Method for removing EDTA-Pb by using iron salt-desulfurization gypsum system
A technology for desulfurization of gypsum and iron salts, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of limited removal rate of metal chelate compounds, etc., and is beneficial to subsequent engineering applications , The effect of good application prospect and wide source of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
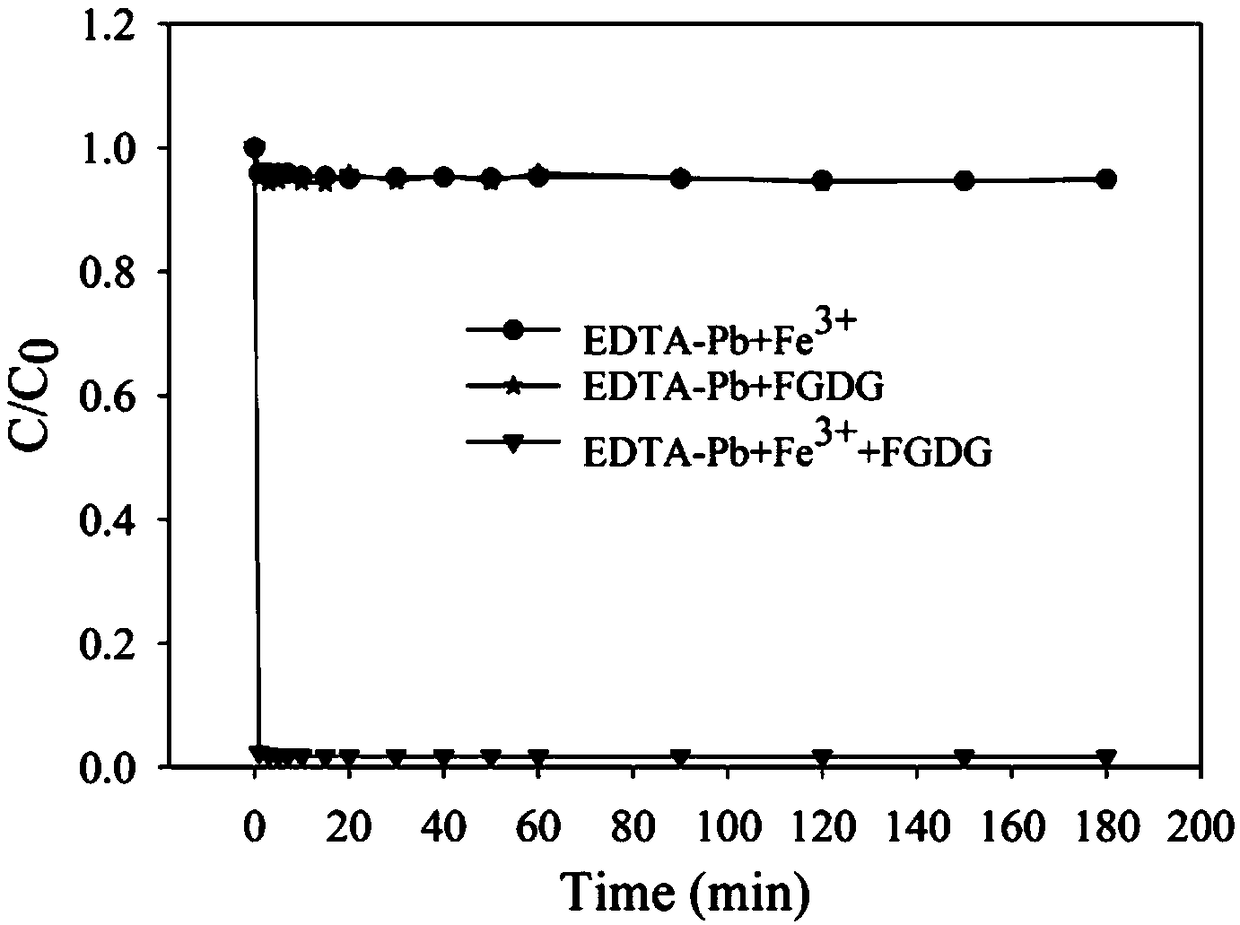
[0024] Example 1: The difference between the iron salt-desulfurization gypsum system and the use of iron salt and desulfurization gypsum respectively
[0025] In this application test, the iron salt is ferric chloride hexahydrate, which is configured as a 100mM ferric chloride solution for use. EDTA-Pb is mixed with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and lead nitrate at a molar ratio of 1:1. Prepare 10 mM EDTA-Pb. In the experiment, 3mM EDTA-Pb was selected as the target pollutant, 15mL of lead stock solution was added to a 100mL Erlenmeyer flask, diluted to 48.5mL, and 1.5mL of ferric chloride solution was added at an iron-lead molar ratio of 1:1, followed by Add 1g / L desulfurization gypsum, seal the Erlenmeyer flask, stay in the reactor for 3h, the temperature is 25±1°C, and the rotation speed is 250r / min. The reaction of the other two groups is similar to this, for the addition of ferric chloride solution and desulfurization gypsum alone, the dosage remains the same as before...
Embodiment 2
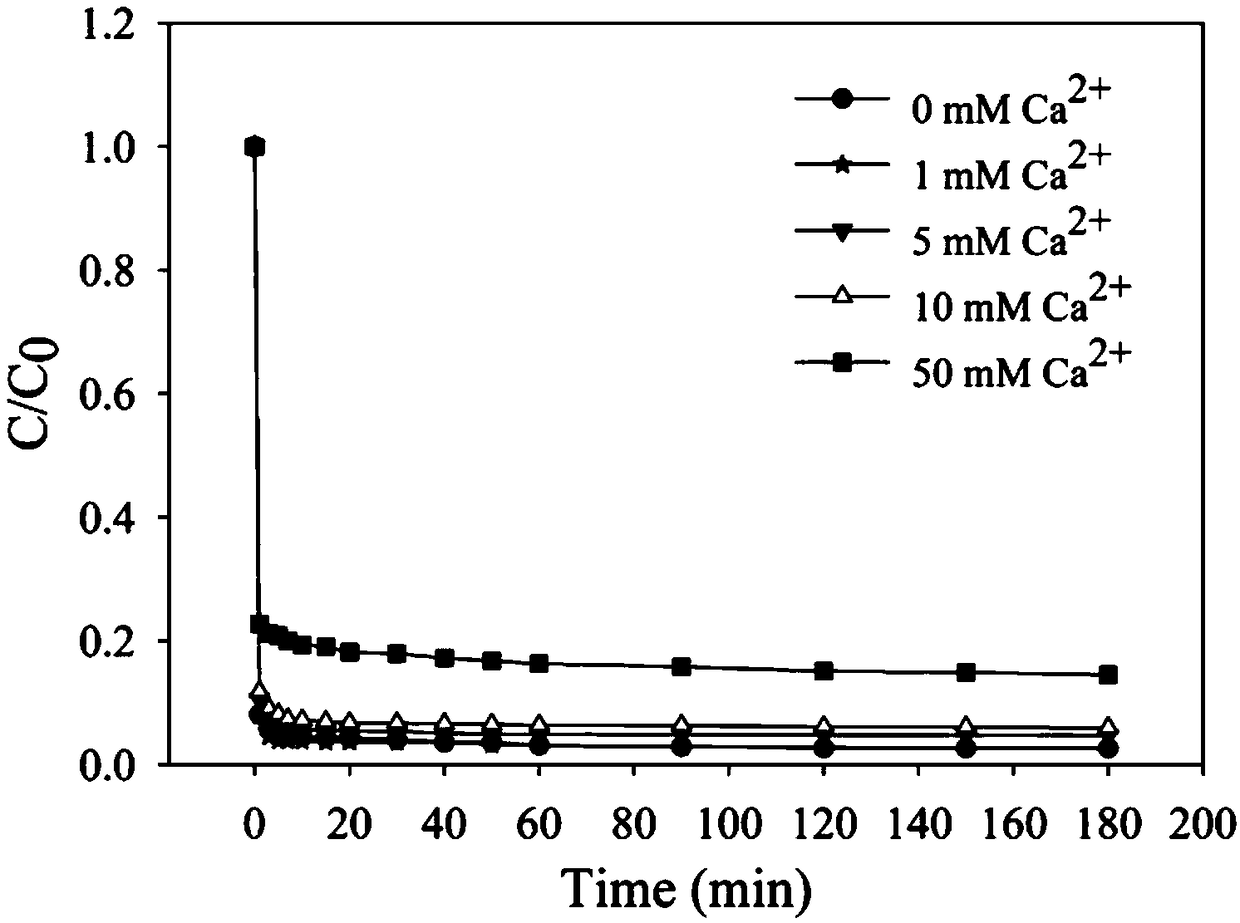
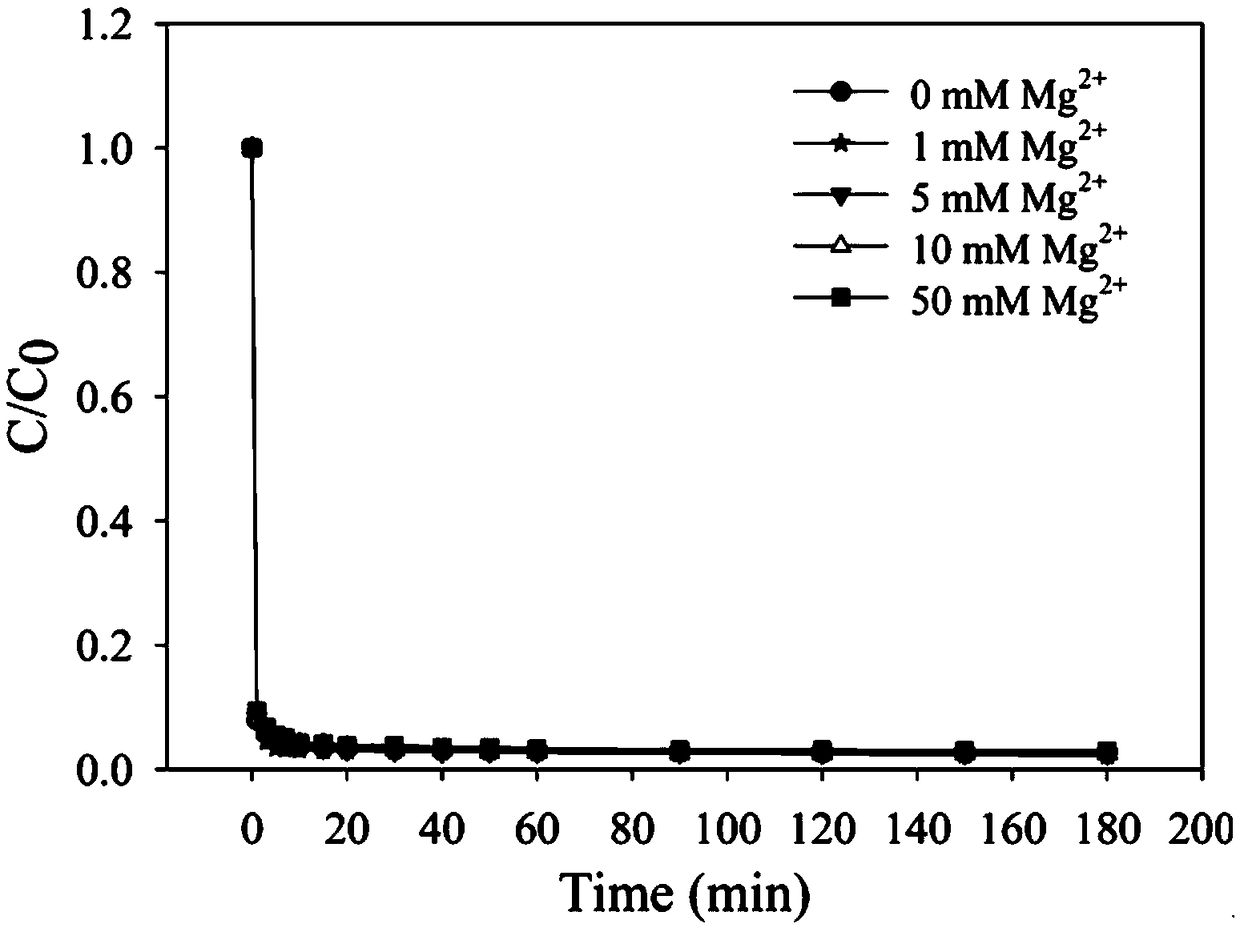
[0026] Example 2: The effect of coexisting ions on the removal of EDTA-Pb by the iron salt-desulfurized gypsum system.
[0027] Calcium, magnesium, and sodium ions are common ions in water, and it is necessary to study their influence on the system. In the experiment, 3mM EDTA-Pb was selected as the target pollutant, and 15mL of lead stock solution was added to a 100mL conical flask, and then added Dilute metal ions of different concentrations to 48.5mL, add ferric chloride solution 1.5mL with iron-lead molar ratio 1:1, then add desulfurization gypsum at 1g / L, seal the conical flask, and stay in the reactor The time is 3h, the temperature is 25±1°C, and the rotation speed is 250r / min. A total of 3 groups of experiments, each group of calcium, magnesium, and sodium, each group of experiments with 5 concentration gradients (concentrations were 0, 1, 5, 10, 50mM Ca 2+ / Mg 2+ / Na + ). figure 2 is the removal effect diagram of EDTA-Pb by the iron salt-desulphurization gypsum s...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Example 3: Effect of pH on the removal effect of EDTA-Pb by the iron salt-desulfurized gypsum system.
[0029] pH refers to the ratio of the total number of hydrogen ions to the total amount of substances in a solution, and is an important parameter that reflects the acidity and alkalinity of a solution, and is also an important parameter that affects the removal process. In the experiment, 3mM EDTA-Pb was selected as the target pollutant, 15mL of lead stock solution was added to five 100mL conical flasks, and then diluted to 48.5mL, the pH of the five samples was adjusted to 2-6, and finally the iron-lead molar ratio Add ferric chloride solution 1.5mL at 1:1, then add desulfurization gypsum at 1g / L, seal the Erlenmeyer flask, stay in the reactor for 3h, temperature is 25±1°C, and rotation speed is 250r / min. Figure 5 It is the removal effect diagram of EDTA-Pb by iron salt-desulphurization gypsum system under different pH conditions, which can be obtained from Figure...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com