Nano-microporous thermal insulation material and preparation method thereof
A thermal insulation, nano-microporous technology, applied in the field of thermal insulation materials, can solve the problems of easy opening and water absorption, low strength, large shrinkage, etc., to achieve enhanced thermal insulation performance, improved thermal insulation capacity, and good thermal insulation effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
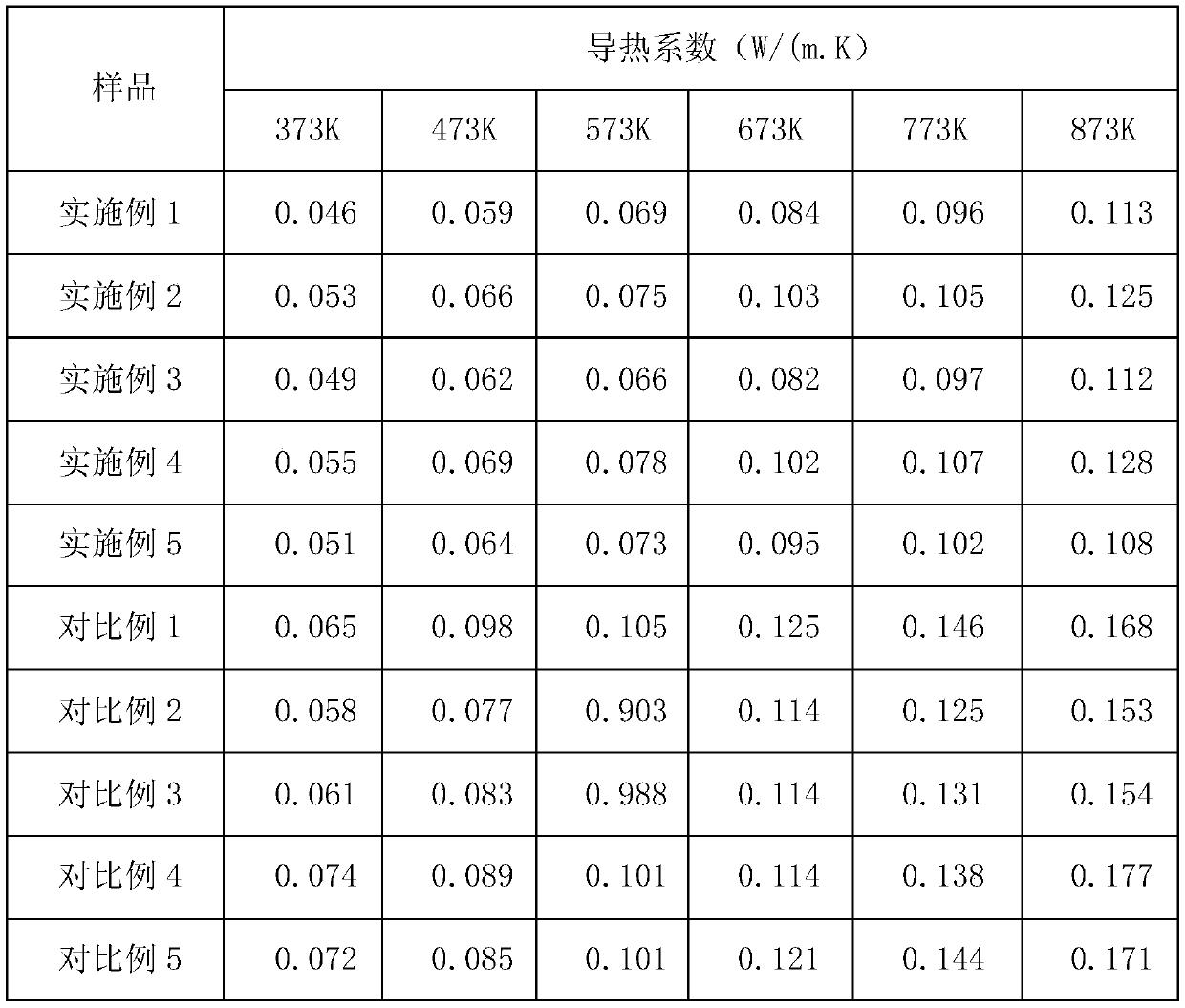
Embodiment 1
[0041] The nano-microporous thermal insulation material of the present embodiment includes a porous base layer and a thermal insulation layer attached to the surface of the base layer. The base layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 28 parts of polymer hollow microspheres, paraffin wax / porous perlite- 1 part of urea-formaldehyde resin phase-change microcapsules, 11 parts of nano-alumina hollow spheres, 5 parts of nano-silica sol, and 3 parts of aluminum silicate fibers;
[0042] The heat insulating layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 44 parts of silica airgel, 14 parts of modified starch, 4 parts of hollow microspheres, 10 parts of nano-titanium oxide, 3 parts of mullite whiskers, foaming 2 doses.
[0043] Wherein, the polymer hollow microspheres are polystyrene hollow microspheres with a particle diameter of 0.2-0.6 μm.
[0044] Wherein, the phase change material in the paraffin wax / porous perlite-urea formaldehy...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The nano-microporous thermal insulation material of the present embodiment includes a porous base layer and a thermal insulation layer attached to the surface of the base layer. The base layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 36 parts of polymer hollow microspheres, paraffin wax / porous perlite- 5 parts of urea-formaldehyde resin phase-change microcapsules, 19 parts of nano-alumina hollow spheres, 12 parts of nano-silica sol, and 7 parts of aluminum silicate fibers;
[0061] The heat insulating layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 54 parts of silica airgel, 18 parts of modified starch, 8 parts of hollow microspheres, 16 parts of nano-titanium oxide, 5 parts of mullite whiskers, foaming 4 doses.
[0062] Wherein, the polymer hollow microspheres are polystyrene hollow microspheres with a particle diameter of 0.2-0.6 μm.
[0063] Wherein, the phase change material in the paraffin wax / porous perlite-urea formalde...
Embodiment 3
[0079] The nano-microporous thermal insulation material of the present embodiment includes a porous base layer and a thermal insulation layer attached to the surface of the base layer. The base layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 32 parts of polymer hollow microspheres, paraffin wax / porous perlite- 3 parts of urea-formaldehyde resin phase-change microcapsules, 15 parts of nano-alumina hollow spheres, 8.5 parts of nano-silica sol, and 5 parts of aluminum silicate fibers;
[0080] The heat insulating layer is composed of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 49 parts of silica airgel, 16 parts of modified starch, 6 parts of hollow microspheres, 13 parts of nano-titanium oxide, 4 parts of mullite whiskers, foam 3 doses.
[0081] Wherein, the polymer hollow microspheres are polystyrene hollow microspheres with a particle diameter of 0.2-0.6 μm.
[0082] Wherein, the phase change material in the paraffin wax / porous perlite-urea formaldehy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com