Split-pupil differential confocal discrete fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence lifetime detection method and device
A differential confocal and fluorescence lifetime technology, which is applied in spectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromator, measuring device, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problem that the spot size of the excitation beam cannot be guaranteed and the resolution of the detection system cannot be guaranteed. Problems such as inability to maintain consistency, failure to obtain fluorescence distribution imaging on the sample surface, etc., to achieve high identification speed and identification accuracy, convenient detection process, and helpful for precise positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
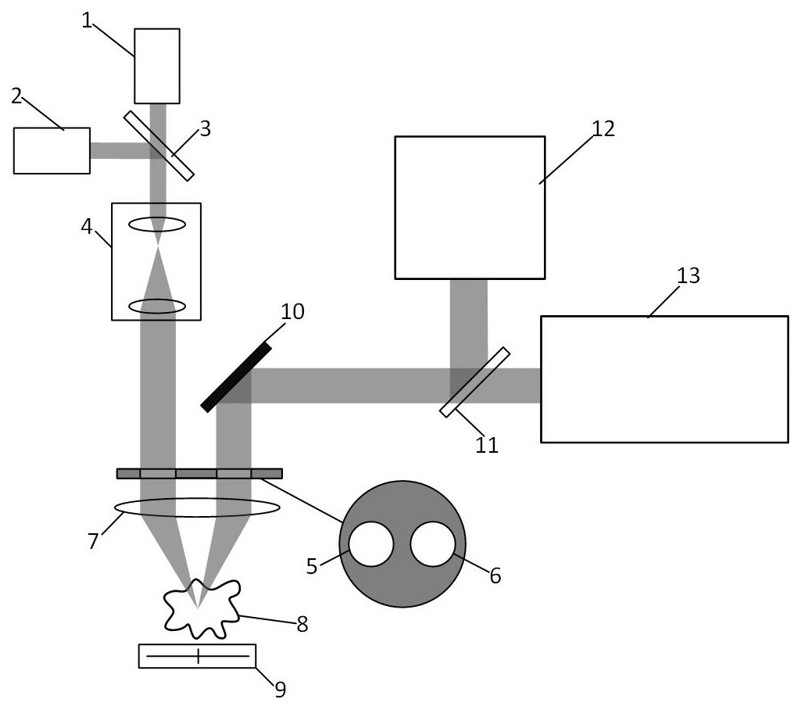
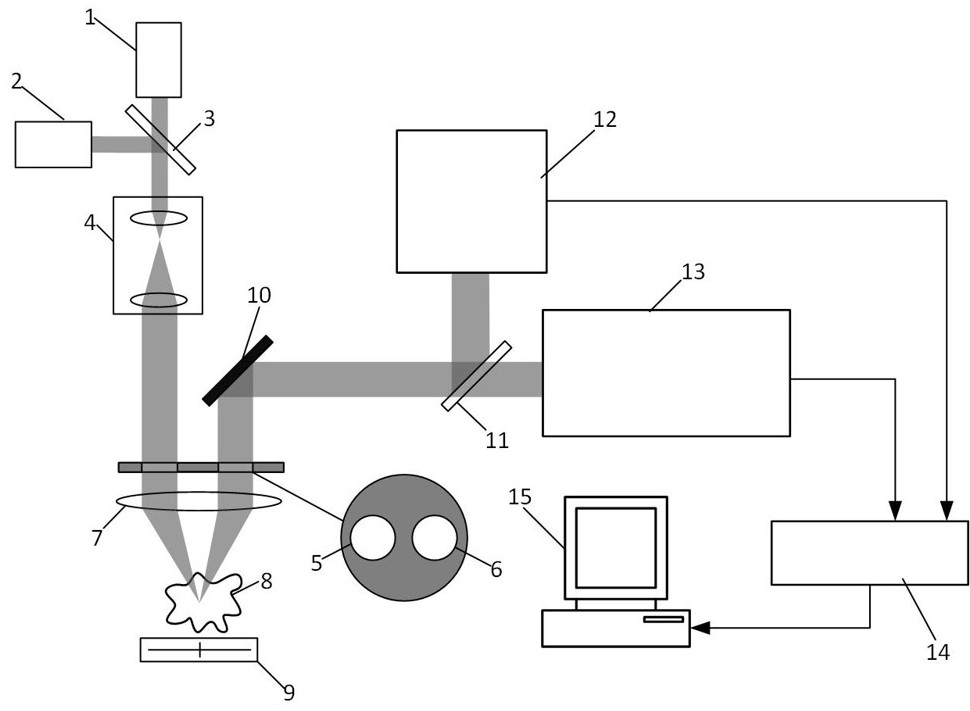
[0042] The problem to be solved in this embodiment is to simultaneously scan the three-dimensional shape of the sample to be tested and analyze the spatial distribution of the tumor tissue in the sample to be tested, and judge the boundary information of the tumor tissue accordingly. In this embodiment, a split-pupil differential confocal detection system is used to measure three-dimensional topography, using the fluorescence lifetimes of four wavelengths of 400 nm, 450 nm, 530 nm and 580 nm excited from the sample by a pulsed laser with a wavelength of 355 nm To judge whether each scanning point is a tumor cell. Since the fluorescence signal of the sample is very weak, this embodiment uses a photomultiplier tube as a light intensity sensor for fluorescence detection to improve the fluorescence light intensity detection sensitivity of the system. Figure 9 It is a specific implementation device for realizing split-pupil differential confocal discrete fluorescence spectroscopy ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Different from Example 1, this example uses discrete fluorescence spectroscopy to determine whether each point on the surface of the sample 8 to be tested is a tumor tissue or a normal tissue. Apparatus used and sample are identical with embodiment 1. In order to improve the stability of fluorescence spectrum measurement, in this embodiment, the light beam emitted by the continuous laser light source 2 is used to excite the sample 8 to generate fluorescence, and the measurement steps are as follows.
[0054] (a) Turn on the continuous laser light source 2, along x with y Move the sample 8 to be tested in the direction to the starting position of the transverse scanning ( x 1 , y 1 ), then at that position along the z Scan the sample 8 to be tested in the direction. Using the split-pupil differential confocal detection system 12, it is measured that the attached Figure 10 The differential confocal response curve FES shown ( z ), and then according to the diffe...
Embodiment 3
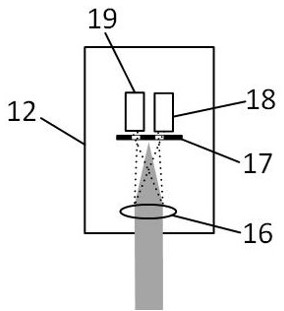
[0060] Different from Example 1, as attached Figure 5 As shown, in order to improve the resolution of the detection beam, a converging lens and a pinhole are respectively added in front of all light intensity sensors. The pinhole is placed at the focus position of the converging lens, and the converging lens converges the fluorescent light beams of different wavelengths to perform spatial filtering through the pinhole. Therefore, the fluorescent signals detected by each light intensity sensor are the filtered fluorescent light intensity information, and these filtered fluorescent lights accurately correspond to the fluorescent signals excited by the focal point of the detection beam, and the fluorescent signals outside the focal point are effectively analyzed. shield.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com