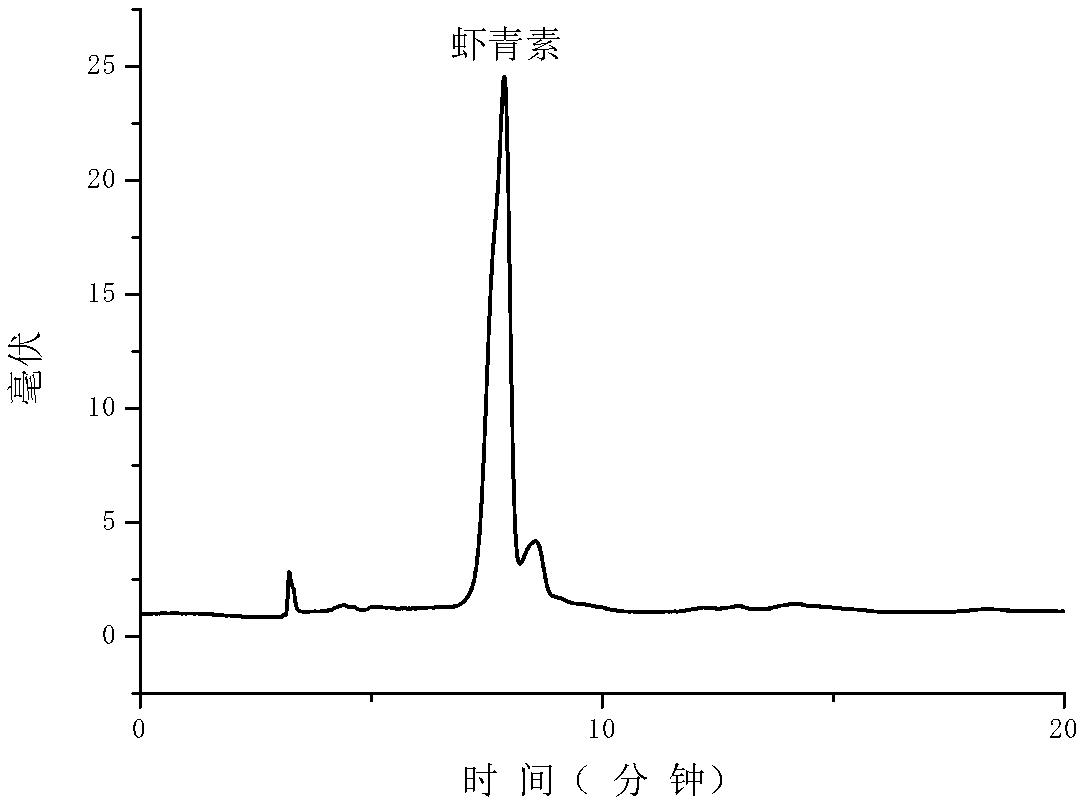
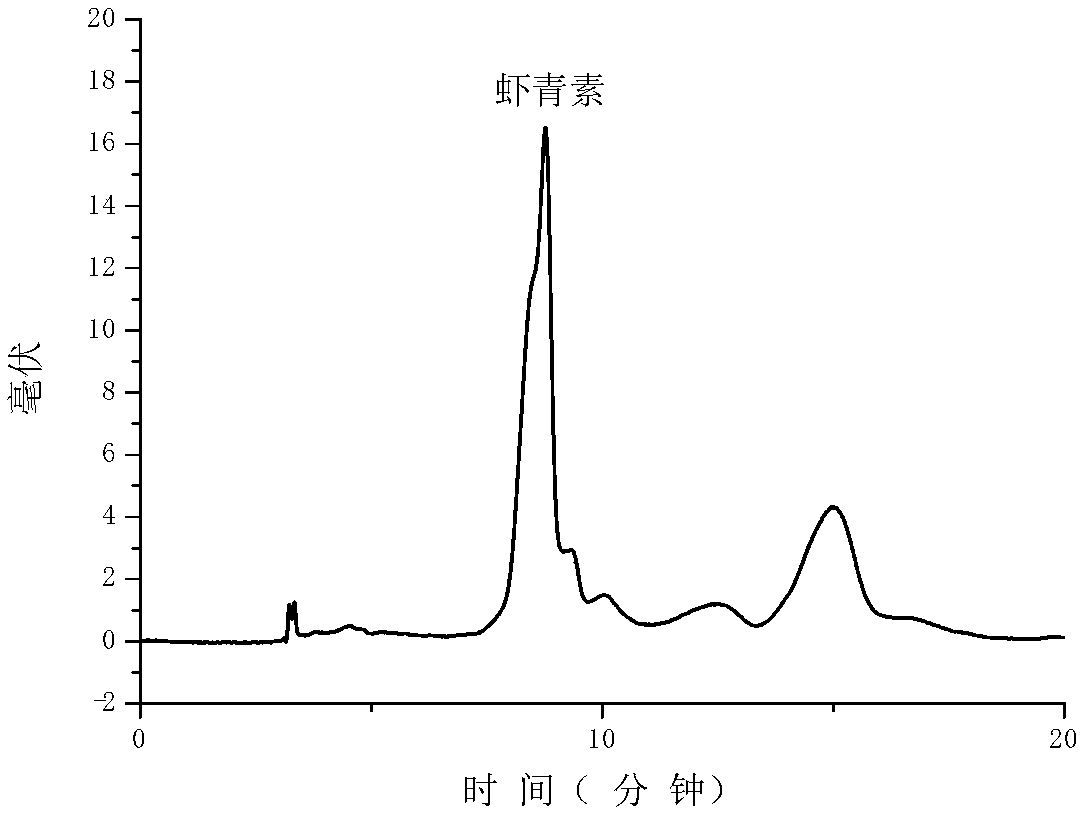
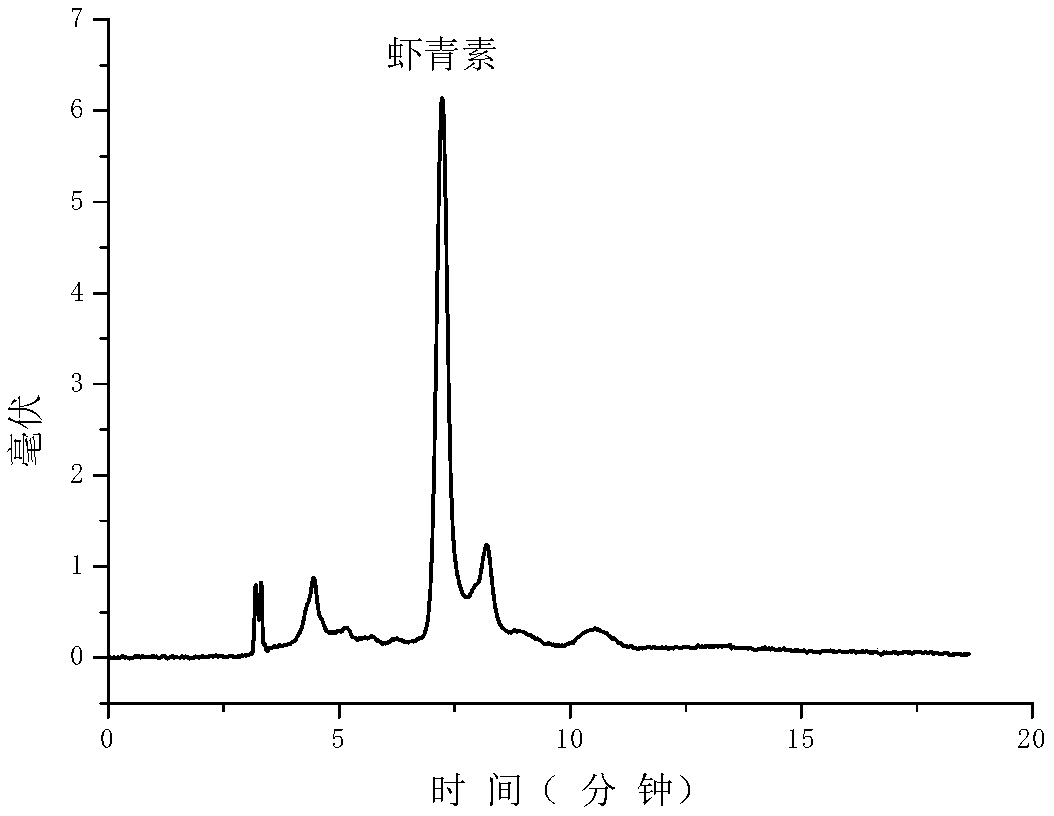
Method for utilizing neutral protease to extract and purify astaxanthin in shrimp shell and crab shell
A technology of neutral protease and astaxanthin, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problems of not obtaining high-purity astaxanthin, poor selectivity of hydrolysis, large amount of organic solvent, etc., and achieve less steps and stable astaxanthin , The effect of low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Astaxanthin is extracted from Argentinian red shrimp shells as follows:
[0043] Step 1: Dissolving biological enzymes
[0044] Dissolve 1g of neutral protease in 500mL of water.
[0045] Step 2: Carry out enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivation and pretreatment
[0046] Crush the shells of Argentinian red shrimps, take 100 g and mix them with the above-mentioned neutral protease solution, and then enzymatically hydrolyze them for 300 min at a pH of 7 and a temperature of 35° C. After the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivate at 70°C, then centrifuge, and mix the lower layer solid with 500mL organic solvent ethanol to obtain the pretreated enzymatic hydrolysis solution.
[0047] Step 3: Extraction and Concentration
[0048] The pretreated enzymolysis solution obtained in the previous step was extracted with magnetic stirring at a constant temperature of 40°C for 120 minutes, filtered, extracted 3 times, and the extracts were combined, and then the combined ex...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Using the head of Argentinian red shrimp as raw material, astaxanthin is extracted according to the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Dissolving biological enzymes
[0055] Get 10g neutral protease and dissolve in 2L water.
[0056]Step 2: Carry out enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivation and pretreatment
[0057] Crush the head of Argentinian red shrimp, take 200g and mix it with the above-mentioned neutral protease solution, and then enzymatically hydrolyze it at pH 5 and temperature 55°C for 30min. After the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivate at 70°C, then centrifuge, and mix the solid in the lower layer with 700 mL of organic solvent ethyl acetate to obtain the pretreated enzymatic hydrolysis solution.
[0058] Step 3: Extraction and Concentration
[0059] The pretreated enzymolysis solution obtained in the previous step was mechanically stirred at a constant temperature of 50°C and 25KHz ultrasonically extracted for 20 minutes, extracted 3 times, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Astaxanthin is extracted from Arctic sweet shrimp shells as follows:
[0065] Step 1: Dissolving biological enzymes
[0066] Dissolve 0.15g of neutral protease in 700mL of water.
[0067] Step 2: Carry out enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivation and pretreatment
[0068] Crush the fresh shrimp shell of arctic sweet shrimp, take 100g and mix it with the above-mentioned biological enzyme solution, and then enzymolyze it for 300min under the conditions of pH 5.5 and temperature 55°C. After the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, inactivate at 70°C, then centrifuge, and mix the lower layer solid with 900mL organic solvent acetone to obtain the pretreated enzymatic hydrolysis solution.
[0069] Step 3: Extraction and Concentration
[0070] The pretreated enzymolysis solution obtained in the previous step was subjected to ultrasonic extraction at a constant temperature of 60°C and 40KHz for 80 minutes, and extracted once, and then the extract was concentrated with a rotary ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com