Immune repertoire biological information analysis process based on molecular markers
A technology of immune repertoire and molecular markers, which is applied in the field of biological information analysis process of immune repertoire, can solve the problems that the biological information analysis of immune repertoire cannot be used well, and achieve the goal of wide application, promotion of development and improvement of accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
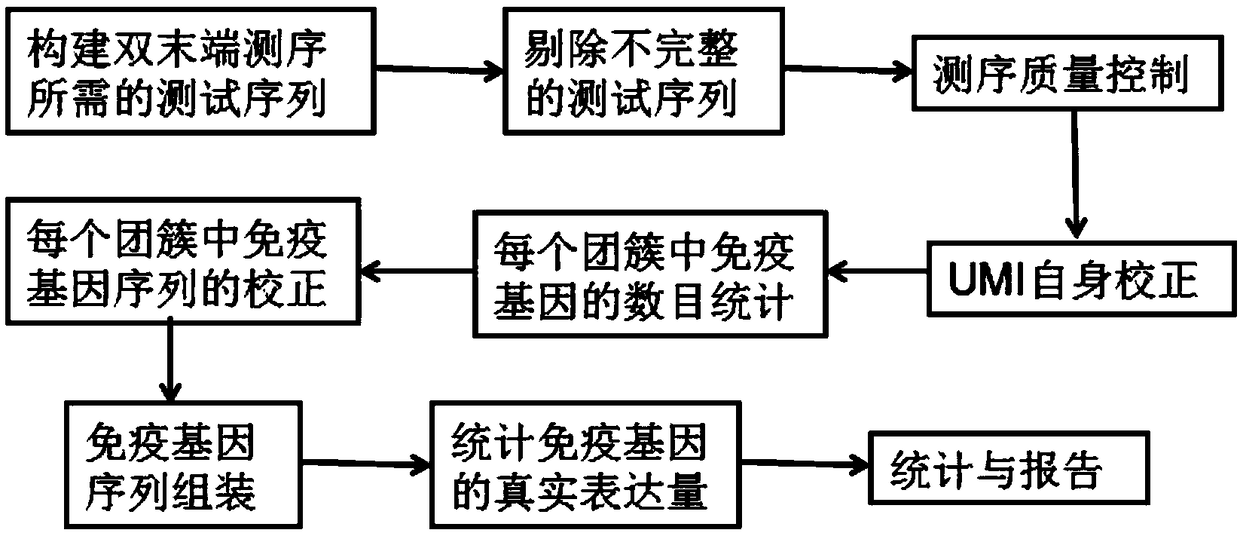
[0039] Construction and screening of test sequences before embodiment 1 UMI self-correction
[0040](1) Construct the test sequence required for paired-end sequencing: take the single-chain immunoglobulin M gene with the same structure and divide it into two equal parts, and add primers to the 3' end of each immunoglobulin M gene in one part And the UMI sequence with the structure UAAAGUCCAGUGCAAU, add primers and the UMI sequence with the structure UAAAGUCCAGUGCAAU to the 5' end of each immunoglobulin M gene in the other copy, one of which has a single-chain immunoglobulin with primers and UMI at the 3' end The M gene and a single-chain immunoglobulin M gene with a primer and UMI at the 5' end are called a pair of test sequences; take the single-chain immunoglobulin A gene with the same structure and divide it into two equal parts, and in one part Add primers and a UMI sequence with the structure UGGCAUAAGCUAGCAU to the 3' end of each Immunoglobulin A gene, and add primers an...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2 UMI self-correction and immune gene number statistics
[0048] (4) Use the following steps to perform UMI self-correction on the test sequence obtained in step (3):
[0049] ① Tree building: use different UMIs as different nodes, connect UMI nodes with a Hamming distance of 1, and build multiple directed acyclic trees;
[0050] ② Assignment: assign values to the nodes of the directed acyclic tree built in step ①, and the assigned value is the number of types of immune gene sequences marked by the UMI;
[0051] ③ Tree cutting: When the value assigned to node A (any node) is greater than the value assigned to the connected node B (any node) × 2+1, cut off the edge between node A and node B; otherwise, keep An edge between node A and node B;
[0052] ④Cluster formation: Perform the operation described in step ③ on each node on the tree built in step ①, and finally divide the tree built in step ① into multiple new trees, each new tree is a cluster, and the clu...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Correction and assembly of immune gene sequences within the cluster
[0055] (6) Correction of immune gene sequences in each cluster: the immune gene sequences in the same cluster are compared with each other using the multi-sequence comparison software muscle. If the proportion of consistent bases at a certain position is greater than 0.6, then the site is the consensus base, otherwise it is replaced by N, and the sequence of the immune gene in each cluster is obtained;
[0056] (7) Immune gene sequence assembly: Assemble the immune genes on each cluster. For full-length sequencing, splice according to the overlapping regions of the ends. For non-full-length sequences, use the method of comparing the reference sequences in the imgt database for splicing , when there is a deletion in the gene sequence, fill in the missing part according to the reference sequence in the imgt database.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com