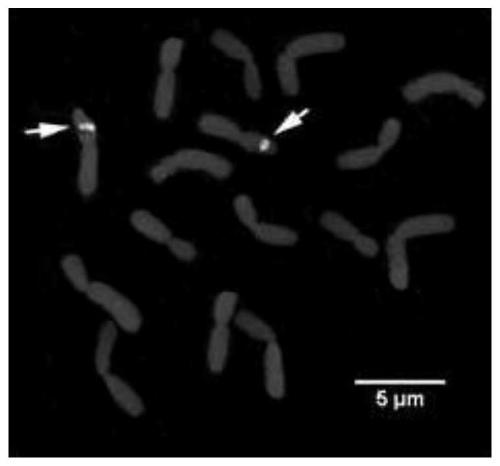
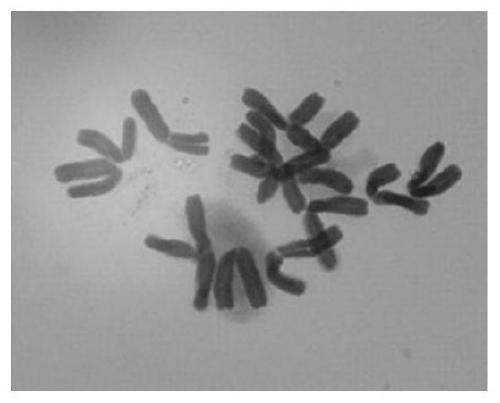
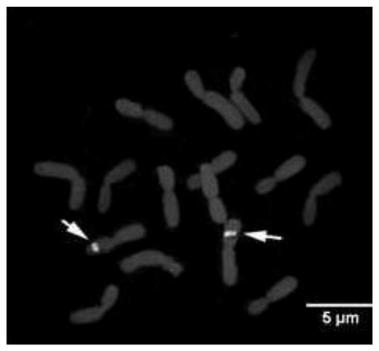
A method for fluorescent in situ hybridization of Mongolian leek chromosome
A fluorescence in situ hybridization and chromosome technology, applied in the field of cytogenetics and molecular biology, to achieve the effect of strong hybridization specificity, time saving and high hybridization specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] This embodiment provides a method for fluorescence in situ hybridization of chromosomes of Allium mongolica, which includes the following steps:
[0046] S1. Preparation of chromosome slide specimens of Allium mongolicum:
[0047] (1) Obtaining materials: Take Mongolian leek seeds and place them in a petri dish with 2 layers of wet filter paper, add water and place them in a thermostat at 22-25°C for 4-5 days. The root tips of the seeds will grow to 0.6cm. The required range of the seed root tip is 0.5-1cm, and then cut the root tip 1-2mm.
[0048] (2) Tablet preparation: Put the cut root tips into a vial, add appropriate amount of water, cover, and quickly place it in a mixture of ice and water at 0°C, and pretreat it in a refrigerator at 0°C for 20-24 hours.
[0049] (3) Fixation: Rinse the pretreated root tips and fix them with freshly prepared Carnot's fixative (glacial acetic acid: alcohol=1:3) at room temperature (25°C) for 12-24 hours.
[0050] (4) Dissociation: Take the ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] This embodiment provides a method for fluorescence in situ hybridization of chromosomes of Allium mongolica, which includes the following steps:
[0069] S1. Preparation of chromosome slide specimens of Allium mongolicum:
[0070] (1) Material: Take Mongolian leek seeds and rinse them with distilled water for 1-3 times, then soak them in the seed soaking solution for 0.5 hours, and then place them in a petri dish with 2 layers of wet filter paper, add water and place in a thermostat at 22- Cultivate for 18 hours at 25°C, the root tip of the seed grows to 0.8cm, which meets the requirements of the seed root tip in the range of 0.5-1cm, and then cut the root tip 1-2mm; the soaking liquid contains 80mg / L brown sugar, 150mg / L mannitol and A mixed aqueous solution of 25mg / L acetone.
[0071] (2) Tablet preparation: Put the cut root tips into a vial, add appropriate amount of water, cover, and quickly place it in a mixture of ice and water at 0°C, and pretreat it in a refrigerator ...
Embodiment 3
[0091] This embodiment provides a method for fluorescence in situ hybridization of chromosomes of Allium mongolica, which includes the following steps:
[0092] S1. Preparation of chromosome slide specimens of Allium mongolicum:
[0093] (1) Material: Take Mongolian leek seeds and rinse them with distilled water for 1-3 times, then soak them in the seed soaking solution for 0.5 hours, then place them in a petri dish with 2 layers of wet filter paper, add water, and place them in a thermostat at 22- Cultivate for 21 hours at 25°C, the root tip of the seed grows to 0.6cm, which meets the requirements of the seed root tip of 0.5-1cm, and then cut the root tip 1-2mm; the seed soaking solution contains 90mg / L brown sugar, 120mg / L mannitol and A mixed aqueous solution of 40mg / L acetone.
[0094] (2) Tablet preparation: Put the cut root tips into a vial, add appropriate amount of water, cover, and quickly place it in a mixture of ice and water at 0°C, and pretreat it in a refrigerator at 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com