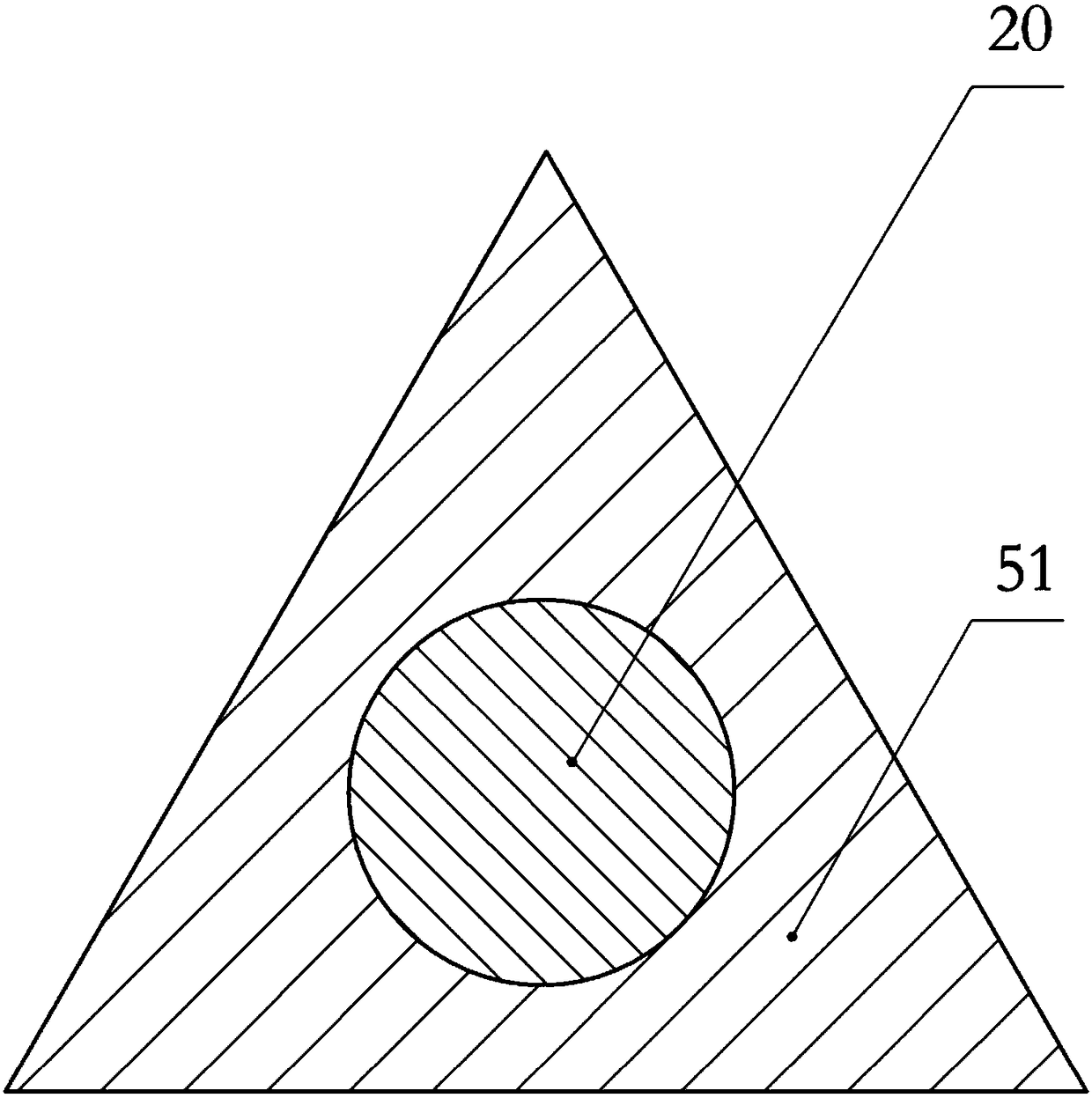
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the grid composite fiber includes a core material and a fixing layer fixed on the surface of the core material, the diameter of the core material is 0.7 mm, and the thickness of the fixing layer is 0.3 mm. The cross-section of the grid composite fiber is triangular, wherein the cross-section of the core material is circular, and the cross-section of the fixing layer is triangular. The core material is carbon fiber, wherein the strength of carbon fiber is 2400MPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 250Gpa. The fixing layer includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 92 parts of zinc alloy coating material and 8 parts of composite material. The composite material includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 36 parts of graphite fiber, 60 parts of polypropylene and 17 parts of silicon nitride; the zinc alloy coating includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: aluminum, cadmium, tin, antimony, magnesium, indium and ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the thickness of the core material is 0.7 mm, and the thickness of the fixing layer is 0.25 mm. The strength of carbon fiber is 2200MPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 230Gpa. The fixing layer includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 94 parts of zinc alloy coating material and 6 parts of composite material. The composite material includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 25 parts of graphite fiber, 75 parts of polypropylene and 25 parts of silicon nitride; the zinc alloy coating includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: aluminum, cadmium, tin, antimony, magnesium, indium and There are 4 parts of rare earth and 96 parts of zinc.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the thickness of the core material is 0.6 mm, and the thickness of the fixing layer is 0.3 mm. The strength of carbon fiber is 2100MPa, and the modulus of elasticity is 240Gpa. The fixing layer includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 95 parts of zinc alloy coating material and 5 parts of composite material. The composite material includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: 20 parts of graphite fiber, 72 parts of polypropylene and 28 parts of silicon nitride; the zinc alloy coating includes the following raw materials in parts by mass: aluminum, cadmium, tin, antimony, magnesium, indium and There are 3 parts of rare earth and 97 parts of zinc.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com