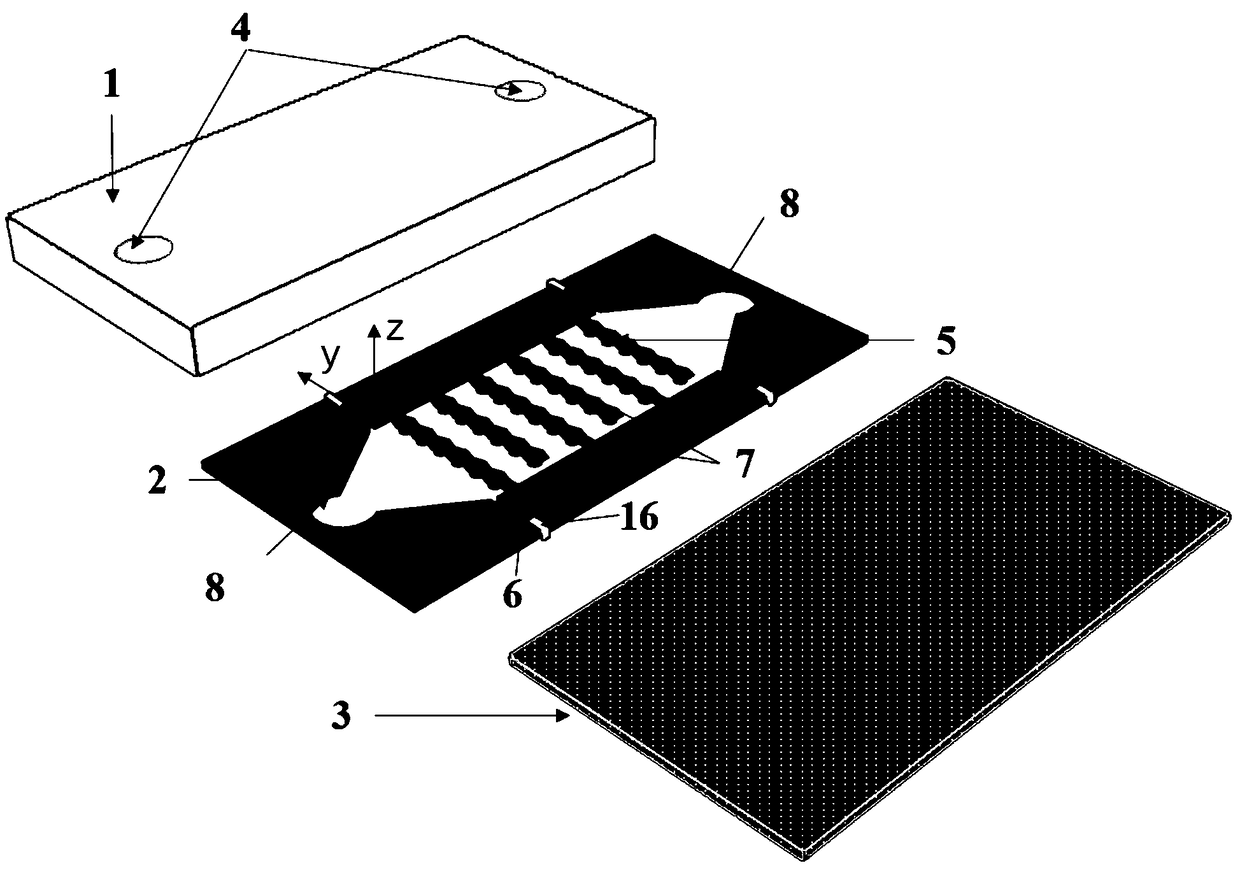
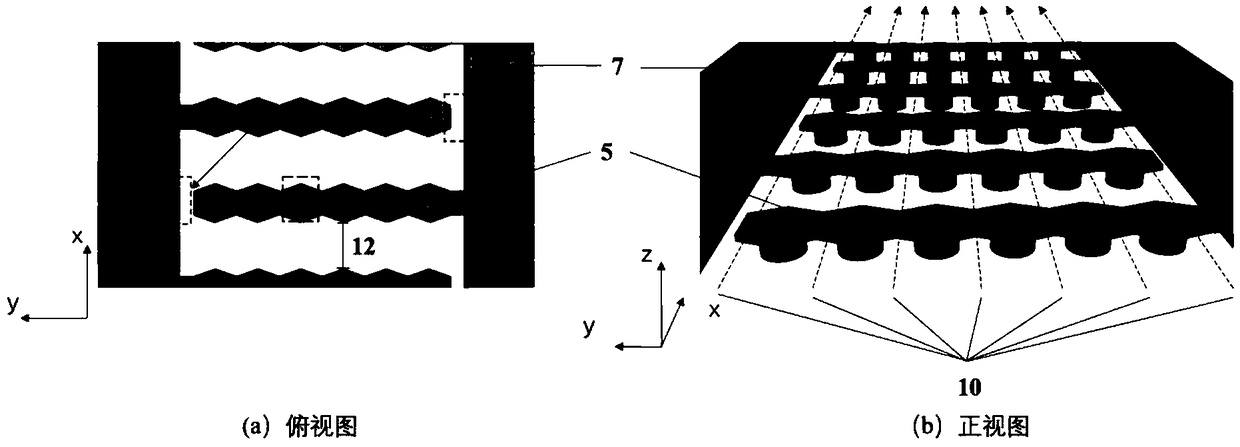
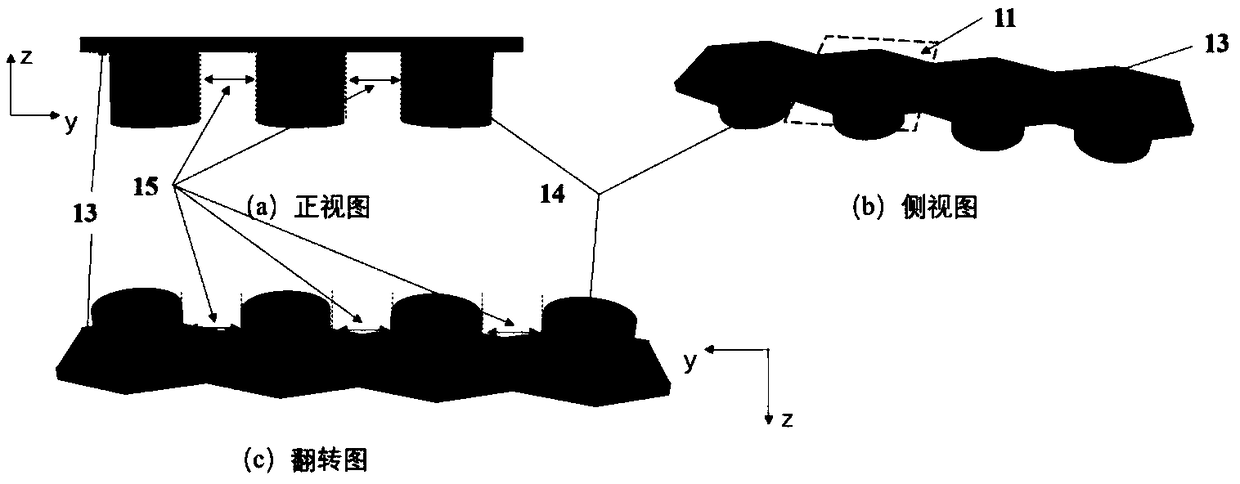
Dielectrophoresis micro-fluidic chip for selecting and focusing cells as well as alignment-free microprocessing method thereof
A microfluidic chip and dielectrophoresis technology, applied in the direction of stress-stimulated microbial growth, biochemical equipment and methods, specific-purpose bioreactors/fermenters, etc., can solve the problem of controlling cell trajectory, inability, and increasing complexity and other problems to achieve the effect of improving the separation purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] In this example, the dielectrophoretic microfluidic chip obtained in the above embodiment and polystyrene microspheres as cell models were used to test the effect of particle sorting. The specific steps are as follows:
[0073] The polystyrene microsphere solution was diluted with deionized water (DI Water) to obtain a mixed solution of 2 μm microspheres and 15 μm microspheres, wherein the concentrations of 2 μm microspheres and 15 μm microspheres were 1×10 8 / ml and 5×10 6 pieces / ml. The mixed solution was injected into the above-mentioned dielectrophoresis microfluidic chip at a flow rate of 0.15 ml / h. The input amplitude from the main electrodes 7 at both ends is 30V pp , a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 20kHz, and observe the trajectory of the microsphere under a microscope.
[0074] It has been observed that when no electrical signal is input, 2 μm microspheres and 15 μm microspheres are dispersed in the entire flow channel and move along the outlet 25 in...
Embodiment 2
[0076] In this example, the dielectrophoretic microfluidic chip obtained in the above embodiment and the mixed solution of red blood cells and polystyrene microspheres were used to test the effect of particle sorting. The specific steps are as follows:
[0077] Use 300mM D-mannitol solution to dilute human blood, mix the diluted blood with a solution of 7 μm microspheres whose size is similar to that of blood cells, and obtain a mixed solution of two kinds of particles, the solution conductivity is 0.01S / m, and The concentration of both blood cells and 7 μm microspheres was 1 × 10 7 pieces / ml. The mixed solution was also injected into the above-mentioned dielectrophoresis microfluidic chip at a flow rate of 0.15 ml / h. The input amplitude from the main electrode 7 at both ends is 35V pp , a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 1MHz, observe the trajectory of the two particles under a microscope.
[0078] It has been observed that when no electrical signal is input, blood ce...
Embodiment 3
[0080] In this example, the dielectrophoretic microfluidic chip obtained in the above embodiment and diluted human blood are used to test the effect of cell focusing. The specific steps are as follows:
[0081] Use 300mM D-mannitol solution to dilute human blood to obtain a blood cell concentration of 4×10 7 A / ml solution, the solution conductivity is 0.02S / m. The mixed solution was also injected into the above-mentioned dielectrophoresis microfluidic chip at a flow rate of 0.15 ml / h. The input amplitude from the main electrode 7 at both ends is 35V pp , a sinusoidal signal with a frequency of 100kHz, observe the movement track of blood cells under a microscope.
[0082] It has been observed that when no electrical signal is input, the blood cells are dispersed in the entire flow channel and move toward the outlet 25 along with the flow direction of the solution, such as Figure 11 (a) shown. After the electrical signal is input, the blood cells are repelled by the negativ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com