Method for removing bismuth from copper electrolyte
A copper electrolyte and solution technology, applied in the field of removing bismuth from copper electrolyte, can solve problems such as substandard quality of electric copper, and achieve the effect of high-efficiency impurity removal capability and good bismuth removal effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
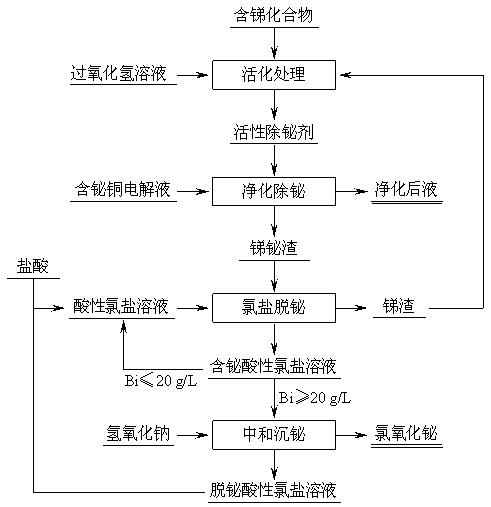
[0015] Mix antimony pentoxide with hydrogen peroxide solution, the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 6 times of the molar amount of antimony. Under the condition of stirring, react at 80°C for 50 minutes to obtain active bismuth removing agent slurry. Take 4 L of copper electrolyte with a bismuth concentration of 0.92 g / L, heat it to 100 °C with stirring, and add an active bismuth removal agent. The molar amount of antimony in the active bismuth removal agent is 7 times that of bismuth in the copper electrolyte, maintaining The reaction was stirred at 100°C for 2 hours. The antimony-bismuth slag and purified liquid were obtained by filtration, and the bismuth content of the purified liquid was reduced to 0.15 g / L. Stir the antimony-bismuth slag with 200 mL of acidic chloride salt solution to carry out the operation of removing bismuth by chloride salt. The pH value of the acidic chloride salt solution is 0.5, the concentration of sodium chloride is 150 g / L, and the reaction temp...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Mix antimony acid with hydrogen peroxide solution, and the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 5 times the molar amount of antimony. Under the condition of stirring, react at 95°C for 10 minutes to obtain active bismuth removing agent slurry. Take 4 L of copper electrolyte with a bismuth concentration of 0.83 g / L, heat it to 85 °C with stirring, and add an active bismuth removal agent. The molar amount of antimony in the active bismuth removal agent is 10 times the molar amount of bismuth in the copper electrolyte. The reaction was stirred at 85°C for 0.5 hours. The antimony-bismuth slag and purified liquid were obtained by filtration, and the bismuth content of the purified liquid was reduced to 0.09g / L. The antimony-bismuth slag was stirred and mixed with 200 mL of acid chloride salt solution to carry out the operation of removing bismuth from chloride salt. The pH value of the acid chloride salt solution was 1.0, the concentration of sodium chloride was 218 g / L, and the ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] The hydrogen peroxide solution is added to the mixture of sodium antimonate and potassium pyroantimonate, and the amount of hydrogen peroxide is 3 times of the molar amount of antimony. Under the condition of stirring, react at 50°C for 30 minutes to obtain active bismuth removing agent slurry. Take 4 L of copper electrolyte with a bismuth concentration of 1.17 g / L, heat it to 60 °C with stirring, and add an active bismuth removal agent. The molar amount of antimony in the active bismuth removal agent is 5 times that of bismuth in the copper electrolyte. The reaction was stirred at 60°C for 2 hours. Antimony-bismuth slag and purified liquid were obtained by filtration, and the bismuth content of the purified liquid was reduced to 0.26 g / L. The antimony-bismuth slag was stirred and mixed with 200 mL of acidic chloride salt solution to carry out the operation of removing bismuth by chloride salt. The pH value of the acid chloride salt solution was 0.5, the concentration ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com