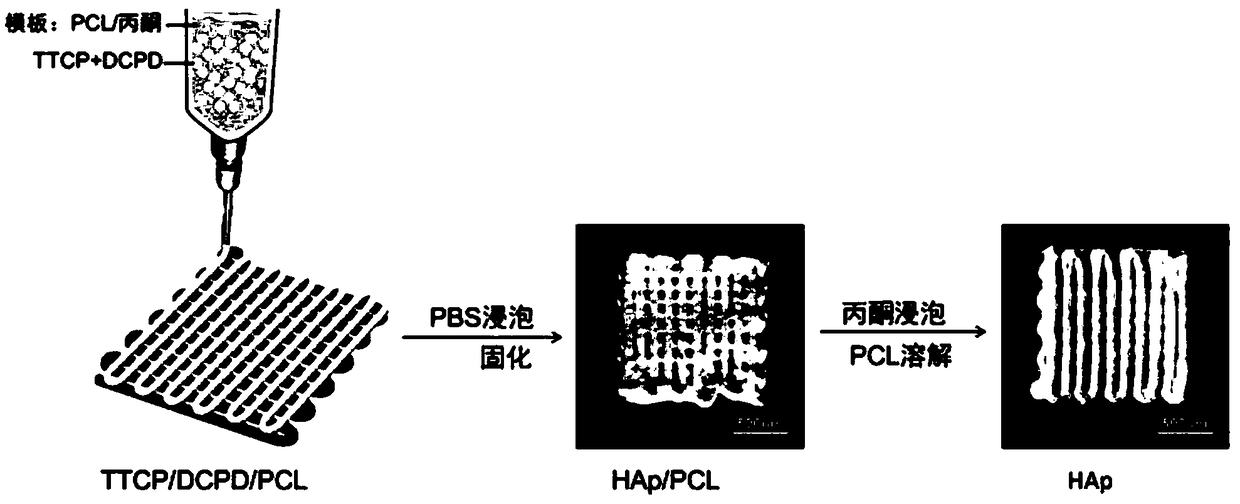
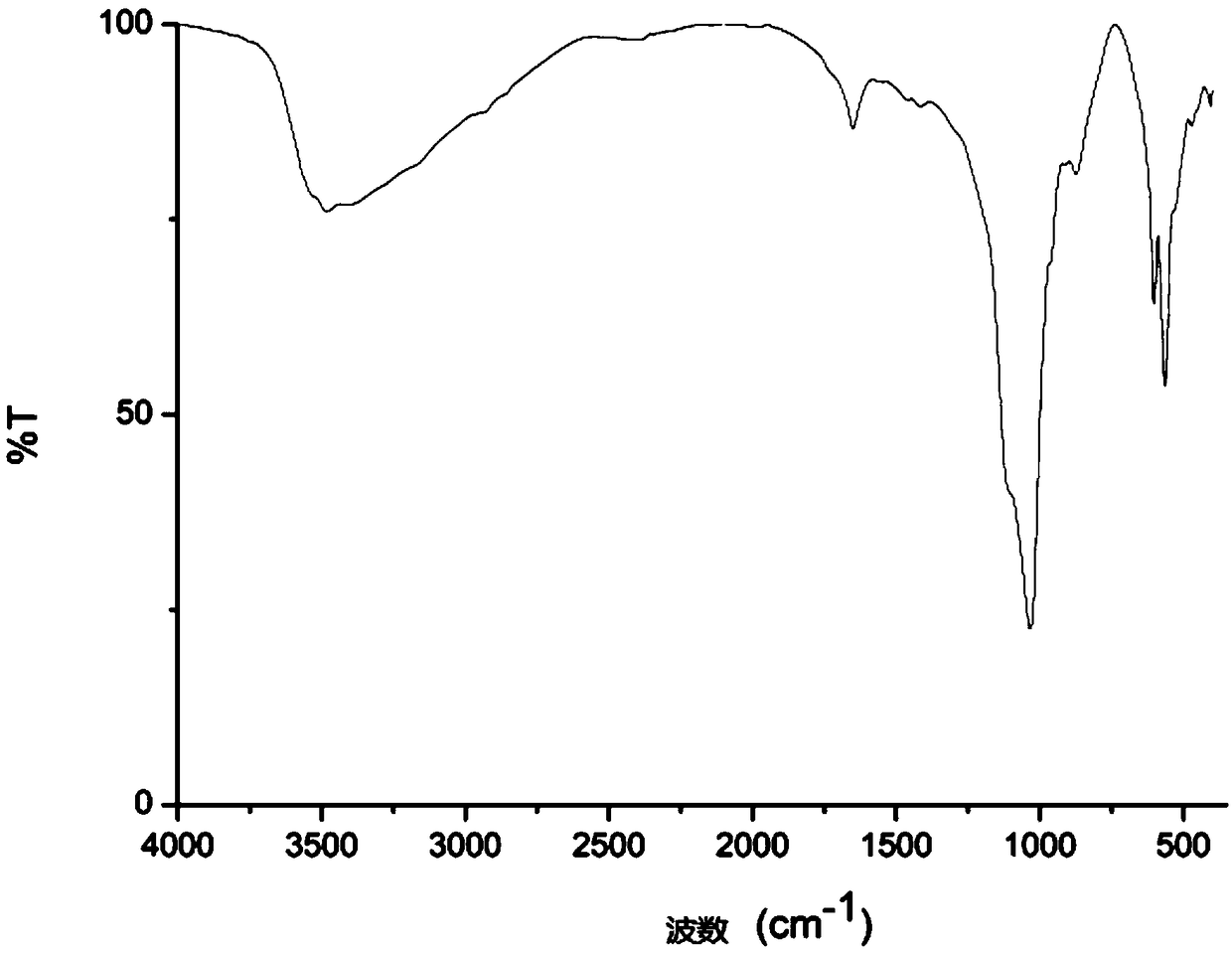
Preparation method for porous calcium phosphate stent
A porous scaffold and calcium phosphate technology, applied in the field of biomedical materials, can solve the problems of reducing energy consumption, pore shrinkage and deformation, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing energy consumption, easy acquisition, and simple process operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Preparation of printing paste
[0037] Weigh polycaprolactone PCL and dissolve it in acetone to prepare a PCL solution with a concentration of 0.032g / mL, mix calcium hydrogen phosphate DCPD and tetracalcium phosphate TTCP powder at a molar ratio of 1:1 to obtain TTCP / DCPD mixed powder , mixing the obtained mixed powder with the PCL solution to make a suspension with a mixed powder content of 1 mg / ml, which is used as a slurry for 3D printing;
[0038] (2) Preparation of calcium phosphate porous scaffolds by 3D printing
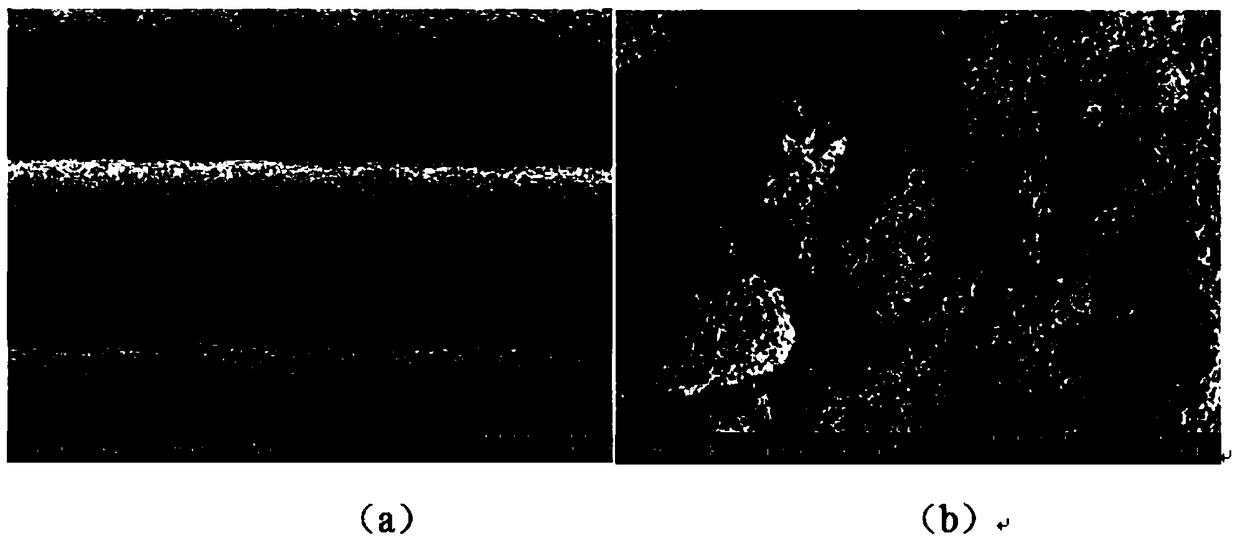
[0039]The slurry obtained in step (1) is subjected to 3D printing, the moving speed of the nozzle is controlled to be 240mm / min, the discharge speed is 0.167mL / min, and the length, width and height are respectively 20mm, 20mm, 10mm rectangular parallelepiped DCPD / TTCP / PCL stent body (see figure 1 ), according to the required pore size of the bracket during printing, the movement of the nozzle is controlled by setting the 3D printing program. Soak...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) Preparation of printing paste
[0045] Weigh polycaprolactone PCL and dissolve it in acetone to prepare a PCL solution with a concentration of 0.064g / mL, mix calcium hydrogen phosphate DCPD and tetracalcium phosphate TTCP powder at a molar ratio of 1:1 to obtain TTCP / DCPD mixed powder , mixing the obtained mixed powder with the PCL solution to make a suspension with a mixed powder content of 2 mg / ml, which is used as a slurry for 3D printing;
[0046] (2) Preparation of calcium phosphate porous scaffolds by 3D printing
[0047] The slurry obtained in step (1) is subjected to 3D printing and molding, the moving speed of the nozzle is controlled to 220mm / min, the discharge speed is 0.167mL / min, and the length, width and height are respectively 20mm, 20mm, For the 10mm rectangular parallelepiped DCPD / TTCP / PCL stent body, according to the required pore size of the stent during printing, the printing is completed by setting the 3D printing program and controlling the no...
Embodiment 3
[0049] (1) Preparation of printing paste
[0050] Weigh polycaprolactone PCL and dissolve it in acetone to prepare a PCL solution with a concentration of 0.064g / mL, mix calcium hydrogen phosphate DCPD and tetracalcium phosphate TTCP powder at a molar ratio of 1:1 to obtain TTCP / DCPD mixed powder , mixing the obtained mixed powder with the PCL solution to make a suspension with a mixed powder content of 1.5 mg / ml, which is used as a slurry for 3D printing;
[0051] (2) Preparation of calcium phosphate porous scaffolds by 3D printing
[0052] The slurry obtained in step (1) is subjected to 3D printing, the moving speed of the nozzle is controlled to be 240mm / min, the discharge speed is 0.167mL / min, and the length, width and height are respectively 20mm, 20mm, 10mm rectangular parallelepiped DCPD / TTCP / PCL stent body. When printing, according to the required pore size of the bracket, the printing is completed by setting the 3D printing program and controlling the movement of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com