General codominance molecular marker for resisting nilaparvata lugens Stal BPH9 multiple alleles of rice, and detection method and application of general codominance molecular marker
An anti-BPH and allele technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of loss of resistance, etc., and achieve efficient detection, efficient and accurate screening, and detection procedures Convenient and fast effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
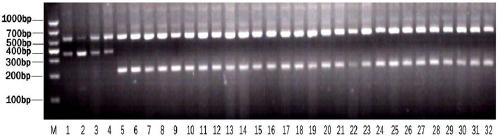
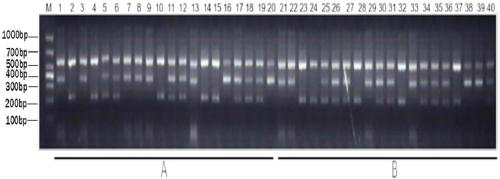
[0042] Example 1 Development of rice universal co-dominant molecular markers for resistance to brown planthopper multiple alleles BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7 and BPH9
[0043] Rice BPH-resistant multiple alleles BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7, and BPH9 are located on the long arm of rice chromosome 12, and can resist BPH parents Mudgo (BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21), ADR52 (BPH2 / 26), T12 (BPH7), Pokkali (BPH9), and the susceptible parents 9311, Nipponbare, Huazhan, 638S and more than 20 kinds of rice material genome sequence determination and comparison analysis, in the third exon of the brown planthopper resistance gene A specific MNP (polynucleotide polymorphism) was found, located at 22874098-22874099 bp on chromosome 12 of Nipponbare, in which BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7, BPH9 insect resistance alleles were 5'- TG-3', the susceptible allele is 5'-CC-3' or 5'-CA-3'. The sequence analysis results of the four types of BPH-resistant multiple alleles BPH7, BPH9, BPH18, BPH26 and 9311, Nippon...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2 Multiple alleles BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7, design of detection primers for co-dominant molecular markers of BPH9 genes
[0045] Detection primers were designed for the multiple allele-specific molecular markers developed in Example 1, and the principle of primer design was as follows.
[0046] Firstly, specific primers for amplifying the brown planthopper-resistant allele (hereinafter referred to as the insect-resistant allele) were designed, and the 5 alleles of the insect-resistant multiple alleles BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7, and BPH9 were designed. The 5'-CA-3' complementary to '-TG-3'MNP is used to design the reverse primer BPH1 / 9-RR at the 3' end of the primer, and then design the forward primer BPH1 / 9-RF paired with it upstream, Primers BPH1 / 9-RR and BPH1 / 9-RF can only specifically amplify BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21 or BPH2 / 26 or BPH7 or BPH9 to produce 360bp bands, but no amplification bands for other alleles;
[0047] Then, design specific primers for amp...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Establishment of a universal molecular marker detection method for rice resistance to brown planthopper multiple alleles BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7 and BPH9
[0052] According to the detection primers of BPH1 / 10 / 18 / 21, BPH2 / 26, BPH7 and BPH9 universal molecular markers designed in Example 2, the reaction program and reaction system of PCR were designed, and through continuous optimization, the following reaction program and system were determined:
[0053] PCR reaction system (10 μL): 1 μL of 10×PCR reaction buffer, 0.8 μL of 10 mM dNTP, 0.15 μL of each of the 4 primers (10 μM), 0.1 μL of Taq DNA polymerase; 2 μL of DNA template, and double distilled water to make up the rest.
[0054] The PCR reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 56°C for 30 seconds, extension at 72°C for 45 seconds, a total of 35 cycles; extension at 72°C for 8 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com