Application of lactobacillus plantarum MG-1 to postharvest fresh keeping of grapes
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum, MG-1, applied in the direction of Lactobacillus, application, preservation of fruits and vegetables, etc., can solve the problem of less inhibitory effect of lactic acid bacteria on mold, and achieve the effect of reducing the rate of decay and weight loss and improving the activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Example 1 Isolation and screening of the bacterial strain MG-1
[0021] Take 10g of naturally fermented Chinese cabbage made in Changsha, dilute it with sterile normal saline, mix it with calcium carbonate-containing 50°C MRS agar medium, pour it on a plate, culture it at a constant temperature at 38°C, and select large single colonies of calcium-dissolving circles for repeated purification after 48 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2 Inhibition of grape white rot and botrytis cinerea
[0024] Preparation of fermentation supernatant: Inoculate 2% of the preserved strain into MRS liquid medium after activation, culture at 37°C for 18h, centrifuge at 12000r / min for 20min, filter the supernatant through a 0.22μm filter membrane, and store at 4°C .
[0025] Method: According to the Oxford cup double-layer plate method, an indicator plate containing different indicator bacteria was made, and the final concentration of bacteria in the semi-solid medium on the upper layer was 10 6 CFU / mL, fungi, yeast cells or spores 10 4 1 / mL, take 60 μL of the fermentation supernatant of the strain and add it to the well, and cultivate it under the optimum growth temperature of each indicator bacteria, use sterile water as the negative control, and hymexazol (diluted 1000 times as the stock solution when used) as the positive For the control, when the negative control reaches the edge of the aperture, measure ...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3 Fresh-keeping effect on grapes after picking
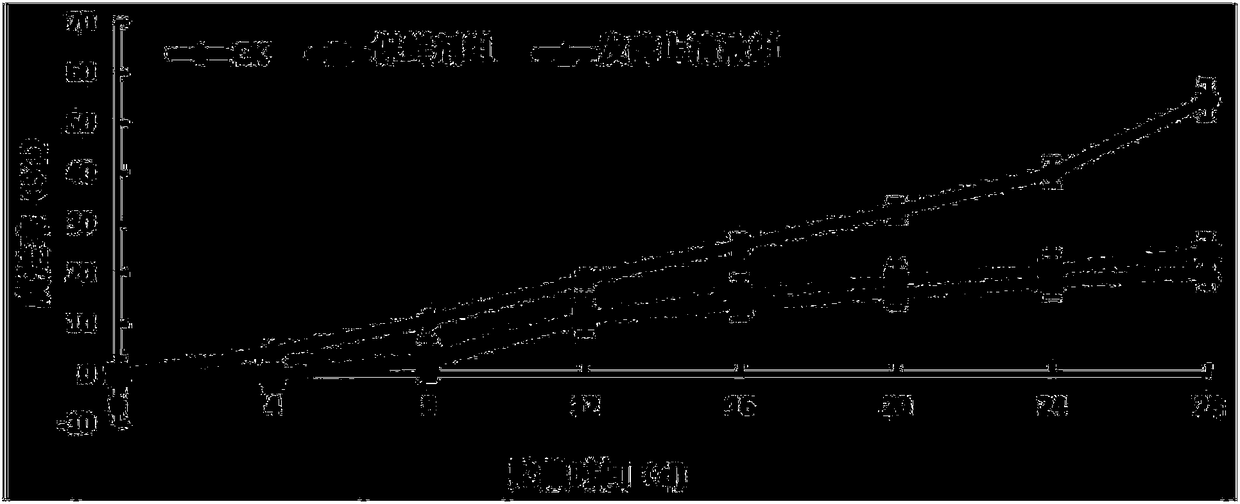
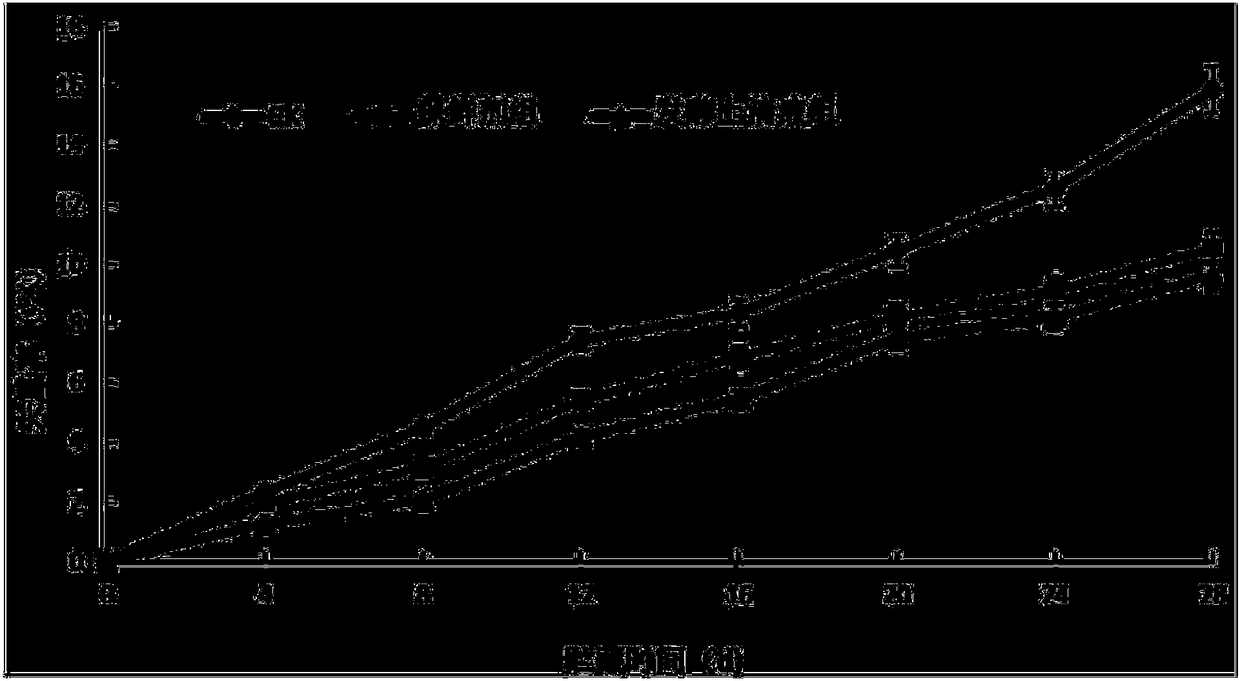
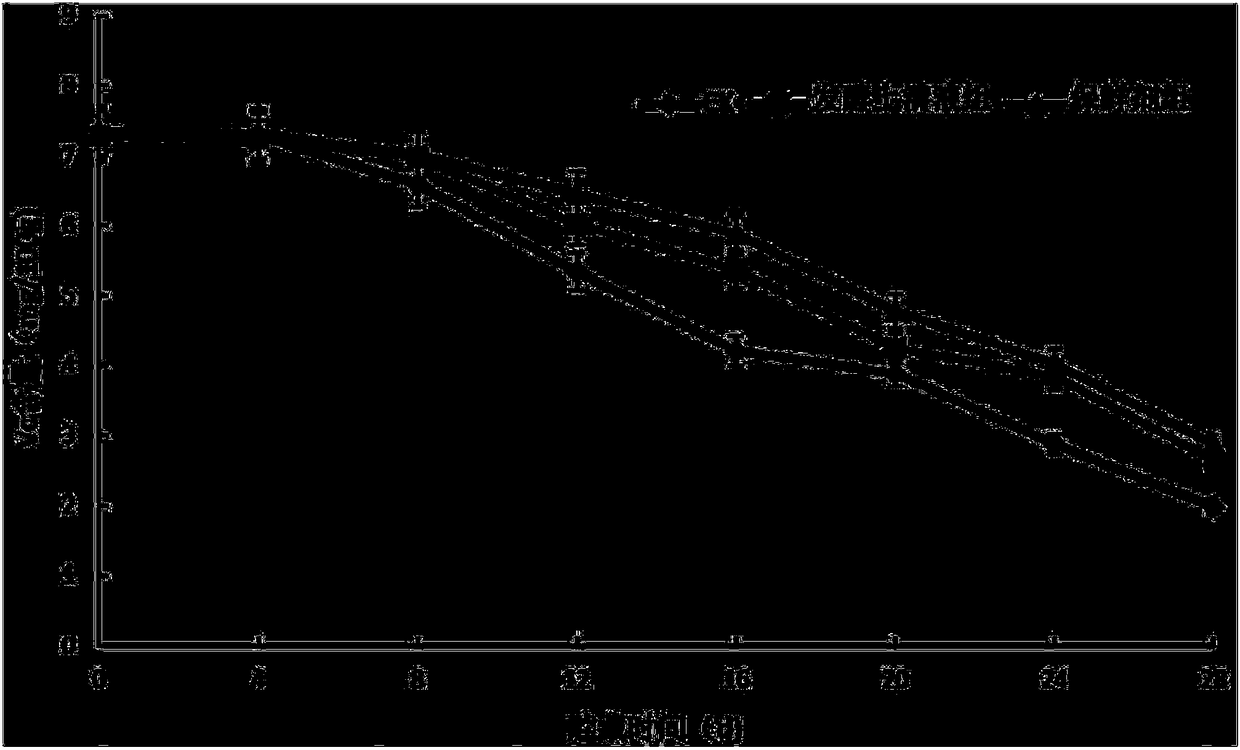
[0029] In the experiment, three treatments were set up: the fermentation supernatant group of the strain MG-1 (hereinafter referred to as the fermentation supernatant group), the NW20 preservative group and the sterile water control group (CK group). NW20 preservative diluted to 10% volume fraction before use. After washing and drying the post-harvest fresh grapes, soak them in the treatment solutions of the three treatment groups for 3 minutes respectively, and then dry them naturally, put them into fresh-keeping bags, seal them, and culture them at a constant temperature at 5°C and 75% humidity. Detection Indicator. 20 fruits per treatment, repeated 3 times. Experimental data with Said, using Excel and SPSS software for data processing and significant difference analysis, p<0.05 means significant difference, p<0.01 means extremely significant difference.
[0030] Effect on grape rot rate: by figure 1 It ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com