Method for regulating fatty acid synthetic gene and promoting mycorrhizal symbiosis of leguminous plants
A technology for fatty acid synthase and leguminous plants, which is applied in the fields of biotechnology and botany, and can solve the problem that there is no homologous gene responsible for type I fatty acid synthase.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0056] As an embodiment of the present invention, the gene encoding fatty acid synthase is cloned into an appropriate vector by a conventional method, and the recombinant vector with the foreign gene is introduced into a plant expressing the fatty acid synthase In the cell, the plant cell is made to express fatty acid synthase. Plants overexpressing fatty acid synthase can be obtained by regenerating said plant cells into plants. Preferably, the gene encoding fatty acid synthase is transferred into plants by using Agrobacterium transformation method.
[0057] Usually, the coding gene of fatty acid synthase is located in the downstream of the promoter in the expression vector, that is, the downstream of the 3' end of the promoter is connected to the 5' end of the coding gene. The coding gene is operably linked to the expression vector. The term "operably linked" or "operably linked to" refers to the condition that certain parts of a linear DNA sequence can regulate or control...
Embodiment 1
[0183] Embodiment 1, the expression pattern analysis of alfalfa fatty acid synthesis pathway gene
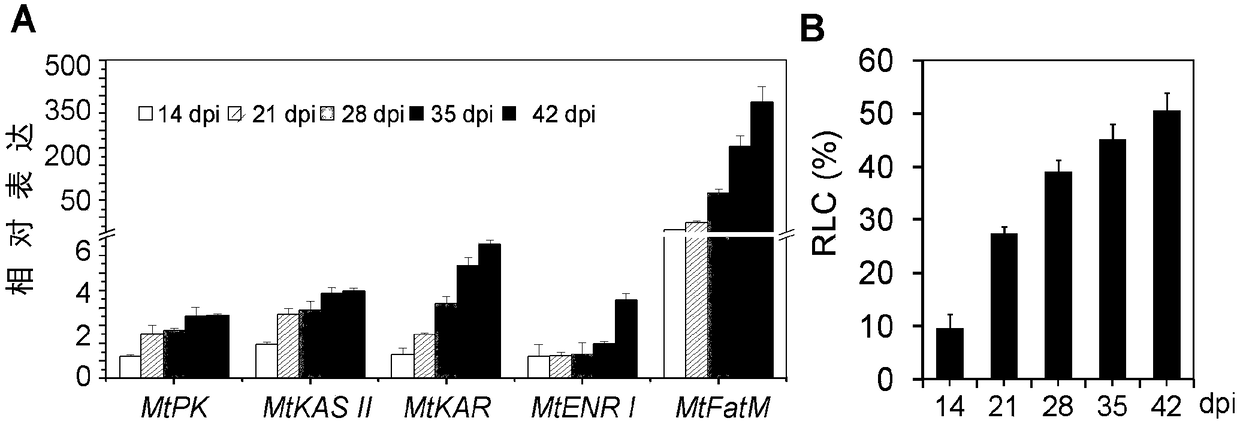
[0184] Wild-type A17 alfalfa was planted in plug trays containing or not containing mycorrhizal fungi: sand: perlite = 1:1, and inoculated with mycorrhizal fungus R. irregularis for infection. At different periods (14, 21, 28, 35, 42 days) of mycorrhizal infection and non-infection control group, total RNA was extracted from alfalfa root samples, and the expression changes of genes were verified by RT-PCR. At the same time, the infection efficiency of mycorrhizae was observed and counted under a microscope by ink staining.
[0185] The results showed that with the improvement of mycorrhizal infection efficiency at different time points ( figure 1 A), the expression levels of genes MtPK, MtKAS II, MtKAR, MtERN I and MtFatM encoded by alfalfa fatty acid synthesis pathway-related enzymes are strongly induced ( figure 1 B).
[0186] The above results indicated that, in the proces...
Embodiment 2
[0187] The mycorrhizal symbiosis level analysis of embodiment 2, fatm mutant
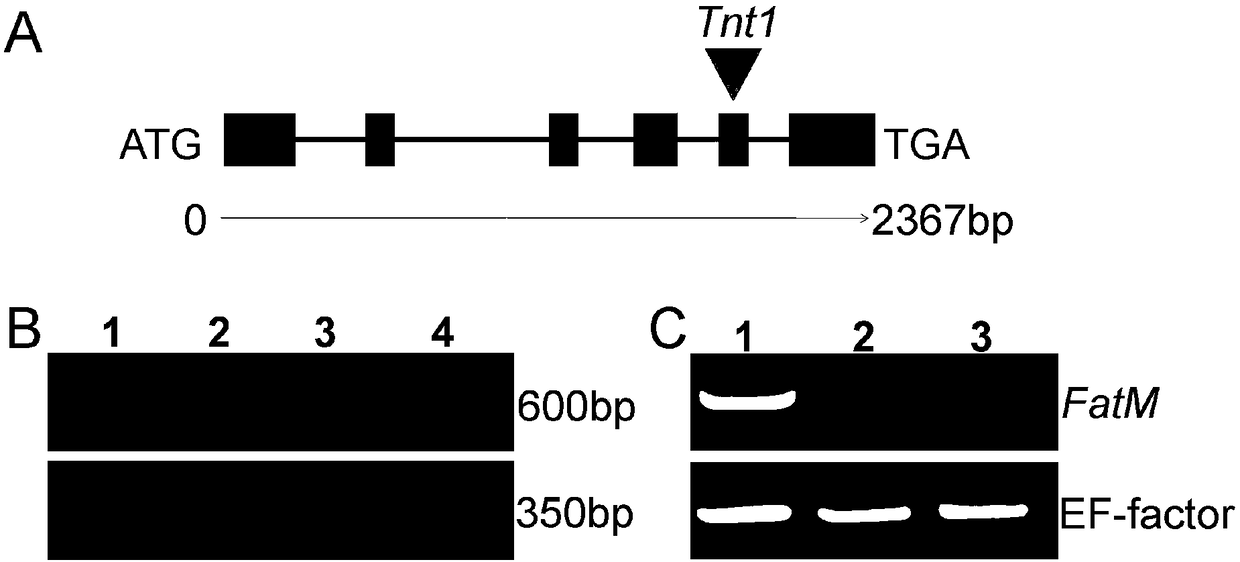
[0188] Through Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation Tnt1population, the inventors screened the Tnt1 mutant fatm (NF7660) of MtFatM, the gene cannot be transcribed and translated normally due to Tnt1 transposon insertion at the 5th exon ( figure 2 A, 2B). Quantitative PCR analysis showed that the expression of MtFatM in fatm mutant pure and strains was significantly down-regulated ( figure 2 C).
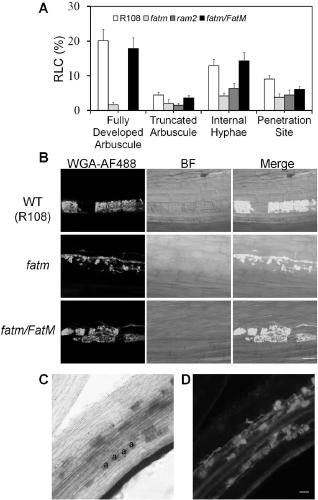
[0189] In order to confirm the mycorrhizal symbiosis level of the fatm mutant, the inventors inoculated the R108, ram2, fatm mutant seedlings and fatm mutant complementary material fatm / FATM into R. irregularis at the same time, and counted the mycorrhizal symbiosis level after 6 weeks of inoculation. . like image 3 As shown in A and 3B, both ram2 and fatm mutants consistently exhibited a significantly lower mycorrhizal symbiosis than the R108 plant phenotype, and the fatm mutant complemented material fat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com