A catalytic cracking catalyst
A catalytic cracking and catalyst technology, applied in catalytic cracking, physical/chemical process catalysts, molecular sieve catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the zeolite structure, reducing the selectivity of zeolite, and not being able to obtain the silicon-aluminum ratio, etc., and achieve less non-framework aluminum content , high heavy oil conversion activity, and low coke selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
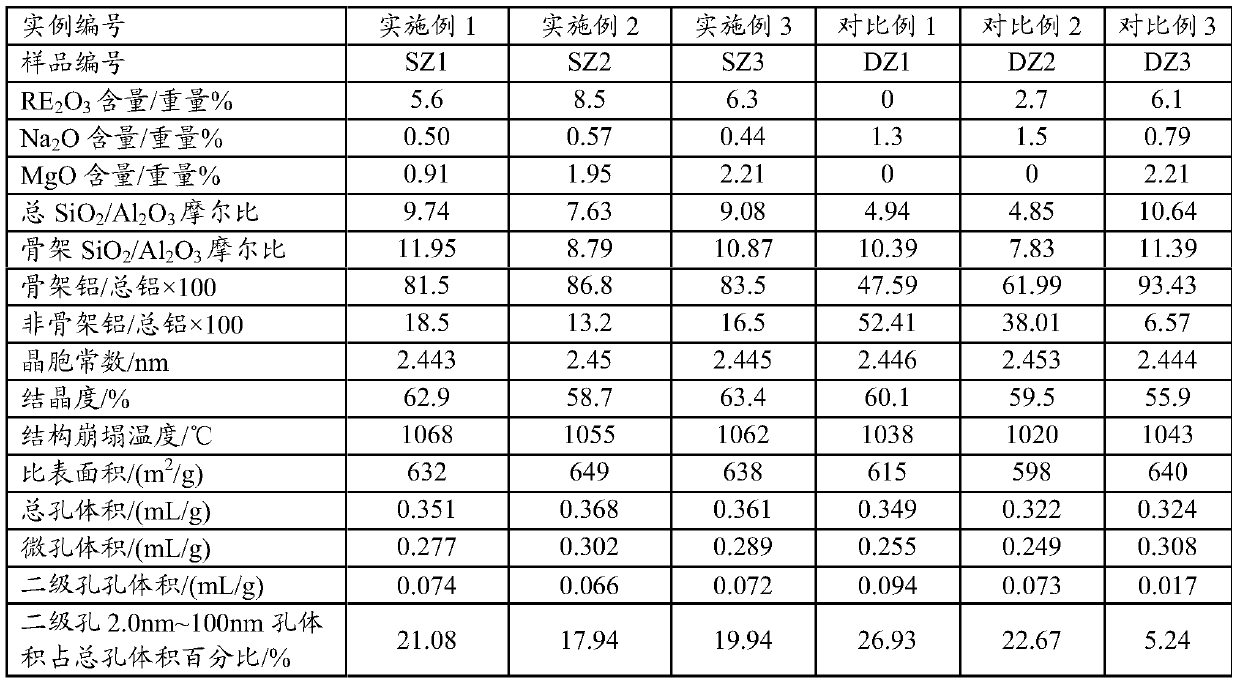
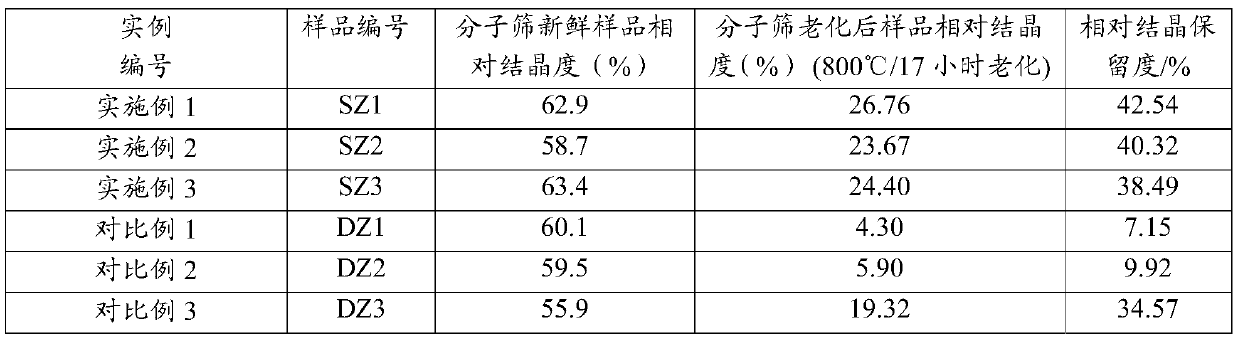
[0038] In the preparation method of catalytic cracking catalyst provided by the present invention, in the preparation method of the magnesium-containing modified Y-type molecular sieve, in step (4), the ultra-stable modified Y-type molecular sieve obtained in step (3) is modified with magnesium compound deal with. One embodiment includes adding the ultra-stable modified Y-type molecular sieve filter cake sample or dried sample obtained in step (3) into a solution containing a magnesium compound such as a magnesium salt, stirring at 5-50°C for 10-120 Minutes, then, add ammonia water, adjust the pH of the solution to 7.5-10, stir evenly, filter, and rinse with neutral water, after that, dry the filter cake and place it in a muffle furnace for 1 hour at 500-650°C For example, within 1-5 hours or 2-3 hours, a magnesium-modified high-silicon ultra-stable Y-type molecular sieve is obtained. Wherein, in the amount of the magnesium-containing compound solution and the molecular sieve...
Embodiment 1
[0050] Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (calculated on a dry basis) and add them to 20 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 600ml of RE(NO 3 ) 3 Solution (rare earth solution concentration is RE 2 o 3 Calculated as 319g / L), stirred, heated to 90-95°C and kept for 1 hour, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 7.0% by weight. 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 8.8% by weight is then calcined for 6 hours at a temperature of 390°C in an atmosphere containing 50% by volume of water vapor and 50% by volume of air to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.455nm. After that, carry out Drying process, so that its water content is less than 1% by weight, and then according to SiCl 4 : Y-type molecular sieve (dry basis) = 0.5: 1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 Gas, at a t...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Get 2000 grams of NaY molecular sieves (on a dry basis) and add them to 25 liters of decationized aqueous solution and stir to make them evenly mixed. Add 800 ml of RECl 3 solution (in RE 2 o 3 The calculated solution concentration is: 319g / L), stirred, heated up to 90-95°C for 1 hour, then filtered, washed, and the filter cake was dried at 120°C to obtain a unit cell constant of 2.471nm and a sodium oxide content of 5.5% by weight , with RE 2 o 3 A Y-type molecular sieve with a total rare earth content of 11.3% by weight is then calcined at a temperature of 450°C and 80% water vapor for 5.5 hours to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve with a unit cell constant of 2.461nm, and then dried to reduce its water content at 1 wt%, then follow SiCl 4 : Y-type zeolite = 0.6:1 weight ratio, feed SiCl vaporized by heating 4 Gas, at a temperature of 480 ° C, reacted for 1.5 hours, after that, washed with 20 liters of decationized water, and then filtered, the molecular sieve filt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com