Artificial wetland capable of strengthening treatment effect of salt-containing wastewater by utilizing intertidal zone bottom mud and application
A technology for artificial wetlands and saline wastewater, applied in water/sludge/sewage treatment, biological water/sewage treatment, biological treatment devices, etc. Promote the application, affect the wetland treatment effect, etc., to achieve the effect of enriching microbial diversity and salt-tolerant populations, good COD removal effect, and improved effluent COD removal rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Construction of Embodiment 1 Constructed Wetland
[0042] Collect wetland plants Phragmites reed, carefully wash the roots and stems of the plants with tap water, put them in clean water for 2 weeks, and then select plants with normal growth and consistent growth for transplanting; after transplanting, add tap water to dry for 3 days until the substrate is saturated, and change the Cultured with 10% Hoagland nutrient solution. After the plants survived, they were inoculated with the supernatant from the secondary sedimentation tank of the sewage treatment plant and cultured for several weeks until the system became stable, and a constructed wetland was obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0044] The structure of the constructed wetland obtained by the construction method of embodiment 1
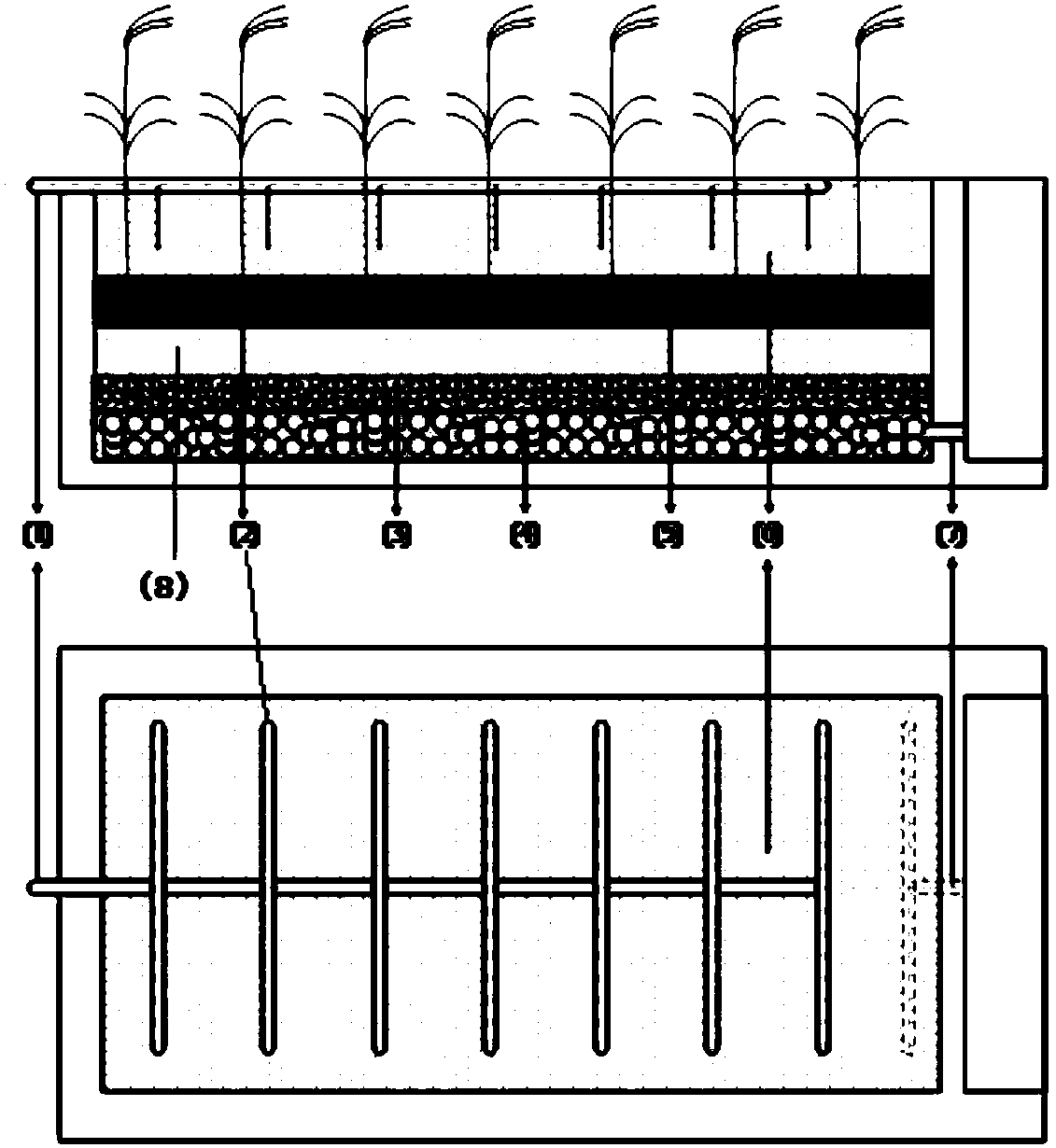
[0045] Depend on figure 1 As shown, a constructed wetland that uses intertidal sediment to enhance the treatment effect of saline wastewater includes a water inlet pipeline 1, a wetland main body, and a water outlet pipeline 7. The water inlet pipeline 1 is located above the wetland main body, and the water outlet pipeline 7 is located at Below the main body of the wetland, the main body of the wetland includes wetland plants 2 and a wetland bed; the main body of the wetland is a subsurface artificial wetland, and the wetland plants 1 are planted on the wetland bed; the wetland bed from top to bottom is the first A sand layer 6, an intertidal bottom mud layer 5, and a filter layer; the filter layer is a second sand layer 8, a gravel layer 3, and a coarse sand layer 4 from top to bottom.
[0046] The water inlet pipe 1 is located in the middle of the top of the constructed wet...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Embodiment 3 waste water treatment
[0049] Salt-containing simulated sewage: prepared from sucrose, ammonium sulfate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, magnesium sulfate, ferrous sulfate, calcium chloride, and tap water. The theoretical influent concentration is COD=180mg / L, NH 4 + -N=45mg / L;
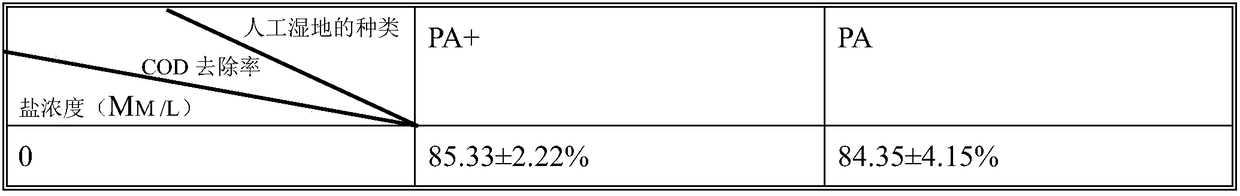
[0050] The salt concentration of the influent is set at four salt concentration gradients of 0, 50, 100, and 150mM / L, and the influent is about 0.8m 3 / d, the hydraulic retention time is 3 days; design 2 groups of wetlands, respectively with plants and sediment (PA+), with plants and no sediment (PA), each group should have at least 3 parallels, and the system should be measured after 3 months of stability The relevant indicators and recorded data are shown in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1 Wastewater treatment effect
[0052]
[0053]
[0054] Summary: From Example 3, it can be seen that under the same salt concentration, the constructed wetland with intertidal bottom mud ha...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com