Radiation crosslinking halogen-free non-red phosphorus flame retardant heat shrinking material and preparation method thereof
A technology of radiation crosslinking and heat shrinkage, which is applied in the field of radiation crosslinking heat shrinkage materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of containing red phosphorus, lead, mercury, etc., and achieve simple preparation methods, expanded types and application ranges, and good performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The preparation method of the radiation-crosslinked halogen-free and red phosphorus-free flame-retardant heat-shrinkable material includes the following steps:
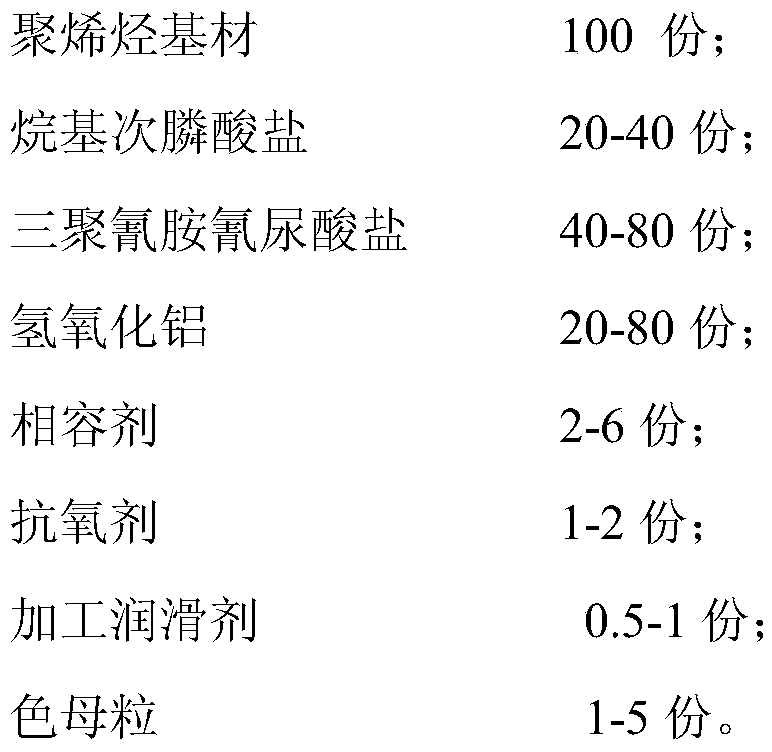
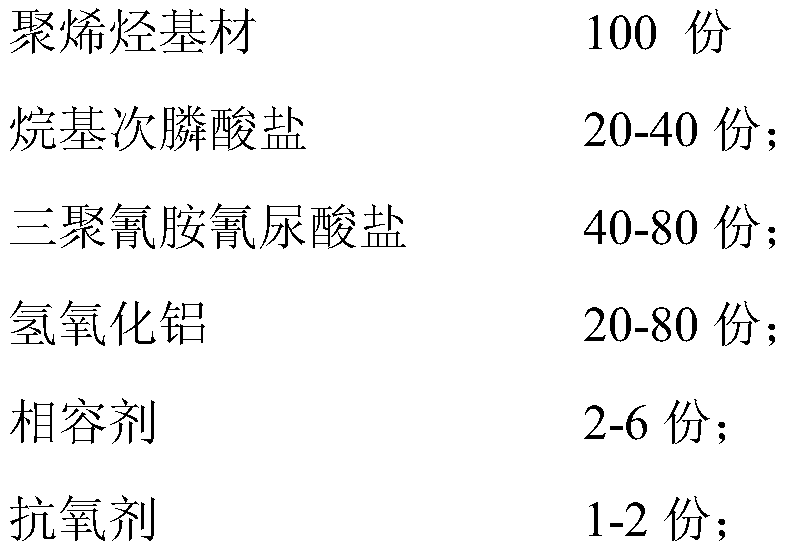
[0049] Step 1: Weighing according to parts by weight: 100 parts of polyolefin substrate, 20-40 parts of alkyl phosphinate, 40-80 parts of melamine cyanurate, 20-80 parts of aluminum hydroxide, compatibilizer 2 -6 parts, 1-2 parts of antioxidant, 0.5-1 part of processing lubricant, 1-5 parts of masterbatch, fully stirred at room temperature, and mixed evenly;
[0050] Step 2: Mix the homogeneously mixed material in step 1 with an internal mixer at a temperature range of 130-180° C., extrude and granulate;
[0051] Step 3: Extrude the water-cooled strands in the temperature range of 130-200°C with a twin-screw extruder after homogenizing the homogeneously mixed material in step 2, pelletize and air-dry;
[0052] Step 4: extruding the above-mentioned pellets into a tubular shape with a single-screw extruder at a ...
preparation Embodiment 1
[0057] Weigh according to parts by weight: 100 parts of polyolefin substrate [take 90 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (J5110, Yamba) and 10 parts of ethylene-octene copolymer (POE8150, Dow)];
[0058] 20 parts of alkyl phosphinate [take 20 parts of aluminum diethyl phosphinate (commercially available)];
[0059] 80 parts of melamine cyanurate (commercially available)
[0060] 20 parts of aluminum hydroxide (commercially available);
[0061] 4 parts of compatibilizer (random copolymer of maleic anhydride and ethylene-acrylic acid butene copolymer, 4210, Arkema);
[0062] 1 part of antioxidant (take antioxidant 1010:antioxidant DLTP=1:1.5, commercially available);
[0063] Processing lubricant (get zinc stearate, commercially available) 0.8 part;
[0064] 1 part of masterbatch (commercially available);
[0065] Stir well at room temperature to mix well. The homogeneously mixed material was kneaded with an internal mixer at a temperature range of 100° C., extruded ...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0070] Weigh according to parts by weight: 100 parts of polyolefin substrate [take 95 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer (J4110, Yamba) and 5 parts of ethylene-octene copolymer (POE8150, Dow)];
[0071] 40 parts of aluminum alkyl phosphinate [take 40 parts of aluminum methyl ethylene phosphinate (commercially available)];
[0072] 55 parts of melamine cyanurate (commercially available);
[0073] 60 parts of aluminum hydroxide (commercially available);
[0074] 6 parts of compatibilizer (graft copolymer of maleic anhydride and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, MC328, Nengzhiguang);
[0075] 2 parts of antioxidant (take antioxidant 1076:antioxidant DLTP=1:1.5, commercially available);
[0076] Processing lubricant (get stearic acid, commercially available) 1 part;
[0077] Color masterbatch (commercially available) 5 parts;
[0078] Stir well at room temperature to mix well. The homogeneously mixed material was kneaded with an internal mixer at a temperature range of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com