High-heat-conductivity long-life blast furnace hearth and brick lining building method
A long-life blast furnace technology, applied in blast furnace, blast furnace details, blast furnace parts and other directions, can solve problems such as hindering heat transfer, shortening hearth life, exceeding safe service temperature, etc., achieving huge economic and social benefits, construction and Equipment cost savings and overall longevity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
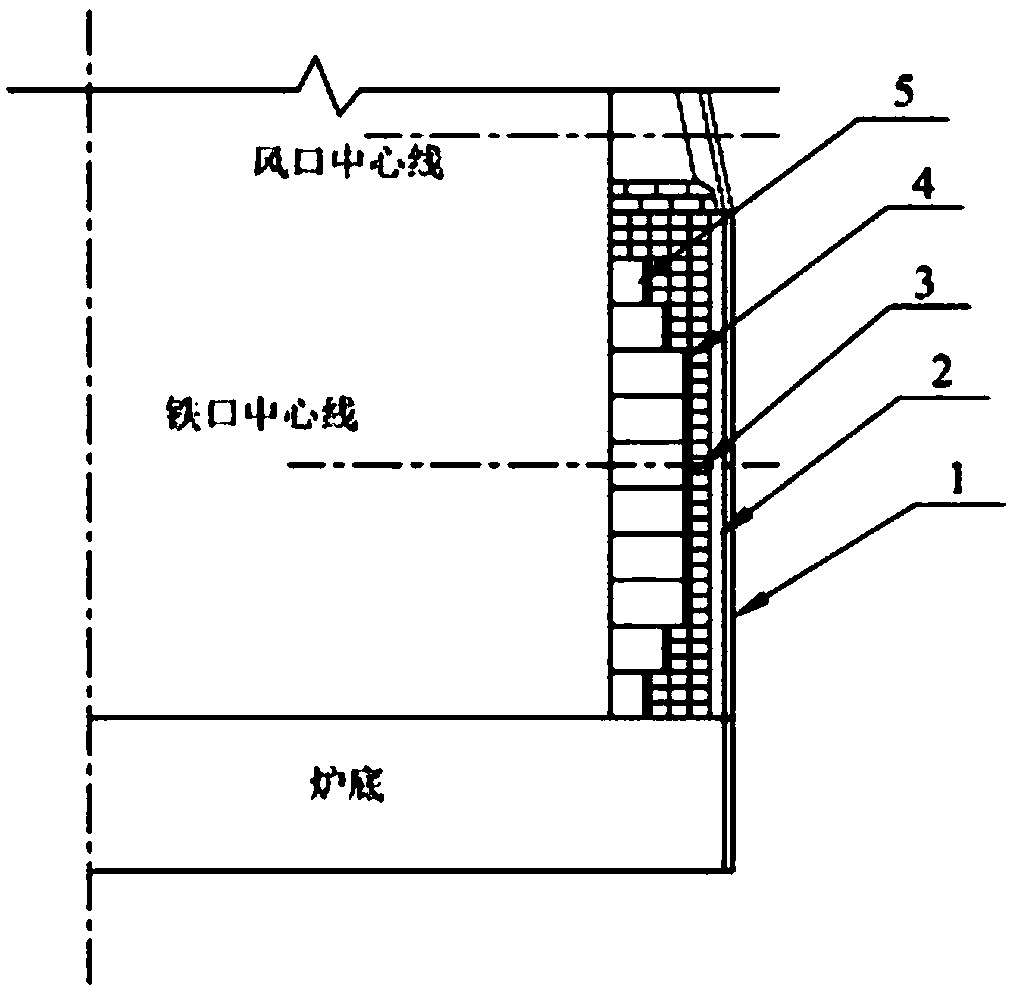
[0050] see image 3 , a blast furnace hearth with high thermal conductivity and long life, suitable for blast furnaces with deep dead iron layer design, which includes furnace shell 1, cooling stave 2 and brick lining arranged sequentially from outside to inside;
[0051] In the lower part of the hearth, the middle and lower part of the hearth, the middle part of the hearth, the upper part of the hearth, and the upper part of the hearth, the brick lining includes a small carbon brick 3, a carbon ramming material layer 4, and a large carbon brick 5 arranged in sequence;
[0052] On the top of the hearth, the brick lining is built by several small pieces of charcoal bricks 3;
[0053] Among them, the size of all small carbon bricks 3 is: length 300mm, width 150mm, height 150mm; in the lower part of the hearth, small pieces of carbon bricks 3 are built 3 times along the circumference of the hearth, and a total of 3 layers are built. The thickness of 4 is 50mm, and the large bloc...
Embodiment 2
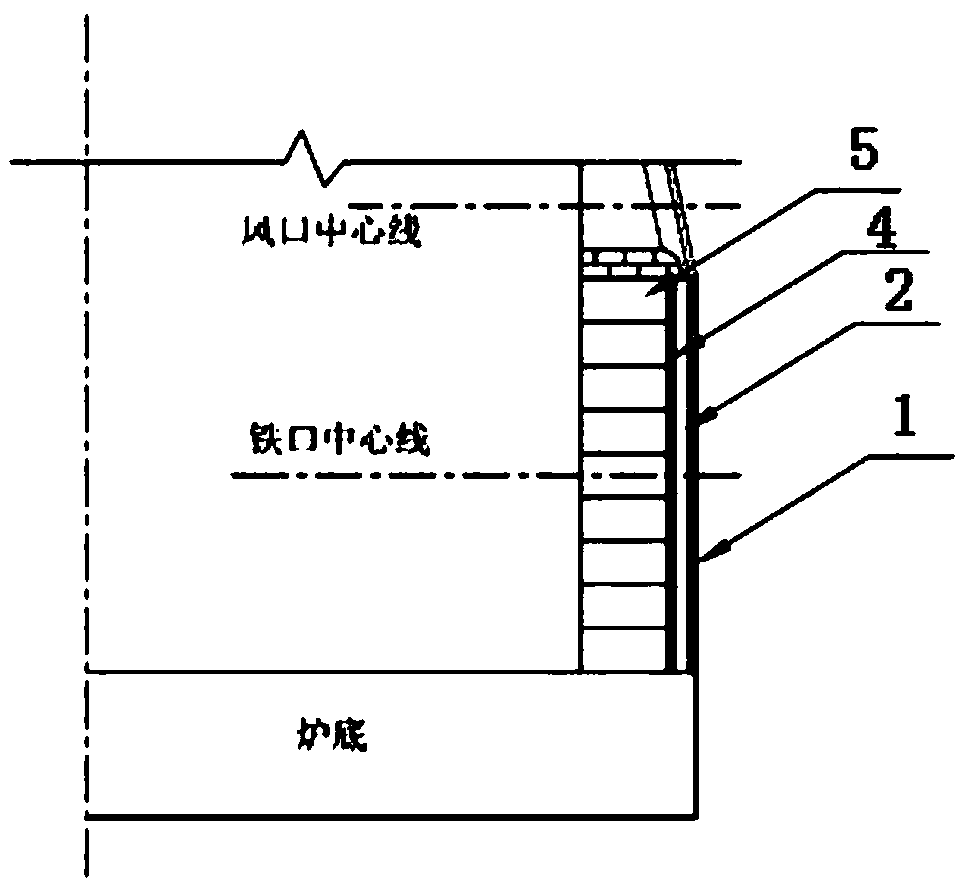
[0063] see Figure 4 , a blast furnace hearth with high thermal conductivity and long life, suitable for blast furnaces with shallow dead iron layer design, which includes furnace shell 1, cooling stave 2 and brick lining arranged sequentially from outside to inside;
[0064] The brick lining at the lower part of the hearth, the middle and lower part of the hearth, the middle part of the hearth, the middle and upper part of the hearth, and the upper part of the hearth includes a small carbon brick 3, a carbon ramming material layer 4, and a large carbon brick 5 arranged in sequence;
[0065] On the top of the hearth, the brick lining is built by several small pieces of charcoal bricks 3;
[0066] Among them, the size of all small carbon bricks 3 is: length 300mm, width 150mm, height 150mm; in the lower part of the hearth, the middle and lower part of the hearth, the middle part of the hearth and the upper part of the hearth, the small pieces of carbon brick 3 are built along the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com