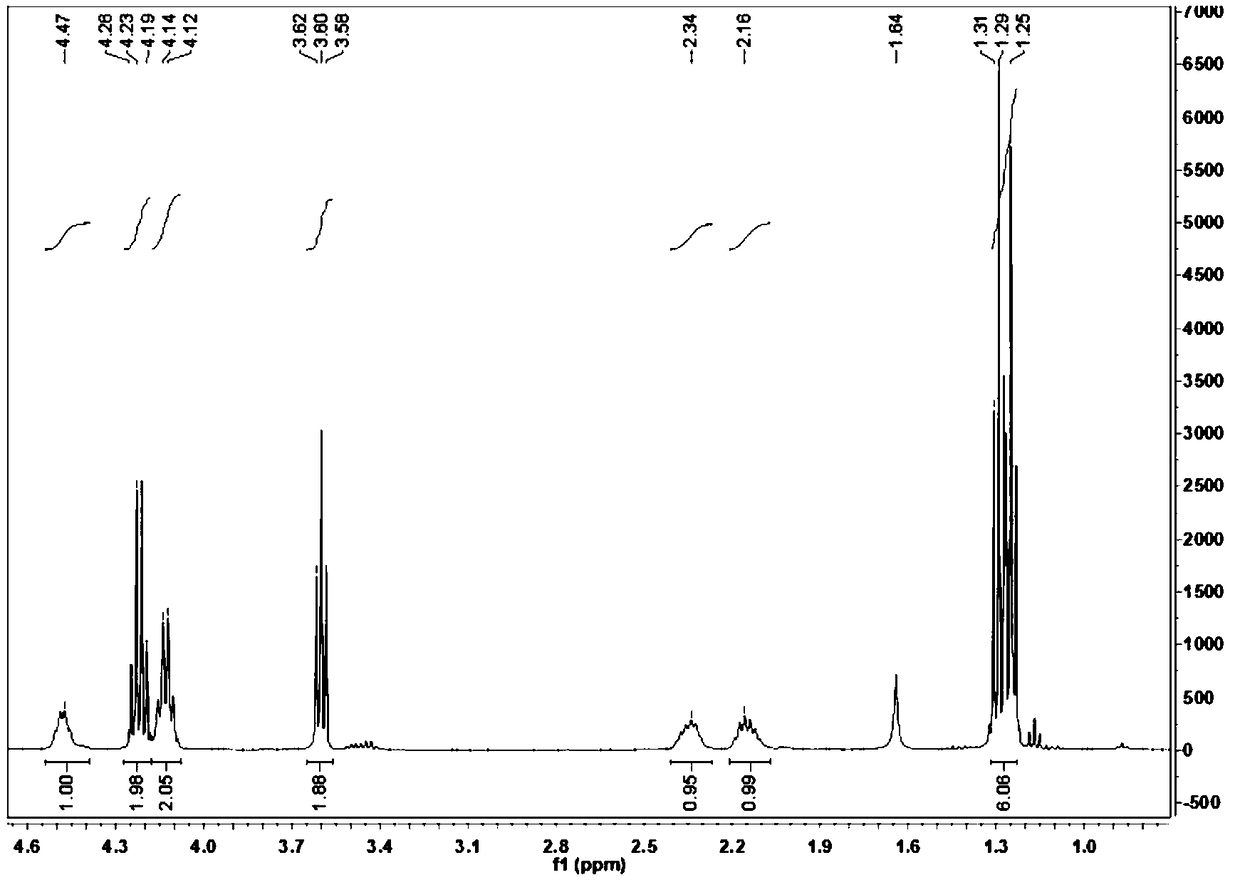
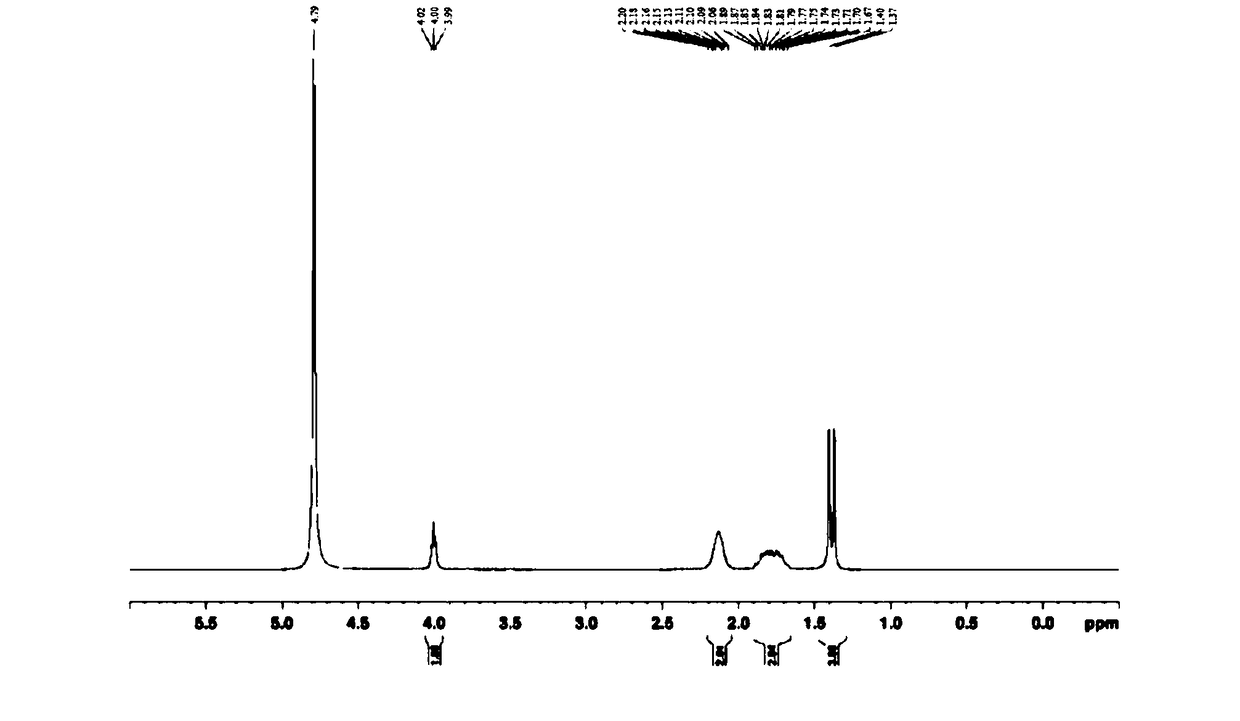
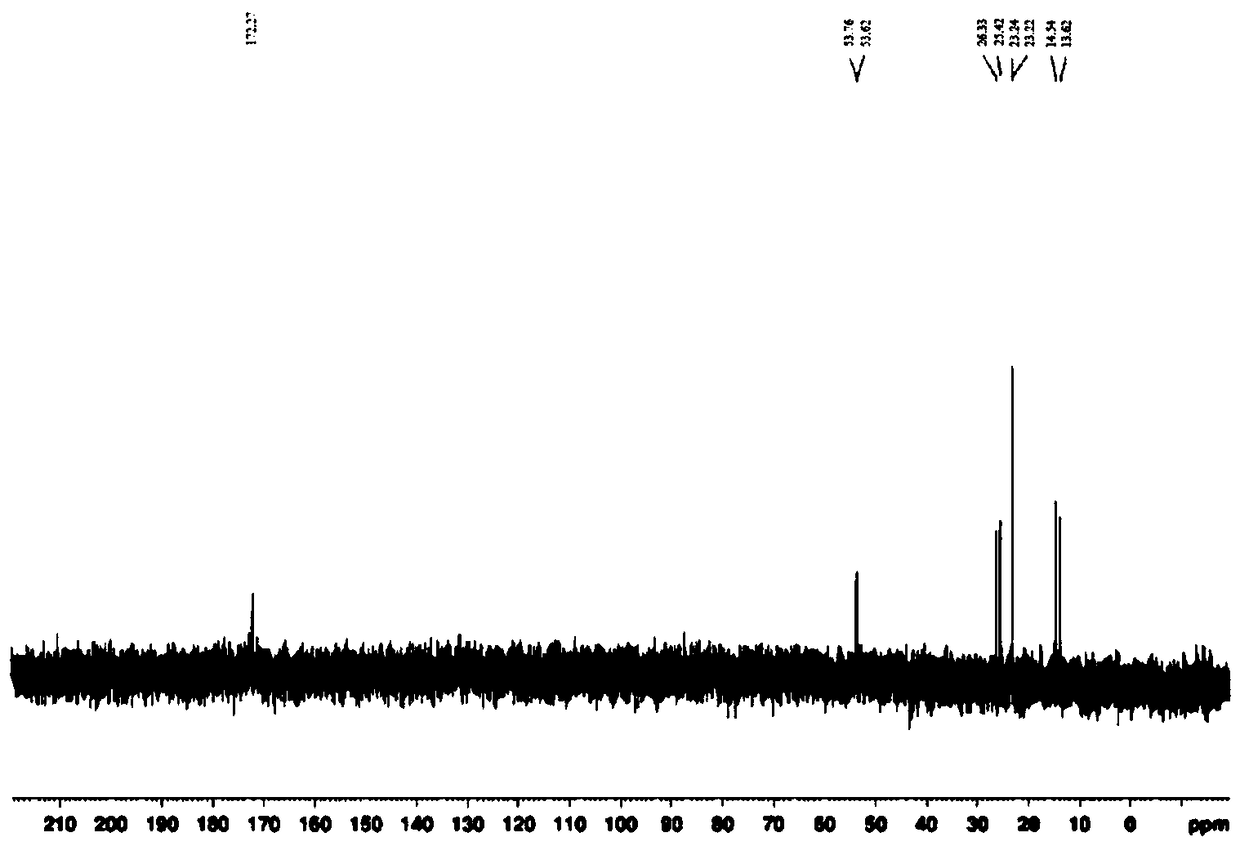
Synthetic method for glufosinate ammonium
A synthetic method, glufosinate-ammonium technology, applied in the field of pesticides, can solve the problems of defective safety, high price, high cost, etc., and achieve the effects of high safety, reduced post-processing steps, and mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: the preparation method of intermediate II α-bromo-γ-butyrolactone:
[0035] Under ice bath, slowly add 330mL liquid bromine dropwise to the mixture of 500g γ-butyrolactone and 31g red phosphorus in a three-neck flask, then raise the temperature to 70°C, and continue to dropwise add 330mL liquid bromine. After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 80° C. for 3 h. Stop heating until cooling, and continue blowing air to blow away excess liquid bromine and generated hydrogen bromide. Then the temperature was raised to 80°C, and 100 mL of water was slowly added dropwise, and 700 mL of water was added after the reaction eased, and refluxed for 4 hours. After cooling, the layers were separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane, the organic layers were combined, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product (b.p.120-125°C / 1.6kPa), which was purified by...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: the preparation method of intermediate IIα-bromo-γ-butyrolactone:
[0037] Under ice bath, slowly add 330mL liquid bromine dropwise to the mixture of 500g γ-butyrolactone and 31g red phosphorus in a three-neck flask, then raise the temperature to 70°C, and continue to dropwise add 250mL liquid bromine. After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 80° C. for 3 h. Stop heating until cooling, and continue blowing air to blow away excess liquid bromine and generated hydrogen bromide. Then the temperature was raised to 80°C, and 100 mL of water was slowly added dropwise, and 750 mL of water was added after the reaction eased, and refluxed for 4 hours. After cooling, the layers were separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane, the organic layers were combined, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The crude product was obtained after distilling off the solvent under reduced pressure, which was purified by distillation un...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Embodiment 3: the preparation method of intermediate II α-bromo-γ-butyrolactone:
[0039] Under ice bath, slowly add 330mL liquid bromine dropwise to the mixture of 500g γ-butyrolactone and 31g red phosphorus in a three-neck flask, then raise the temperature to 70°C, and continue to dropwise add 150mL liquid bromine. After the dropwise addition, the temperature was raised to 80° C. for 3 h. Stop heating until cooling, and continue blowing air to blow away excess liquid bromine and generated hydrogen bromide. Then the temperature was raised to 80°C, and 100 mL of water was slowly added dropwise, and 750 mL of water was added after the reaction eased, and refluxed for 4 hours. After cooling, the layers were separated, the aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane, the organic layers were combined, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. After the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, the crude product was obtained, which was purified by distillation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com