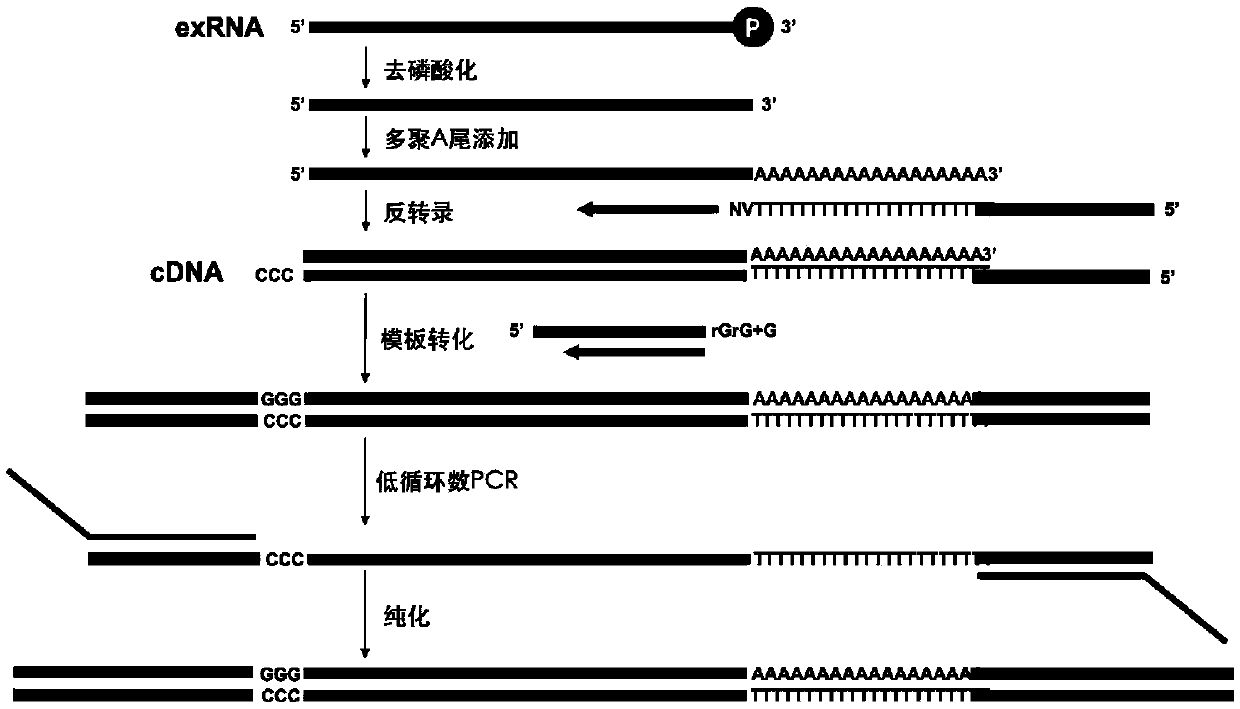
High-throughput sequencing library construction method for trace free RNA of body fluid
A sequencing library and construction method technology, applied in the field of high-throughput sequencing library construction of trace free RNA in body fluids, can solve the problems of inaccessibility, high cost of library construction, and limited amount of RNA, so as to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of data and build a library The effect of cost reduction and labor cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1. Extracting exRNA from plasma samples and constructing a high-throughput sequencing library
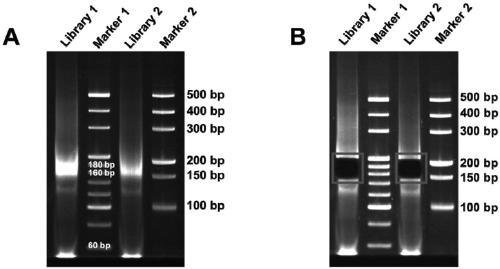
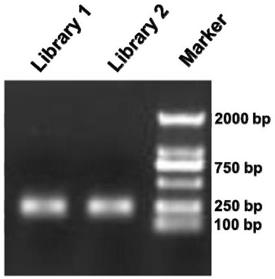
[0051] The liquid samples to be tested in this embodiment are the plasma of 2 liver cancer patients, library 1 (Library1) represents the first one, and library 2 (Library2) represents the second one. This example will describe in detail the specific method for extracting exRNA from plasma samples and constructing a high-throughput sequencing library, and evaluate the method by identifying the quality of the obtained library.
[0052] 1. Extraction and purification of exRNA
[0053] 1. Pipette 1 mL of plasma sample into a 15 mL tube, add 1 mL of Digestion Buffer (the composition is Tris hydrochloric acid buffer, which provides a reaction environment for enzymatic reactions, zymo product number R1059) and mix well.
[0054] 2. Add 25μL (50unit) of prepared proteinase K, mix well and incubate at room temperature for 2 hours.
[0055] 3. Add 2mL Binding buffer (the comp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com