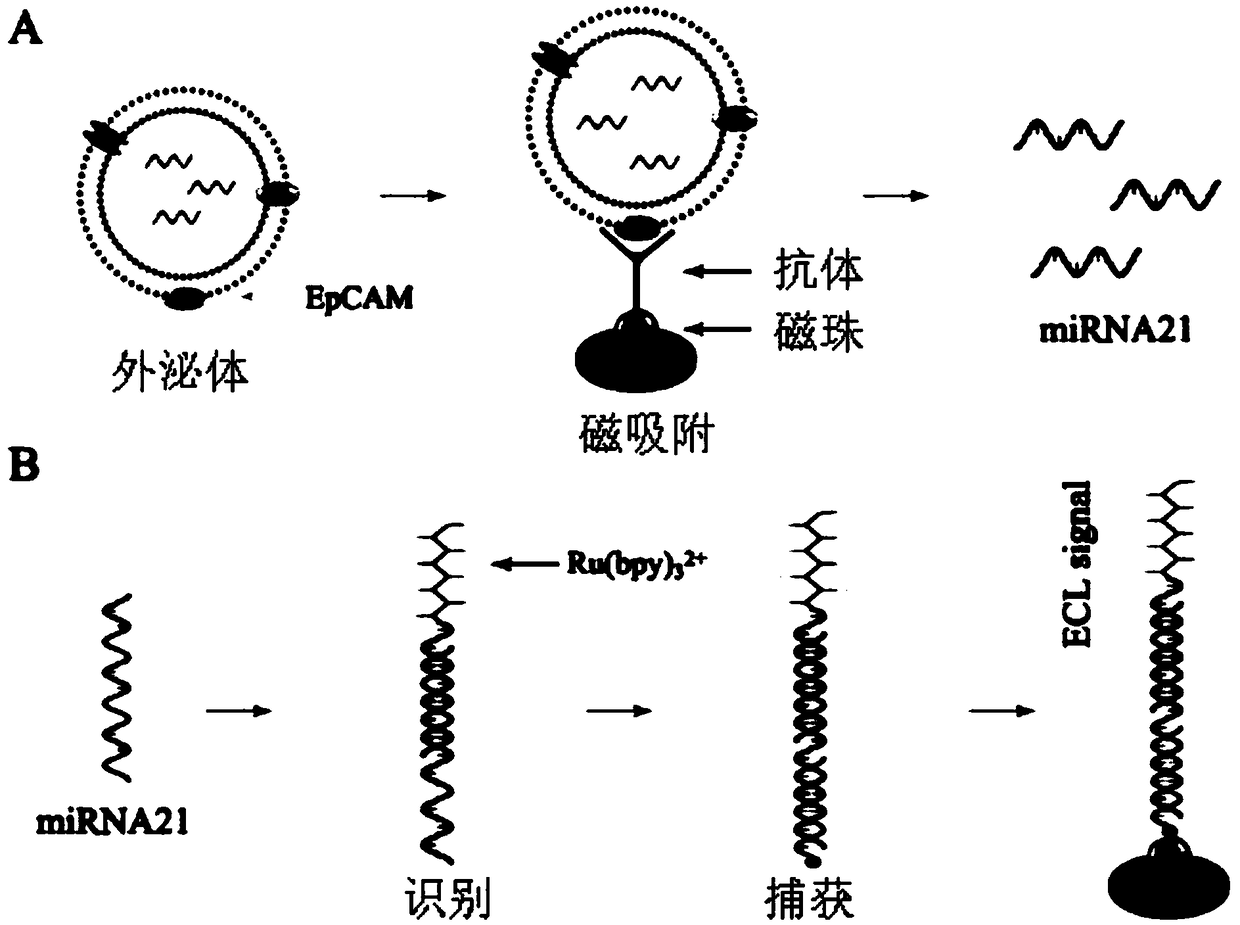
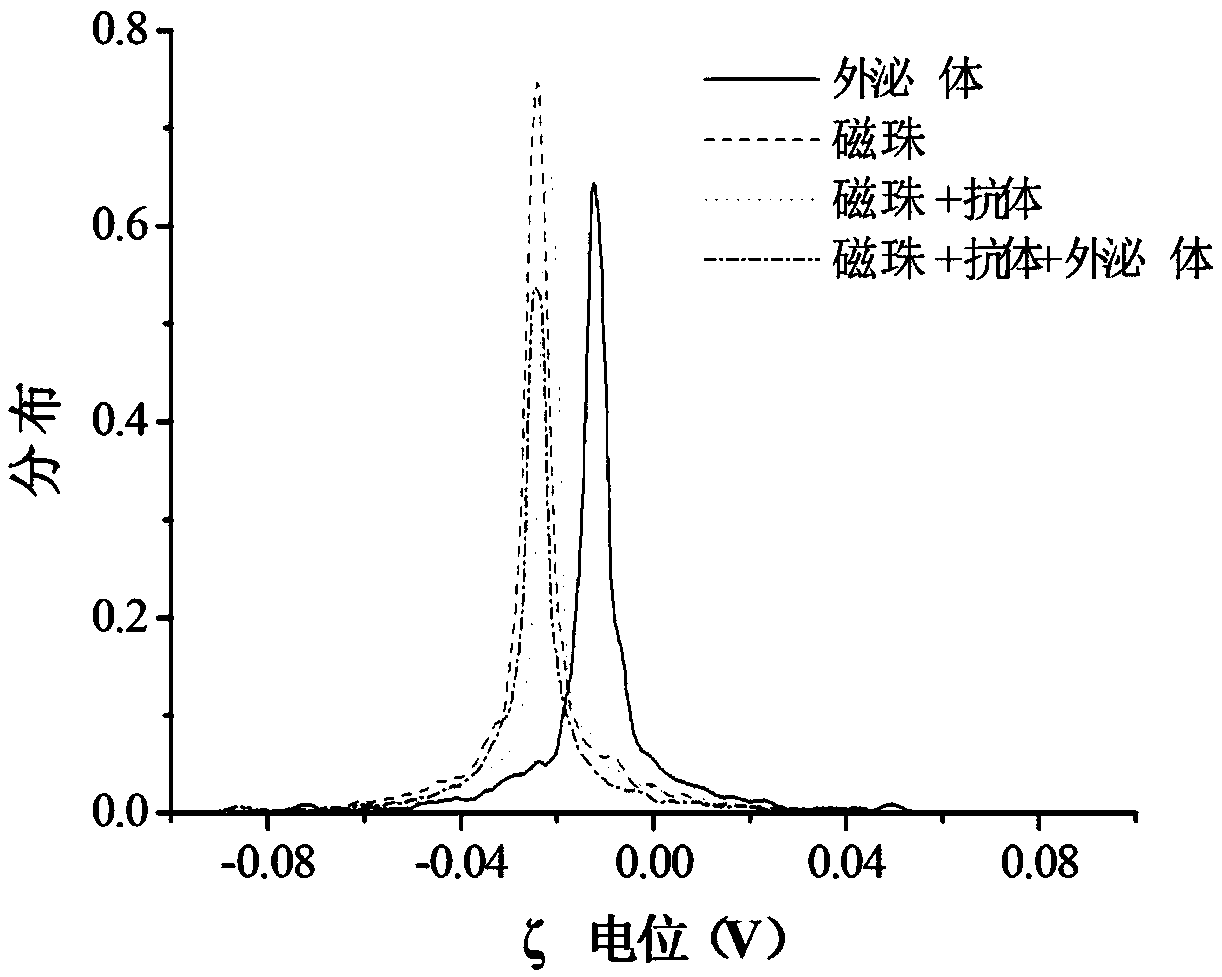
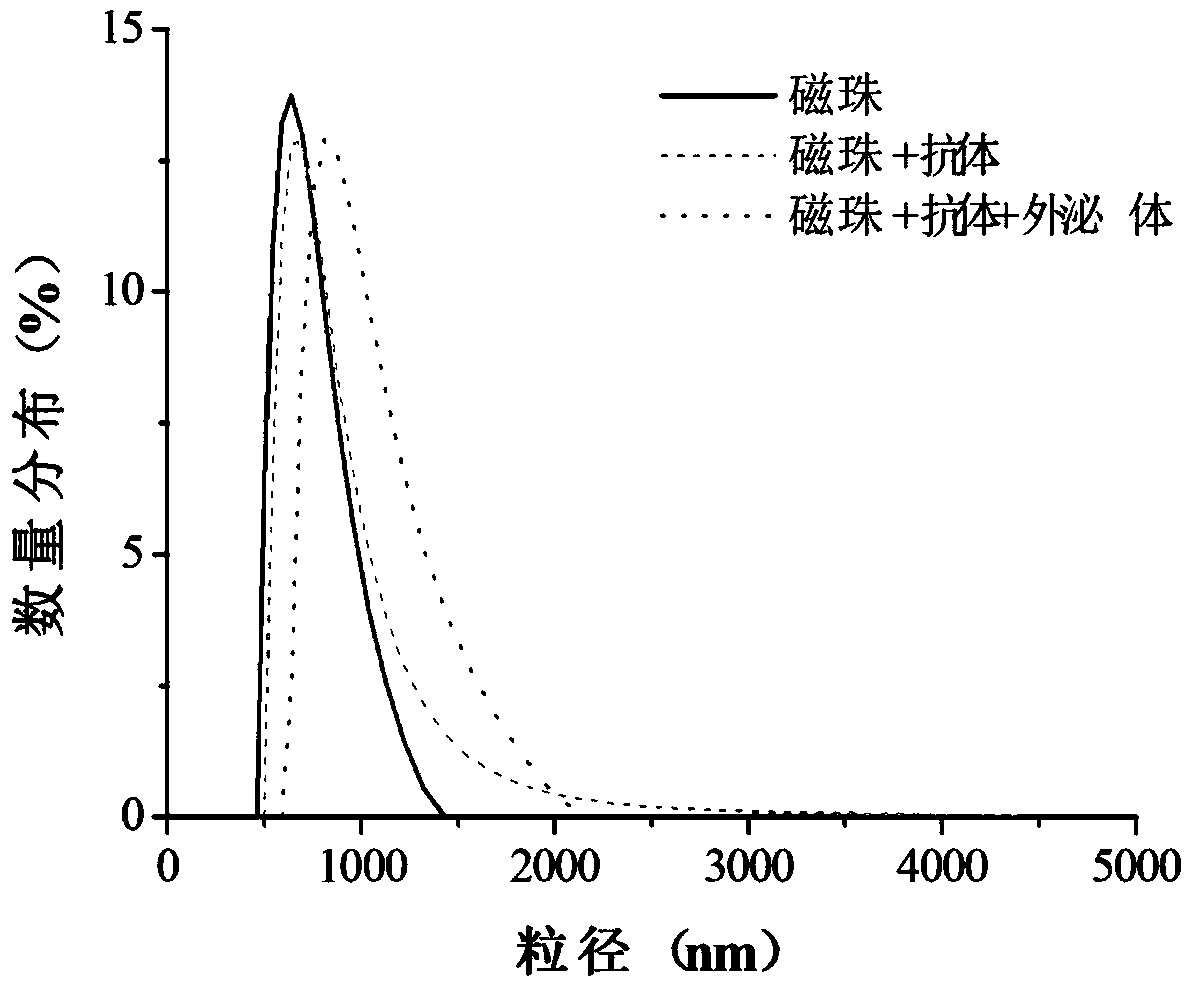
Exosome nucleic acid detection technology based on magnetism-enriched electrochemical luminescence
A detection technology, exosome technology, applied in the field of exosome separation and nucleic acid detection, can solve the problems of limited exosome content in biological fluids, difficulty in reaching the detection range of the target nucleic acid sequence concentration, detection interference, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0194] Example 1 Sample pretreatment and separation of exosome standard
[0195] (1) Sample collection
[0196] 1) Collection of animal or human cell culture fluid
[0197] The cell culture medium is DMEM, and the added volume fraction is 10% calf serum (FCS). Cells were trypsinized, transferred to a cell culture dish, and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO 2 The cells were cultured in a saturated water vapor carbon dioxide incubator for 24 hours to make the cells confluent to 50%-60%, and then replaced with serum-free DMEM culture medium for 24-48 hours. Recover the serum-free DMEM cell culture medium, store it at 4°C for a short period of time, and store it at -80°C for a long time.
[0198] 2) Animal or human blood sample collection
[0199] Draw blood from animal or human vein, add anticoagulant, centrifuge to remove cellular components in the blood, and obtain plasma; or take serum after blood coagulation, and the obtained blood sample can be stored at -80°C or used immediately...
Embodiment 2
[0208] Synthesis of Example 2 Immunomagnetic Beads
[0209] (1) Activation of streptavidin magnetic beads, the process is as follows:
[0210] 1) Electronic balance weighing: EDTA (0.292g) (CAS: 60-00-4), NaCl (29.22g) (CAS: 7647-14-5), TRIS (2.423g) (CAS: 77-86-1 ) in a 1L beaker.
[0211] 2) Add water to make the volume to 800ml, stir and mix evenly under a magnetic stirrer.
[0212] 3) Transfer the obtained solution to a 1L volumetric flask and dilute to 1L with water.
[0213] 4) Then adjust the pH value to 7.5 with 1mol / L HCl, and calibrate with precision pH test paper.
[0214] 5) The obtained solution was filtered with filter paper, and the obtained reaction solution I was divided into equipment for use.
[0215] 6) Mix the mother solution of streptavidin magnetic beads, take 500ug and put it in a 1.5ml EP tube, remove the protective reagent by magnetic separation, add 1ml PBS to the EP tube and mix well.
[0216] 7) Place the EP tube in the magnetic separation rac...
Embodiment 3
[0223] Example 3 The combination of immunomagnetic beads and exosomes (capture and enrichment of exosomes), the process is as follows:
[0224] 1) Mix the sample with the immunomagnetic beads obtained in Example 2. The mixing ratio of the sample and the immunomagnetic beads is: 1ml of serum: 50ug of immunomagnetic beads or 1L of urine: 30ug of immunomagnetic beads.
[0225] 2) Incubation: place on a shaker at room temperature for 10-30 minutes, and the time is appropriately adjusted according to the room temperature and the concentration of exosomes in the sample.
[0226] 3) Place the incubated sample on the magnetic separation rack and let it stand for 30 seconds to remove the liquid retaining magnetic beads.
[0227] 4) Wash the magnetic beads obtained in 3) 2-3 times with PBS to remove sample residues, and the process of pipetting should be gentle to avoid exosomes falling off.
[0228] 5) Magnetic separation to obtain purified magnetic bead-exosome complexes. The result...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com