a li 7 la 3 zr 2 o 12 Preparation method of solid electrolyte
A technology of solid electrolyte and preparation steps, which is applied to circuits, electrical components, secondary batteries, etc., can solve the problems of complex precursor preparation process, large particle size of material particles, and high sintering temperature, and achieves short test period and simple preparation method. , the effect of low sintering temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] (1) 0.5820 g of lanthanum oxide, 0.6984 g of lithium carbonate, and 0.65 g of zirconium oxynitrate hydrate were placed in a beaker containing ethanol to obtain a suspension;
[0027] (2) under stirring, 15% dilute nitric acid was added to the suspension of step (1) to obtain a colorless transparent sol;
[0028] (3) Evaporating and drying the sol in step (2) in a water bath at 80° C. for 4 h to obtain a gel;
[0029] (4) drying the gel in step (3) at 200° C. for 2 h, and pyrolyzing to obtain a precursor;
[0030] (5) The sol-gel precursor in step (4) was ground uniformly, sintered at 800 °C for 6 h, and cooled naturally to obtain 1.0 g of LLZO solid electrolyte material with a cube-like structure.
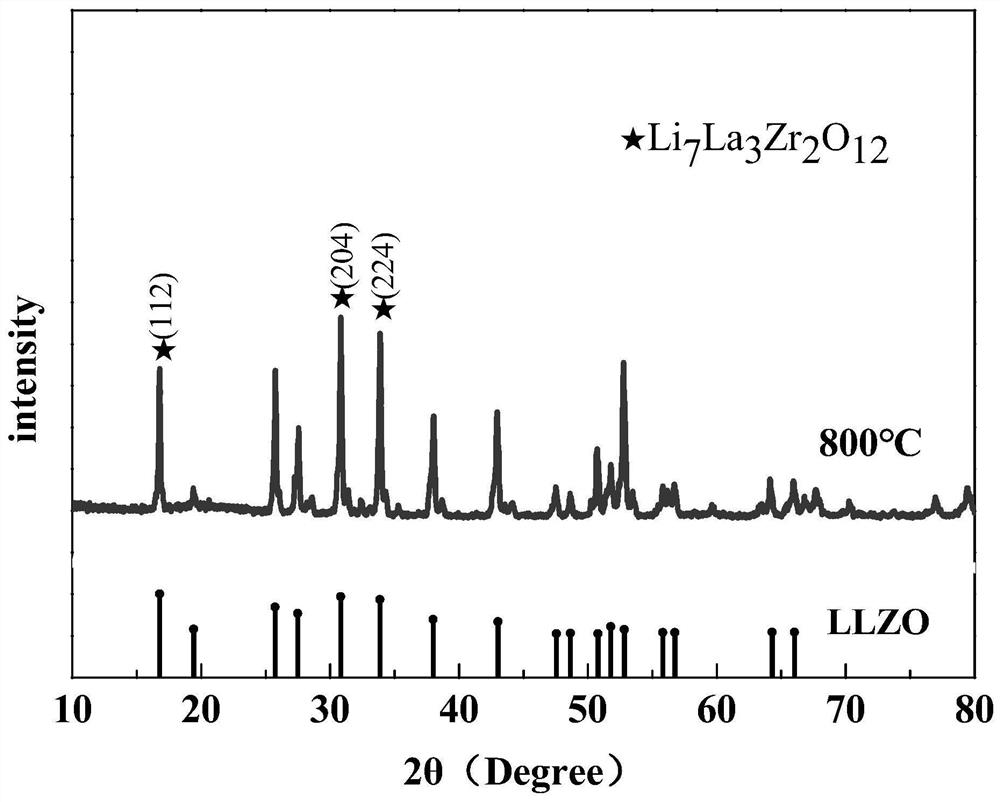
[0031] figure 1 It is the XRD pattern of the garnet-type solid electrolyte LLZO prepared according to Example 1. Depend on figure 1 It was found that the prepared product had a tetragonal crystal structure (PDF#40-0894).
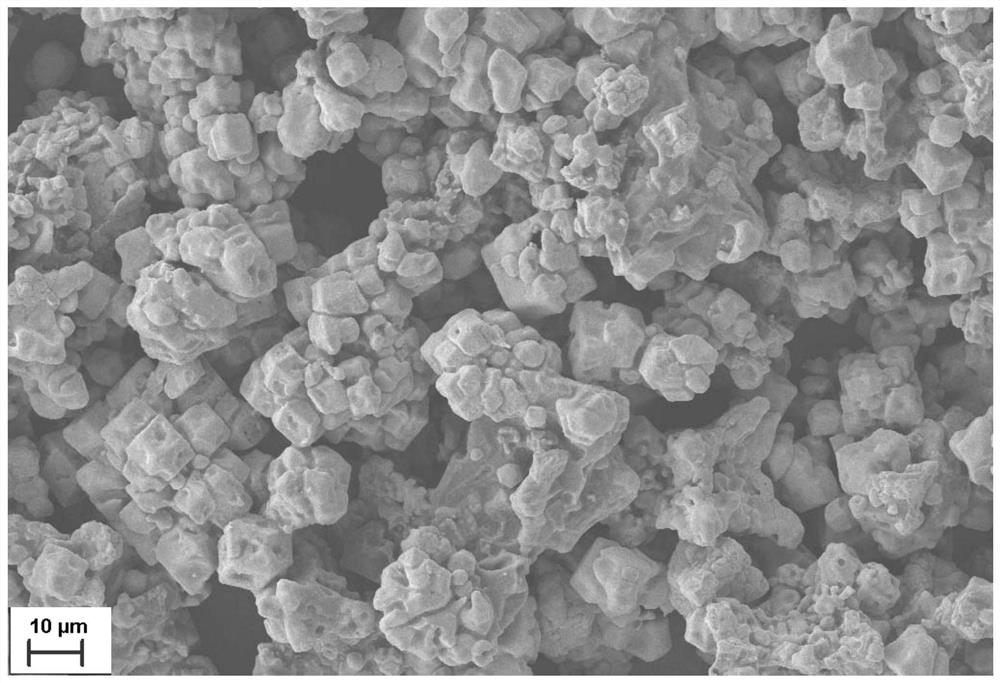
[0032] figure 2 This is a scanning electron m...
Embodiment 2
[0034] (1) Place 0.6893 g of lanthanum hydroxide, 0.3498 to 0.4050 g of lithium hydroxide, and 0.2753 g of zirconium nitrate hydrate in a beaker containing ethanol to obtain a suspension;
[0035] (2) under stirring, 40% dilute nitric acid was added to the suspension of step (1) to obtain a colorless transparent sol;
[0036] (3) Evaporating and drying the sol in step (2) in a water bath at 100° C. for 3 h to obtain a gel;
[0037] (4) drying the gel in step (3) at 200° C. for 2 h, and pyrolyzing to obtain a precursor;
[0038] (5) The sol-gel precursor in step (4) was ground uniformly, sintered at 750 °C for 6 h, and cooled naturally to obtain 1.0 g of LLZO solid electrolyte material.
Embodiment 3
[0040] (1) Place 0.5820 g of lanthanum oxide, 0.6775-0.6984 g of lithium carbonate, and 0.6500 g of zirconium oxynitrate hydrate in a beaker containing ethanol to obtain a suspension;
[0041] (2) under stirring, 30% dilute nitric acid was added to the suspension of step (1) to obtain a colorless transparent sol;
[0042] (3) Evaporating and drying the sol in step (2) in a water bath at 100° C. for 3 h to obtain a gel;
[0043] (4) drying the gel in step (3) at 200° C. for 4 h, and pyrolyzing to obtain a precursor;
[0044] (5) The sol-gel precursor in step (4) was ground uniformly, sintered at 850 °C for 6 h, and cooled naturally to obtain 1.0 g of LLZO solid electrolyte material.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com